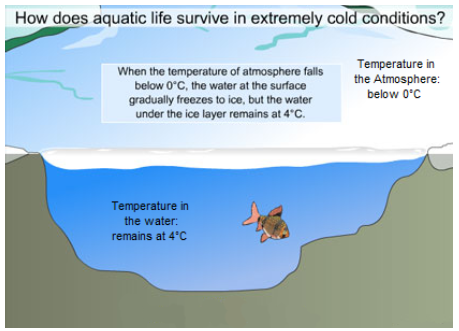
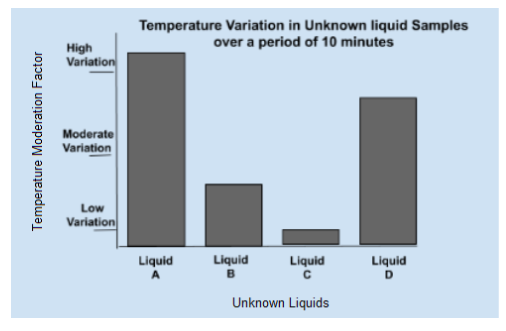
Temperature moderation refers to water’s ability to maintain a fairly consistent temperature. Water molecules are attracted to one another by hydrogen bonds and this limits the movement of the molecules. This strong attraction between water molecules means that a large amount of energy is required to increase or decrease the temperature of water. Large bodies of water are slow to change temperature (such as lakes and oceans) which is good for the organisms living in them.
Heat capacity is related to a substance's ability to retain heat and the rate at which it will heat up or cool down. For example, a substance with a low heat capacity, such as iron, will heat and cool quickly, while a substance with a high heat capacity, such as water, heats and cools slowly.