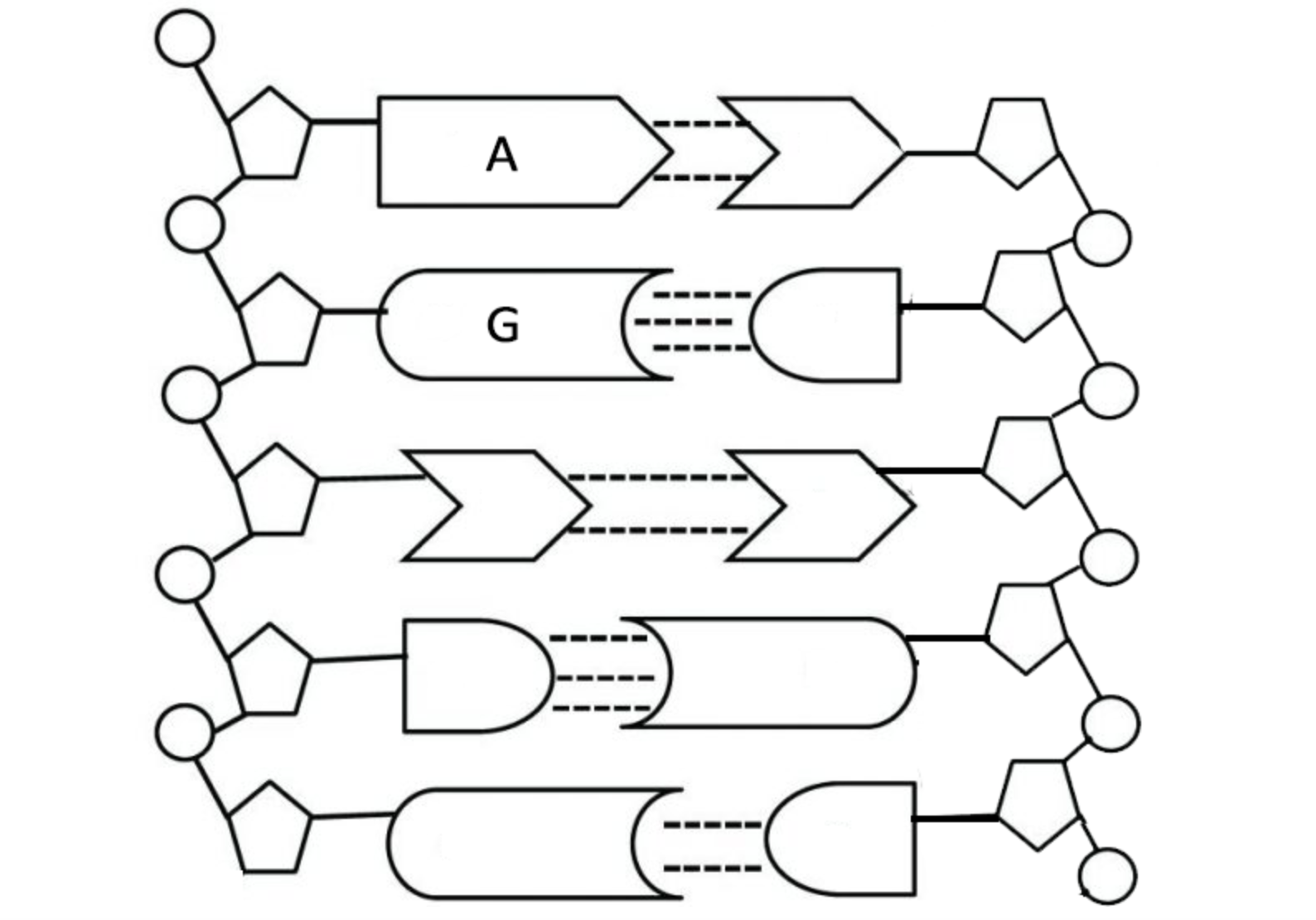
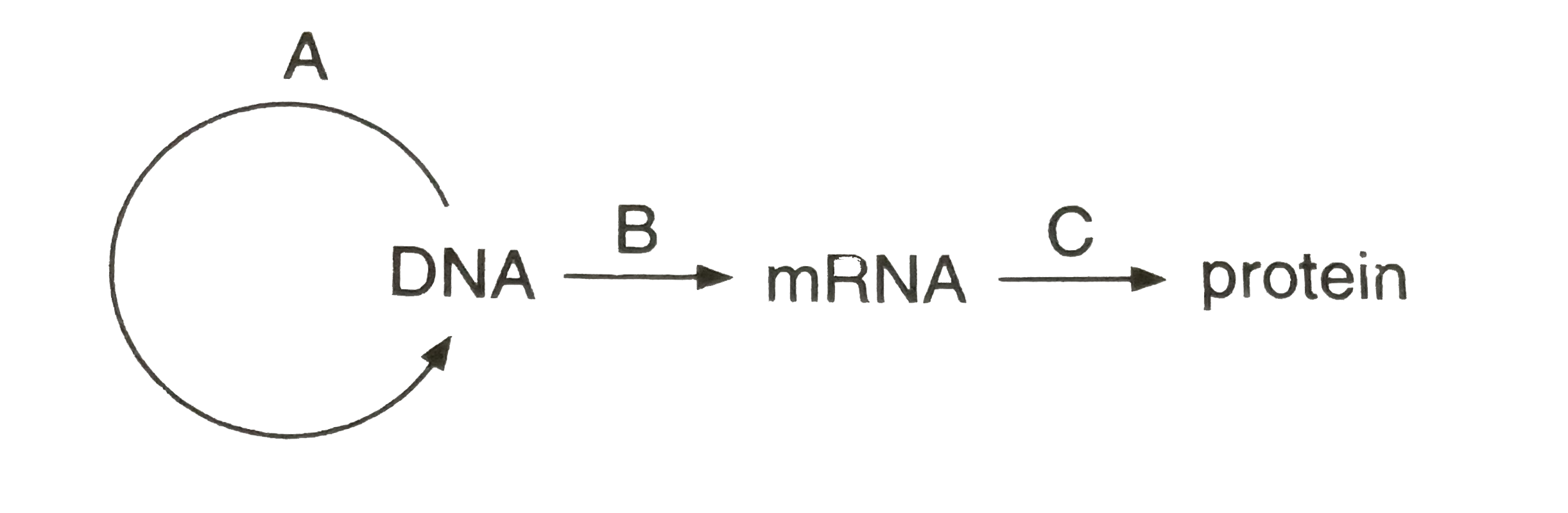Nucleic Acids
star
star
star
star
star
Last updated 3 months ago
17 questions
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
6
Required
6
Required
2
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
3
Required
9
Required
2
Required
3
Required
5
1