Formative_DE_LE_Unit4
star
star
star
star
star
Last updated almost 3 years ago
33 questions
4.1 Genetics
2
3
1
1
1
1
1
4.2 DNA
2
1
2
2
1
1
2
4.3 Transcription and Translation
1
1
2
1
1
3
2
2
1
4.4 Genetic Disorders and Technology
1
2
1
2
1
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
E | arrow_right_alt | cell |
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt |
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
heterozygous | arrow_right_alt | Phenotype: Blue eyes Genotype: two recessive blue alleles |
homozygous recessive | arrow_right_alt | Phenotype: Brown eyes Genotype: Two dominant brown alleles |
homozygous dominant | arrow_right_alt | Phenotype: Brown eyes Genotype: One dominant brown allele and one recessive blue allele |
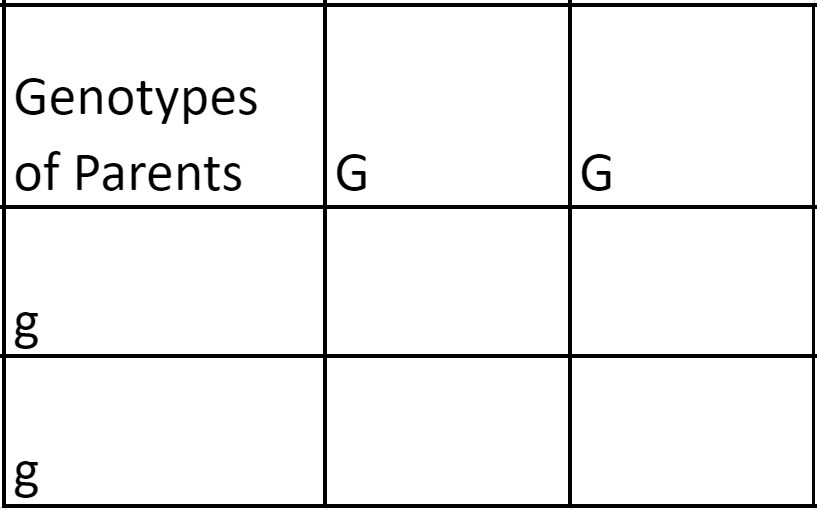
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
replication fork | arrow_right_alt | the shape of a DNA molecule; two spiral strands wrapped around each other |
double helix | arrow_right_alt | Y-shaped structure that forms during the process of DNA replication; the unseparated double stranded DNA represents the base of the Y |
helicase | arrow_right_alt | |
| arrow_right_alt |
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt |
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
Messenger RNA (mRNA) | arrow_right_alt | It contains a sequence of nucleotides that direct the assembly of amino acids into proteins. It carries this information from the cell nucleus to ribosomes in the cytoplasm. |
Transfer RNA (tRNA) | arrow_right_alt | It transfers amino acids to the ribosome as the protein is built. It also connects each three-letter genetic code carried in mRNA to a corresponding amino acid. There are 64 different three-letter codes for 20 amino acids. |
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) | arrow_right_alt | It is present in the subunits of a ribosome that allow for decoding of mRNA. It also interacts with tRNA during protein synthesis to help form peptide bonds between amino acids. |
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
insertion | arrow_right_alt | |
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt |