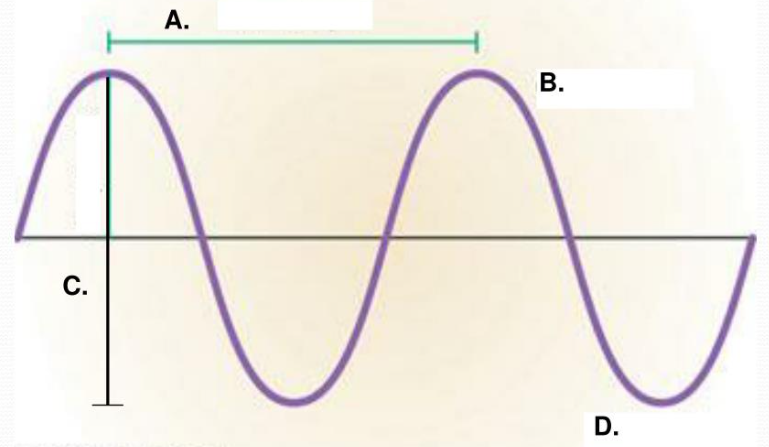
Earthquakes ___________________ that travels through solid ground in the form of seismic waves. Potential energy builds up as a result of ___________ on rocks along cracks in Earth’s crust called ___________ . The stress occurs because pieces of Earth’s lithosphere called tectonic plates are in constant motion. This motion causes rock on either side of a fault to ___________ , or show strain. Eventually, the stress becomes so great that ________________ , moving suddenly along the fault. Earthquakes generate several different types of seismic waves. Some seismic waves travel through Earth’s interior. Geologists refer to these as _________ waves because they move through bodies of rock. Other seismic waves, called ____________ waves, travel along the surface of the ground.