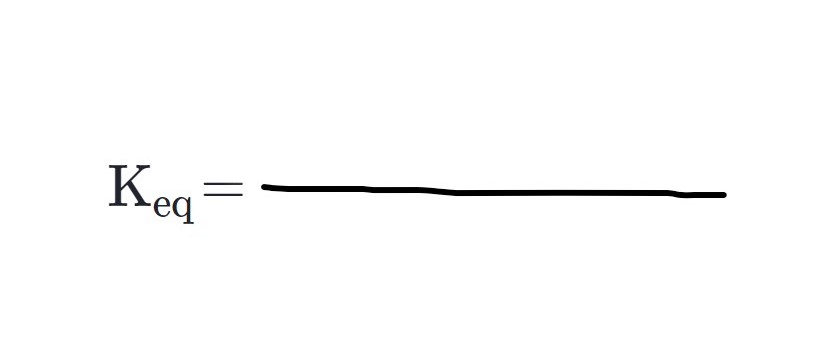Meyer_DE_CH_5.4 & 5.5_Chemical Equilibrium & Reaction Rate
star
star
star
star
star
Last updated almost 3 years ago
27 questions
Background Knowledge
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
2
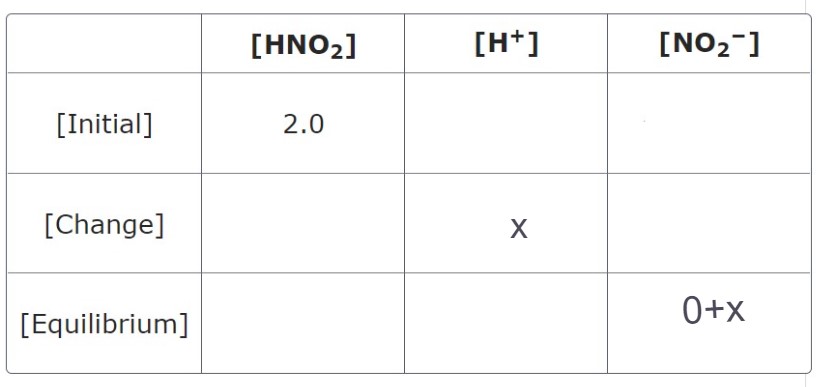
Equilibrium Constant (5.4_1)
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Le Chatelier's Principle (5.4_2)
Required
1
Required
1
Solubility Product Constant (5.4_3)
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Factors that Influence Reaction Rate (5.5_1)
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Rate Laws (5.5_2)