Ancient Greece Vocabulary
star
star
star
star
star
Last updated almost 4 years ago
6 questions
7
4
6
6
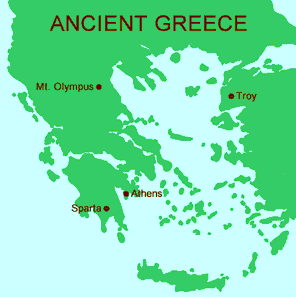
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt |
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
Socrates | arrow_right_alt | A Greek philosopher who developed the socratic method--questioning; sentenced to death for "corrupting Athens 'youth" |
Socratic Method | arrow_right_alt | way of teaching developed by Socrates that used a question-and-answer format to force students to use their reason to see things for themselve |
Plato | arrow_right_alt | |
| arrow_right_alt |
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt |
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt |