E-Day Alternative Project: Energy
star
star
star
star
star
Last updated about 1 year ago
29 questions
Note from the author:
Required
8
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
3
Required
1
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt |
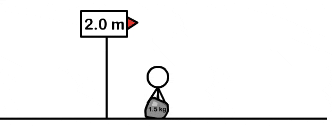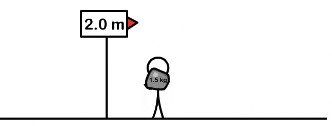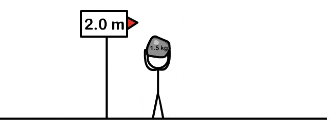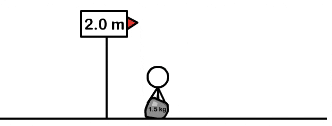

| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
Mechanical energy | arrow_right_alt | increases |
Kinetic energy | arrow_right_alt | decreases |
Gravitational potential energy | arrow_right_alt | remains the same |
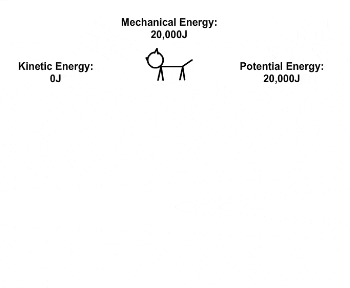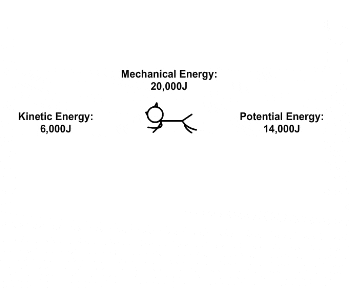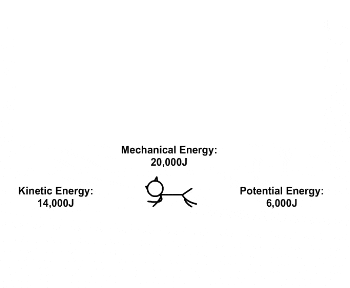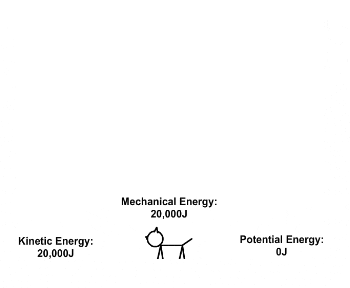
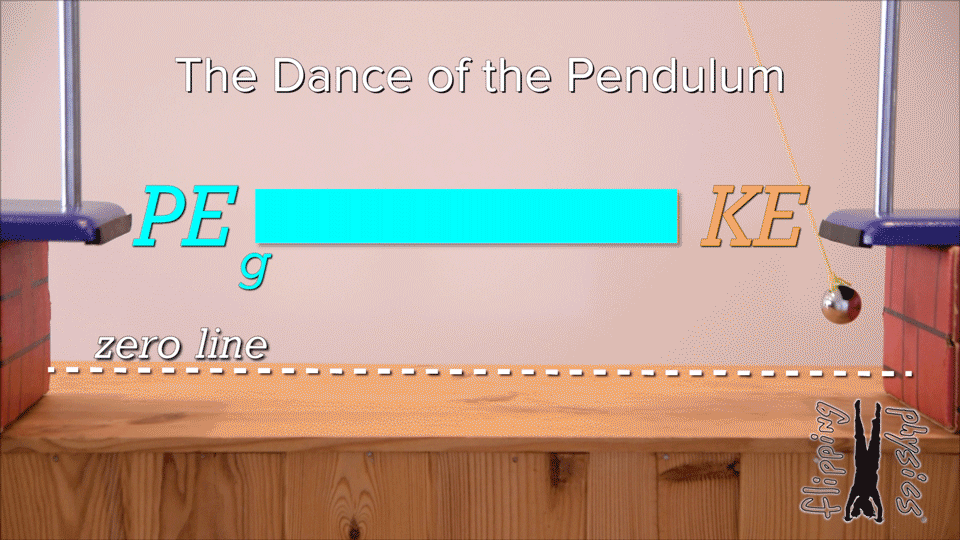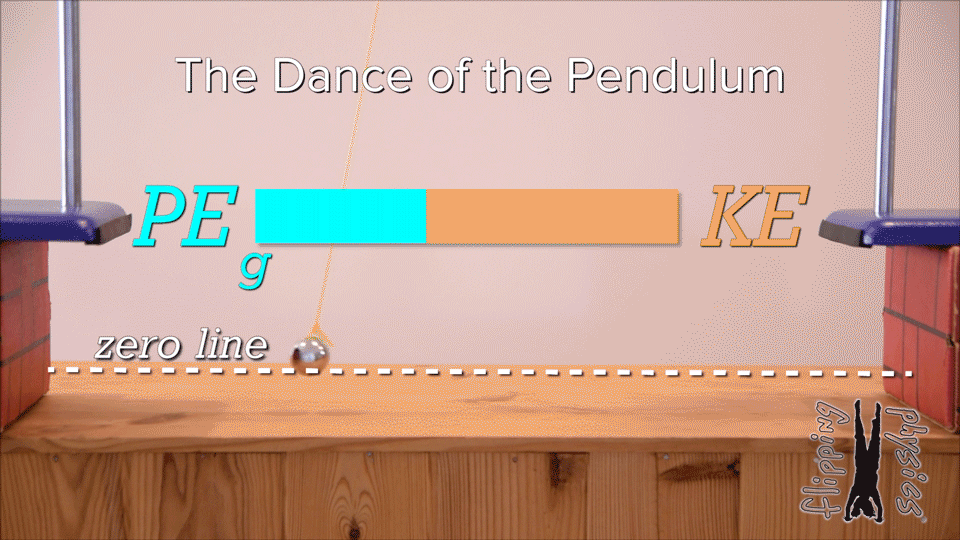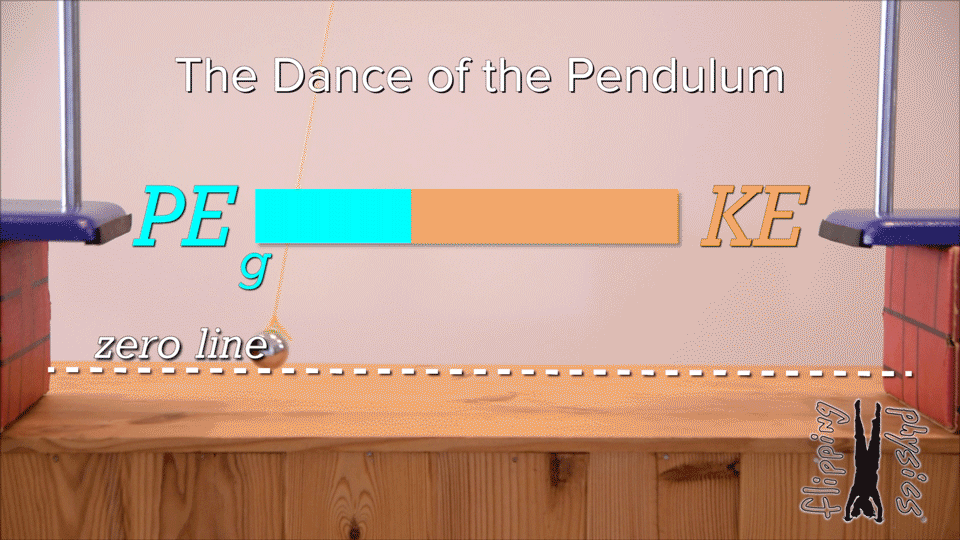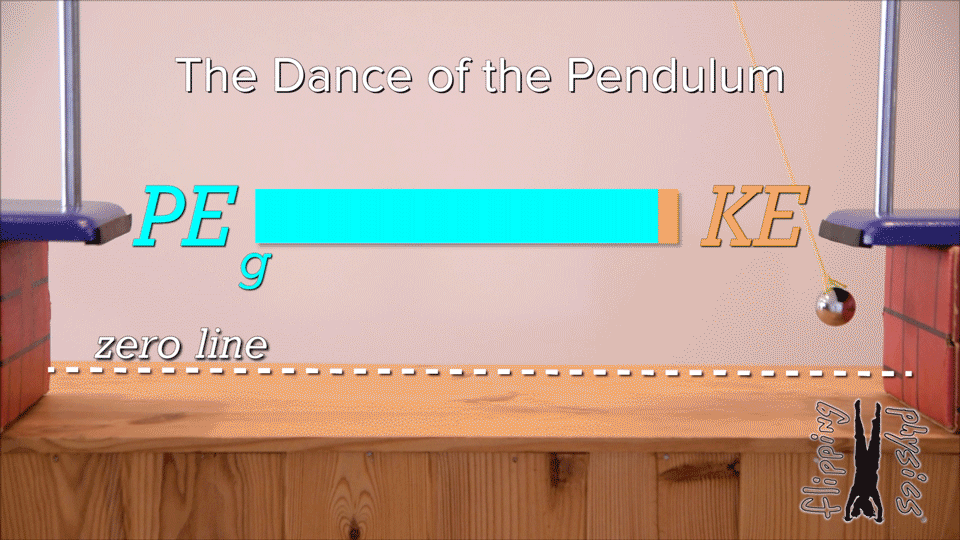
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
EK = 20 000 J | arrow_right_alt | EP = 20 000 J |
EK = 2 000 J | arrow_right_alt | |
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt |