DE_Chem_2.4_StructureOfThePeriodicTable
star
star
star
star
star
Last updated almost 3 years ago
32 questions
Engage
Required
2
Required
1
Required
4
Required
1
Required
2
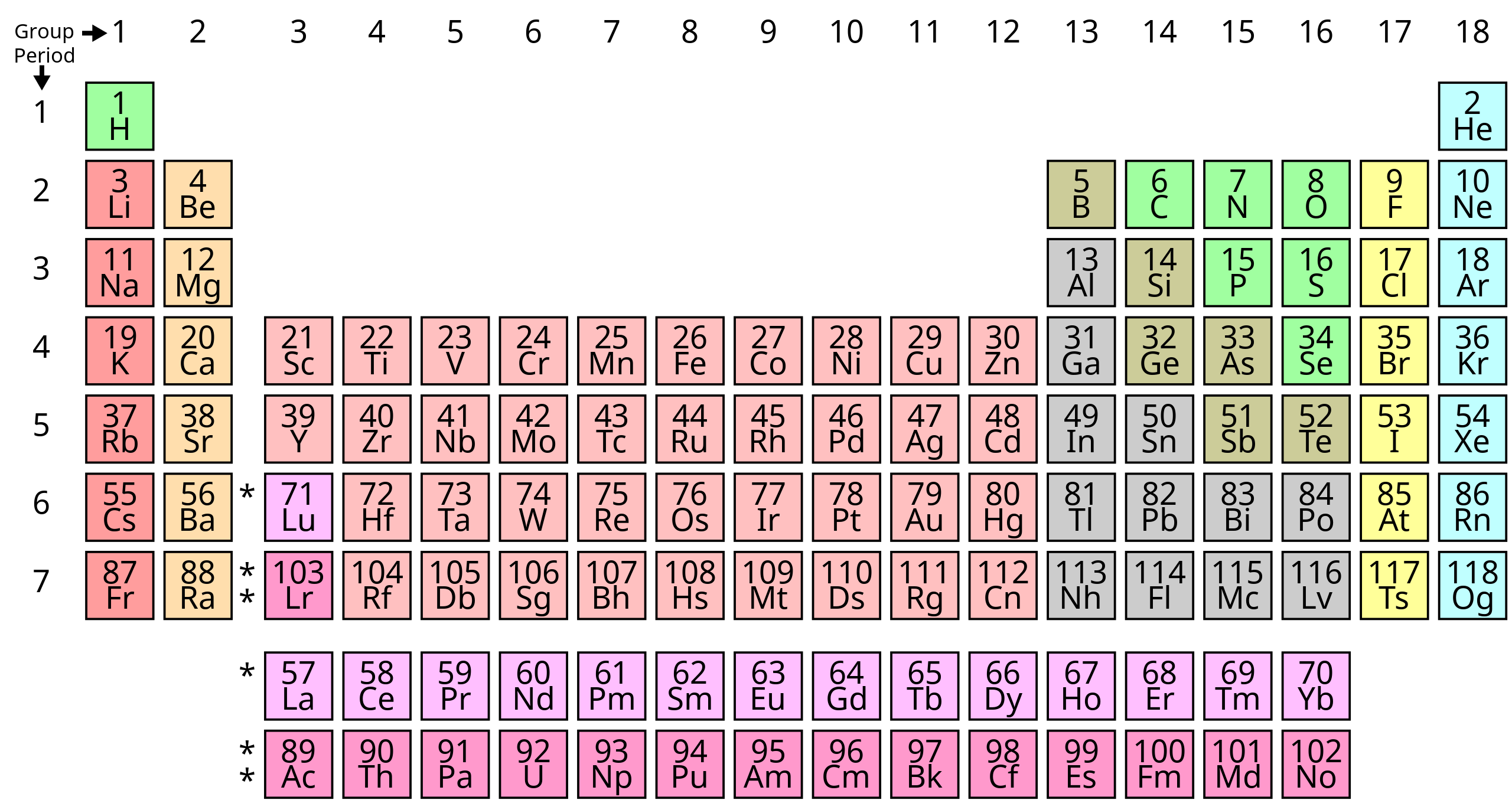
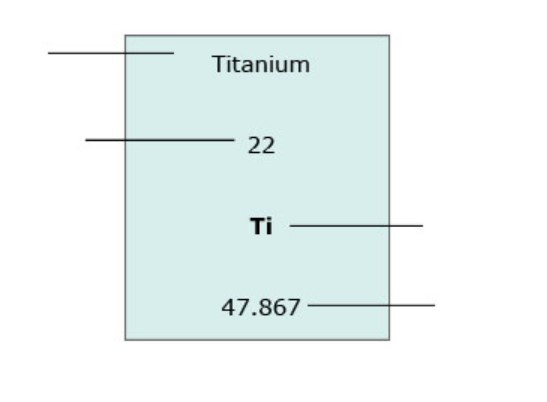
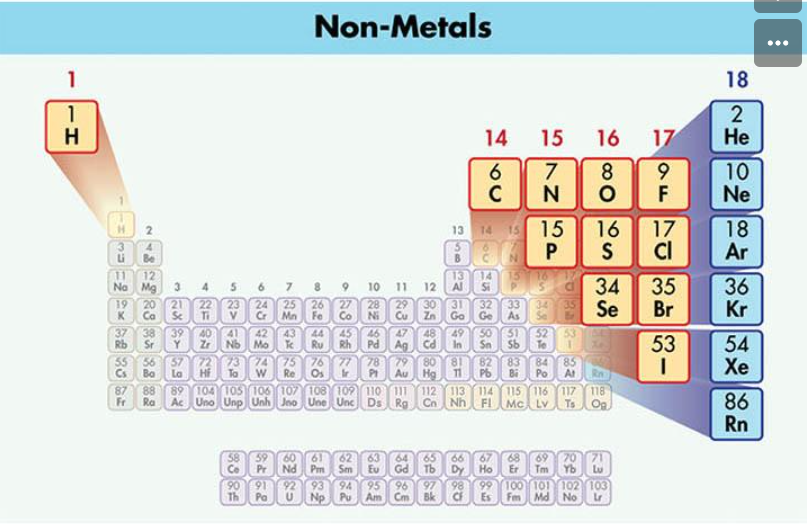
Explore 1: How do scientists distinguish between metals, metalloids, and nonmetals?
Required
2
Required
2
Required
1
Required
3
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
4
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1