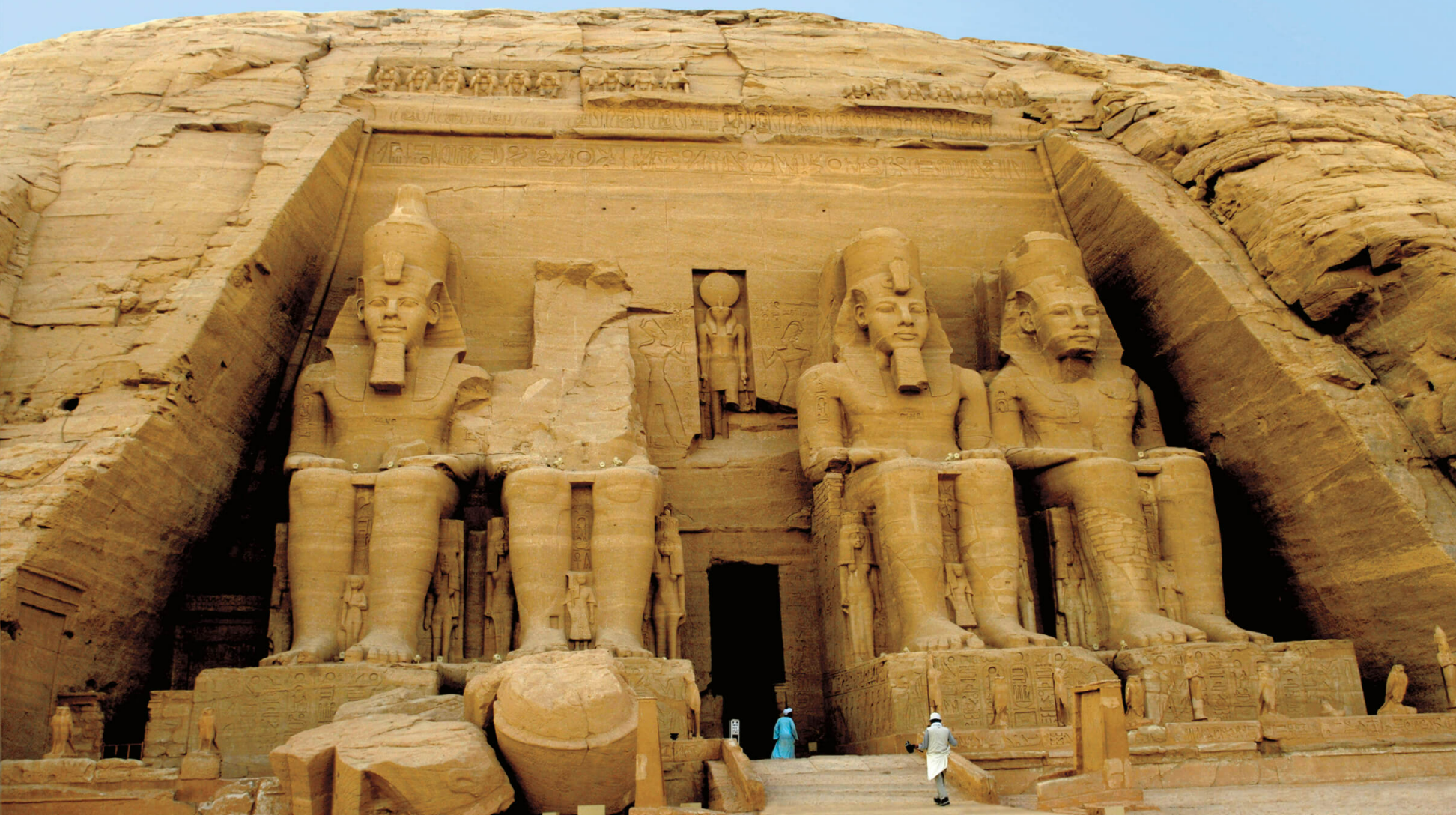
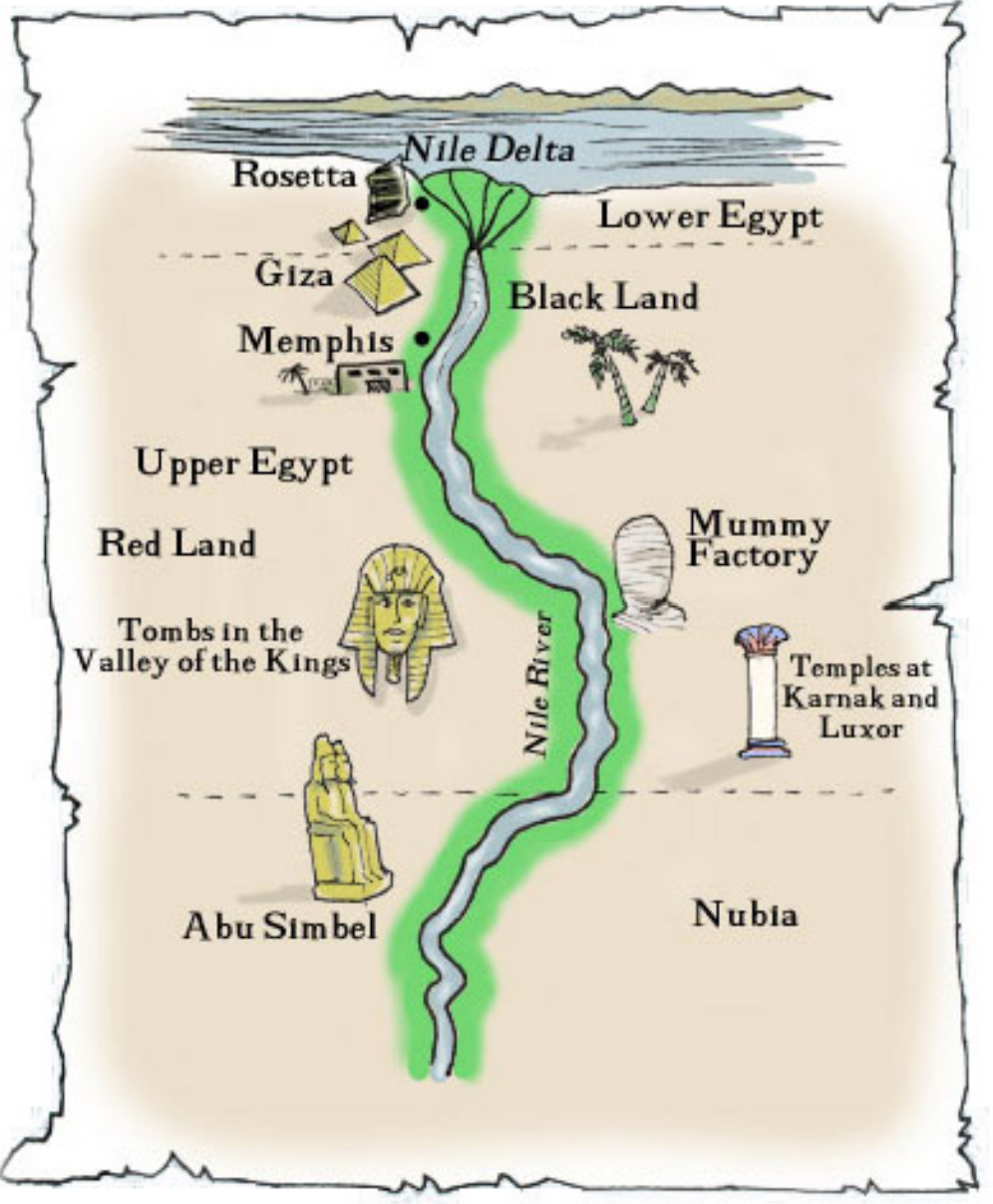
The four statues of King Ramses II at this temple provide an example of ancient Egyptian art. Small figures of Ramses’ children, his queen, and his mother are carved around his feet. Dedicated to the sun gods, the temple was built in such a way that, on two days of the year, the first rays of the morning sun shine through the building and light up the entire temple. What do the number and size of the figures of Ramses II indicate about his importance in ancient Egyptian society?