Semester 1 - Physics Final Review Sheet
star
star
star
star
star
Last updated over 3 years ago
51 questions
2
1
1
1
1
2
6
6
2
2
1
8
4
4
4
4
9
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
2
6
4
6
6
2
6
6
4
2
8
2
4
4
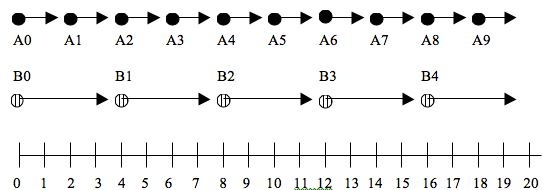
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
blue | arrow_right_alt | B |
green | arrow_right_alt | A |
red | arrow_right_alt | C |

