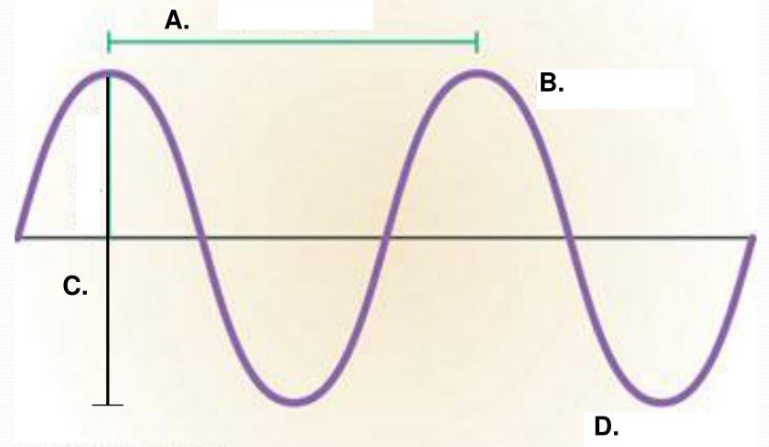
Some waves move through matter. The matter that a wave moves through is called the ___________ of the wave. A traveling wave is a disturbance that moves through space and time, transferring ___________ without transferring matter. Waves originate from an initial disturbance, or ________________ , that provides some energy to the system. In general, as particles in a medium oscillate or vibrate, they _____________ the energy of this oscillation to particles around them, and this process continues to transmit the energy of an oscillation to particles across a distance. Through this process, a wave “_______________ ” through a medium. In this way, waves transfer energy without transferring matter. When particles oscillate in a direction __________________ to the direction that the wave propagates, the wave is a _______________ wave. This is the most familiar type of wave. However, sometimes the particles in a wave oscillate in the _________ direction that the wave propagates. These waves are called ______________________ waves. Sound waves and seismic “P-waves” are examples of longitudinal waves. They are occasionally known as _____________ waves or compression waves.