This test is open note and open book. You may NOT do a Google search and ALL WORK MUST BE YOUR OWN understanding. If you have paper copy notes, you may use those as well. GoGuardian will be running a blocked scene that will only allow the test, & resources posted through GC.
Read each question carefully.
If a question has boxes to check, that means there are multiple correct answers. If a question has a circle to select, it means there is one correct answer.
If asked a short answer question, follow the RACE strategy (restate, answer, cite, explain) and make sure you follow the rules of English conventions (spelling, grammar/usage, capitalization, punctuation) as errors do impact meaning.
Do your best. When finished, submit the test on Formative and Google Classroom.
You have the length of the class period to complete this test; if you need extended time you MUST communicate with Mrs. Richardson BEFORE THE END OF THE TEST!!
Identify important historical events and eras on a timeline.
Explain the purpose for treaties with the Native Americans.
Explain the process for creating treaties between the US Government & Native American tribes.
Analyze primary sources (visual & written).
Explain the concept and actions of “assimilation” and its lasting effects to tribal cultures today.
Explain how Washington became an official state.
Explain how new technologies and their availability impact growth to WA and the economy.
Explain the role of immigration in the change and growth to WA’s economy.
Analyze the perception of minority groups and women and how they impacted those groups.
Analyze the growth of new cities in WA and the idea of “urbanization”.
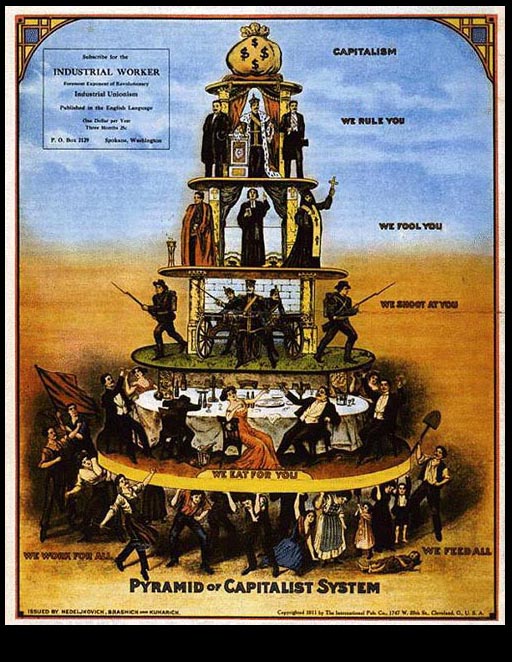
Evaluate the impact of labor unions on the economy.
Explain the need for reform during the “Gilded Age” of the US and in Washington.
Analyze the impact of WWI on Washington’s economy, politics, and social change.
Connect past ideas and events to present day problems and movements.
Explain how cultural differences led to conflict and violence between native tribes, minority groups, and white.