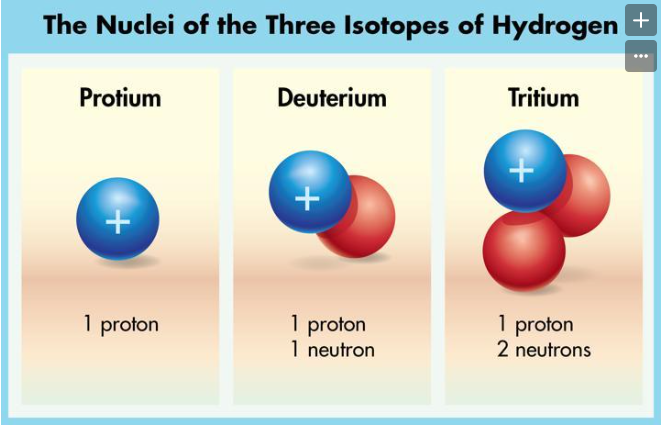
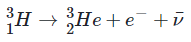(Engage) Every active star in the universe is generating energy through __________ reactions. The sun is composed of gases, primarily hydrogen and helium, which are compressed into a form of matter called __________. The __________ of such a large mass of gas causes intense pressure at the core of the sun which, combined with the extreme temperature (15,000,000°C), allows nuclear reactions to occur.