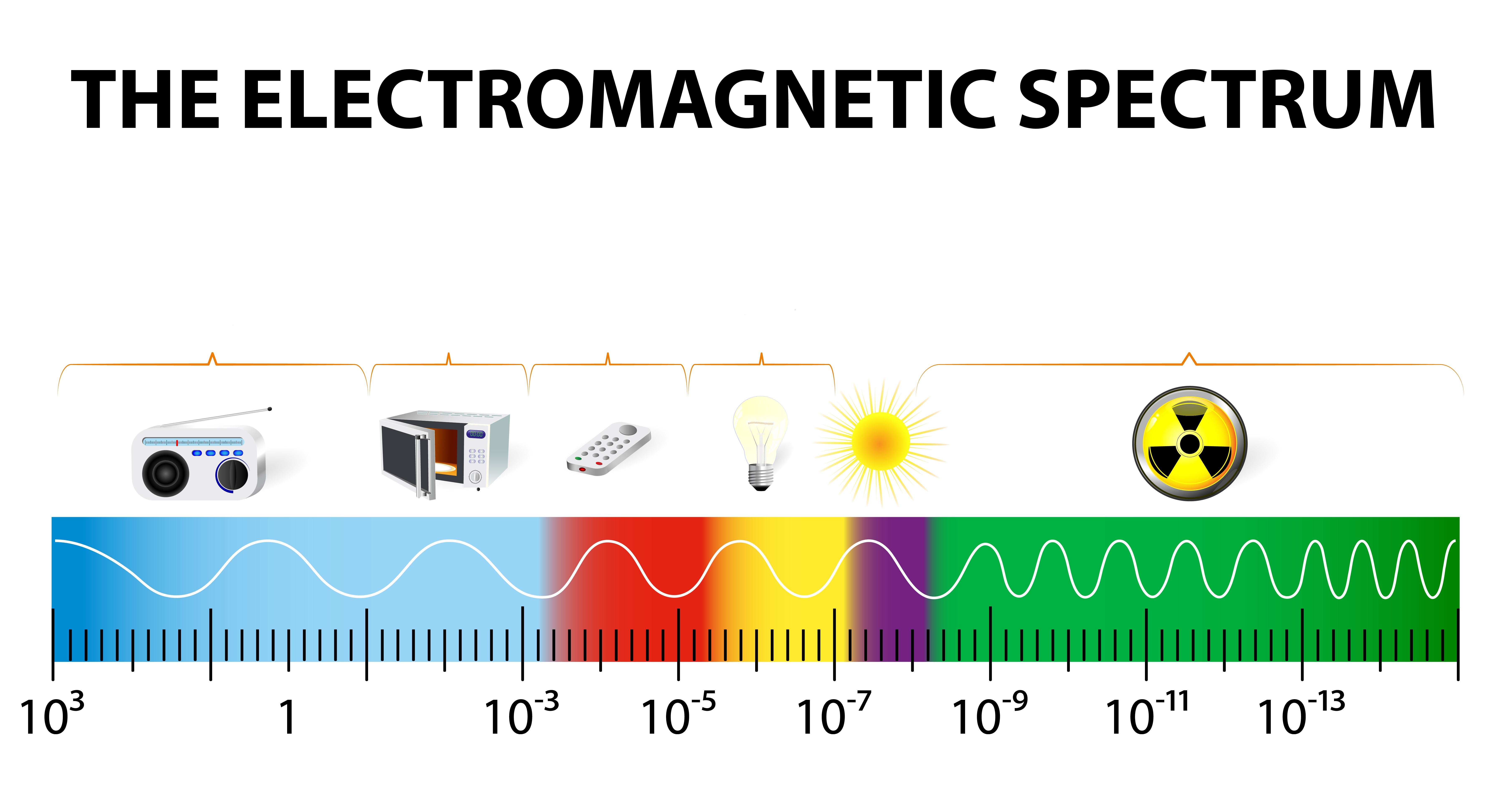
DE_Phys_3.1 Types of Energy
star
star
star
star
star
Last updated almost 3 years ago
18 questions
Background Knowledge (Engage)
1
2
2
Two Main Types of Energy (Explore 1)
1
1
1
2
2
1
Kinetic Energy, Mass, and Velocity (Explore 2)
1
1
1
1
1
Conversions between Kinetic and Potential Energy (Explore 3)
1
1
1
1