Due Sep. 23, 2022 - Homework Prokaryotes Vs. Eukaryotes
By Caleb Guesno
starstarstarstarstar
Last updated almost 2 years ago
14 Questions
Note from the author:
Scientists can classify things into two categories: living and nonliving. Of the living things, scientists can further classify living organisms into unicellular and multicellular subcategories.
Scientists can classify things into two categories: living and nonliving. Of the living things, scientists can further classify living organisms into unicellular and multicellular subcategories.
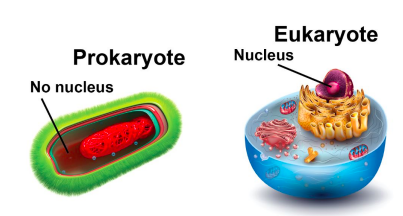
How can you sort organisms based on the the types of cells living things contain? Organisms composed of only one cell that have no nucleus are called prokaryotes, whereas all other cells having a nucleus, whether found in single or many-celled organisms, are called eukaryotes.
Prokaryotic cells include all species of bacteria. Prokaryotic cells have the basic structures common to all cells, which include a cell membrane surrounding the cytoplasm and DNA.
However, prokaryotic cells do not have membrane-enclosed organelles such as mitochondria or a nucleus. Prokaryotic cells do contain ribosomes, but there is debate as to whether or not a ribosome counts as a type of organelle. Therefore, the question of whether or not prokaryotic cells contain any organelles is still up for debate.
Eukaryotic cells include the cells of plants, animals, fungi (such as mushrooms), and protists (such as the unicellular microorganisms Euglena and Amoeba). Similar to prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have a cell membrane, cytoplasm, and DNA. However, eukaryotic cells are more complex. They have something that prokaryotic cells do not: organelles surrounded by membranes. These include mitochondria and a nucleus, where DNA is stored.