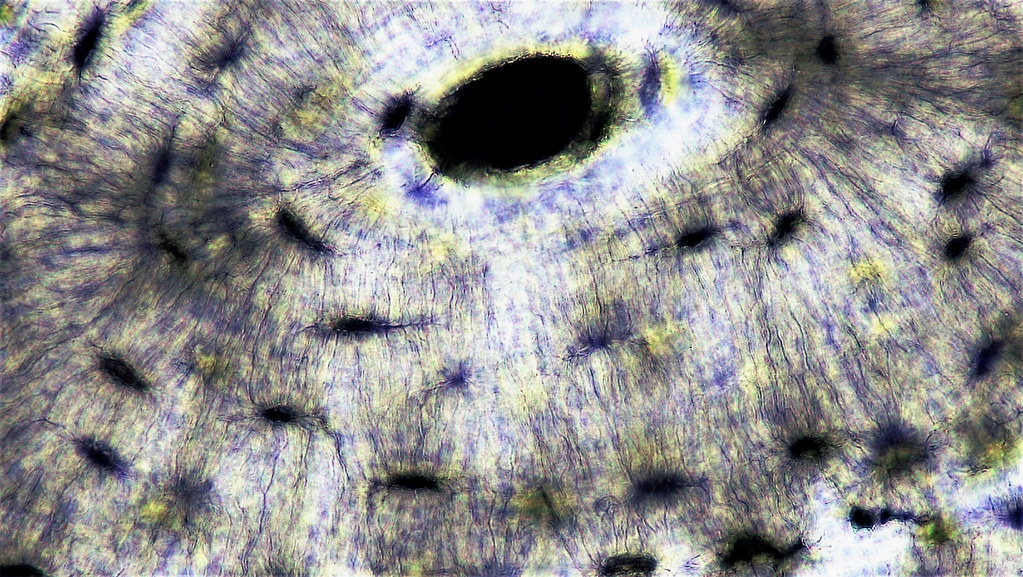
Skeletal System Overview Lab
star
star
star
star
star
Last updated over 3 years ago
35 questions
Required
4
Required
4
Required
3
Required
2
Required
2
Required
2
Required
10
Required
7
Required
0
Required
1
6
5
5
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Required
10
Required
1
Required
4
5
Required
4
Required
1
Required
2
Required
5
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
4
Required
1