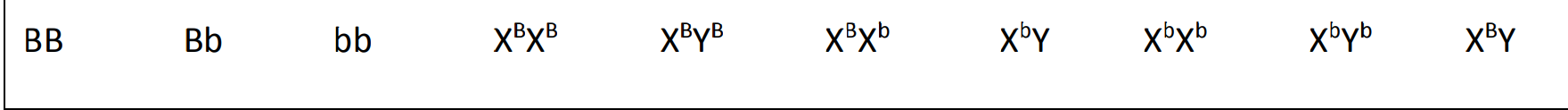Biology - Genetics 2 - Classwork
star
star
star
star
star
Last updated 8 months ago
116 questions
Note from the author:
Section 1 - Dihybrid Crosses
1
1
1
1
1
1
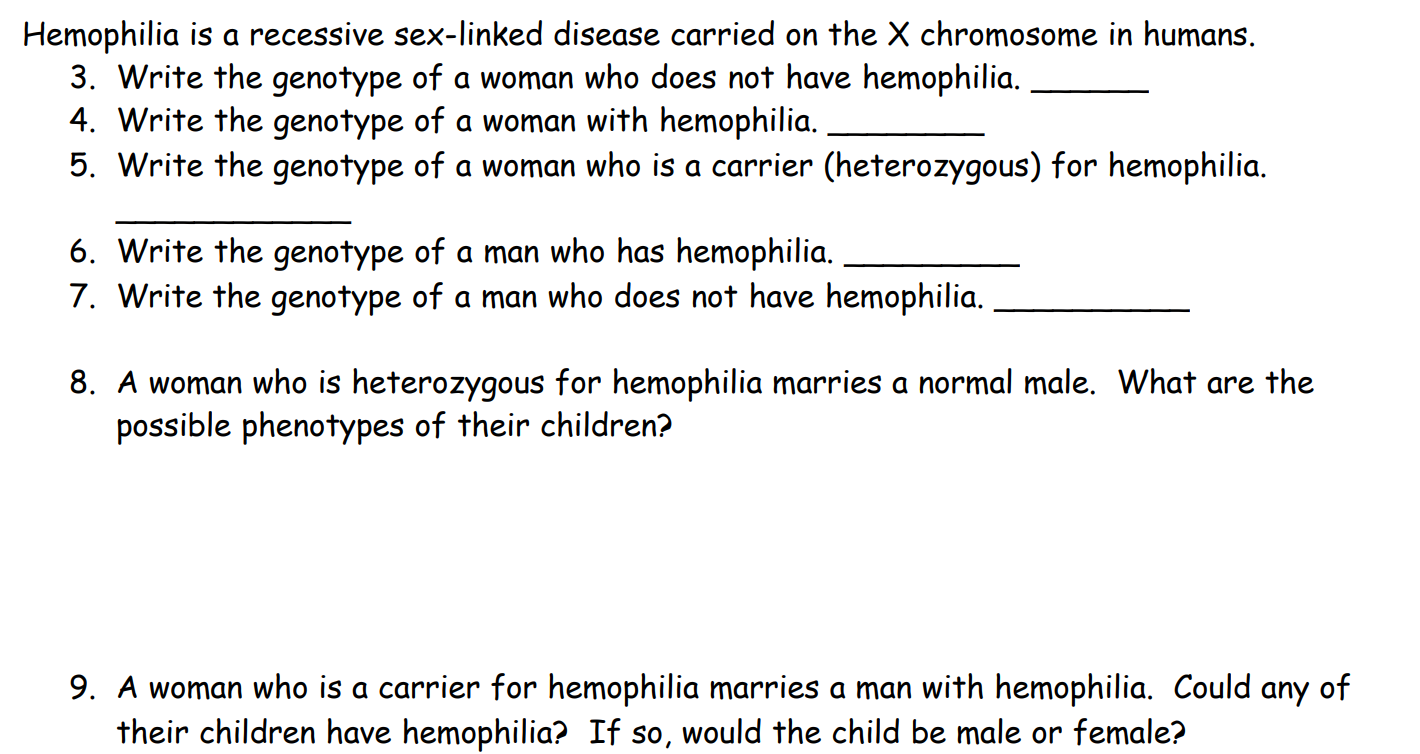
Section 2 - Sex-linked Traits
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Section 3 - Incomplete and Codominance
1
1
1
1
1
1
Section 4 - Pedigrees
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
3
5
Section 4b - New Section - Heredity and Traits STEM Case
Section 5 - Quiz Review
1