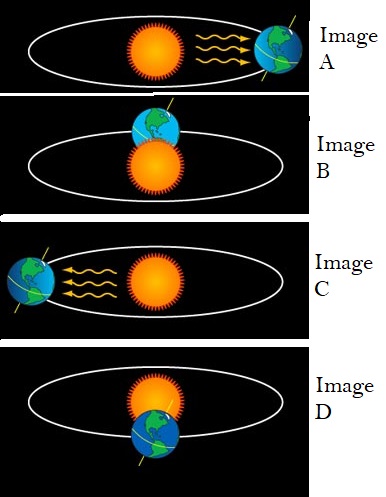
Have you ever wondered why the days are shorter in winter and longer in summer? Or why some parts of the world experience extreme temperature changes while others do not? Well, the answer to these questions can be found by understanding the Earth's tilt and orbit around the sun. The Earth spins on its axis at a tilt of 23.5 degrees, which means that different parts of the Earth face towards or away from the sun at different times of the year as it orbits. When the Northern Hemisphere is facing towards the sun, it receives more direct sunlight and experiences summer. In contrast, when the Southern Hemisphere is tilted towards the sun, it experiences winter. During the equinoxes, the sun is directly above the Earth's equator, so the entire planet experiences roughly the same amount of daylight. During the solstices, the Northern Hemisphere experiences the longest day (summer solstice) and shortest day (winter solstice) of the year. The tilt of the Earth's axis also causes the seasons to shift slightly from year to year. Understanding these movements helps us predict seasonal changes in weather, animal behavior, and vegetation growth.