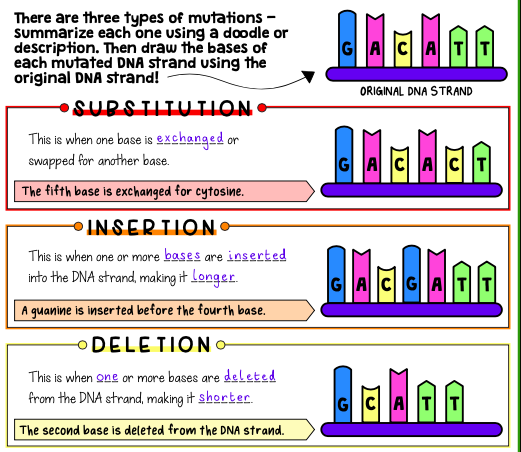
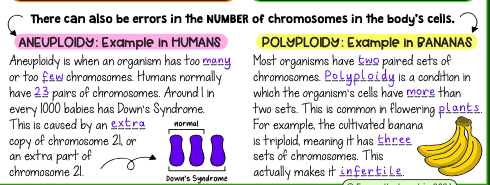
The impact of a mutation depends on if it affects a protein’s structure and function. While many mutations have no effect, e.g. a silent mutation, some mutations alter proteins, affecting the organism’s phenotype (its physical characteristics). The organism’s external environment determines if the new phenotype is beneficial, neutral, or negative.