Lab #20 NYS Relationships and Biodiversity
star
star
star
star
star
Last updated over 1 year ago
76 questions
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
25
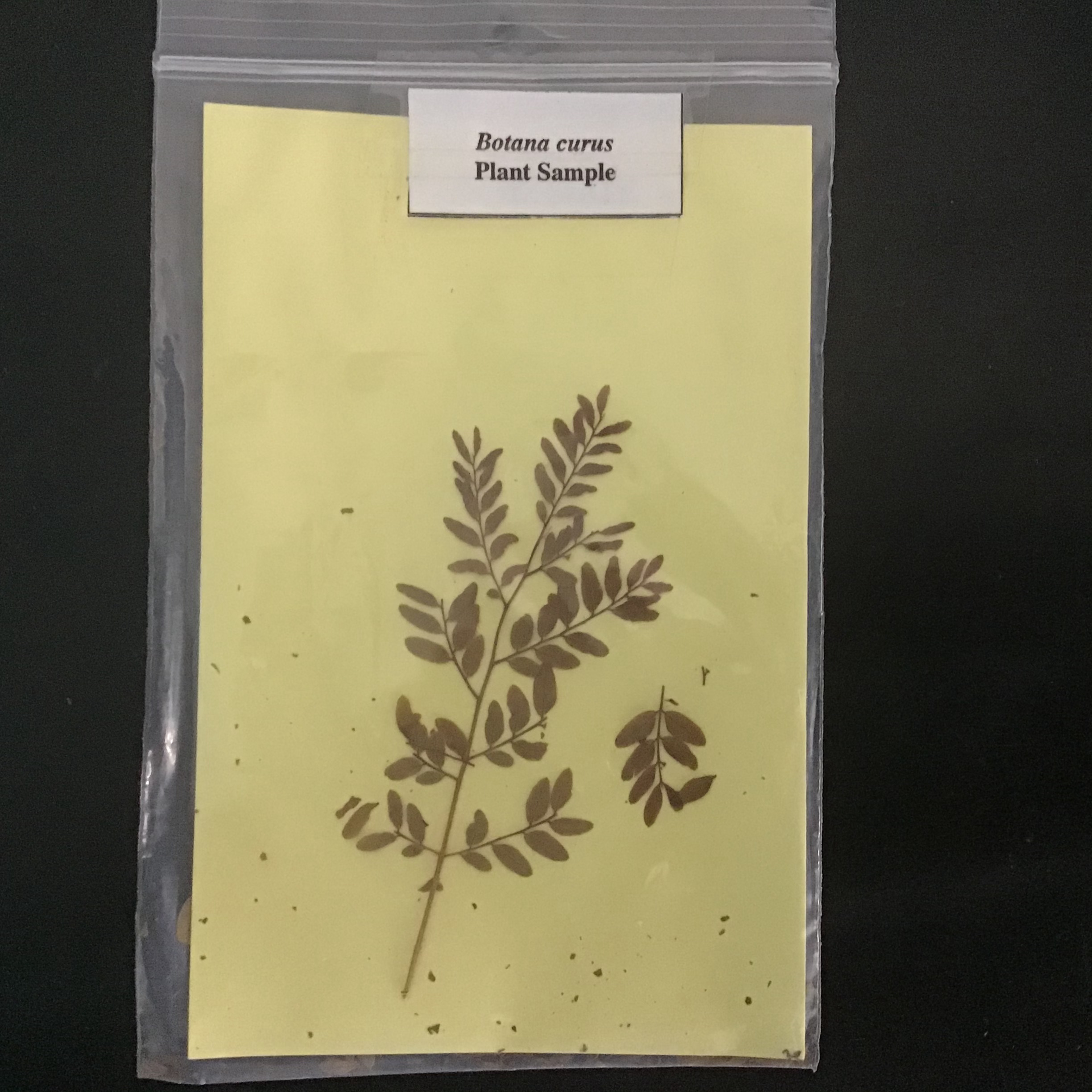
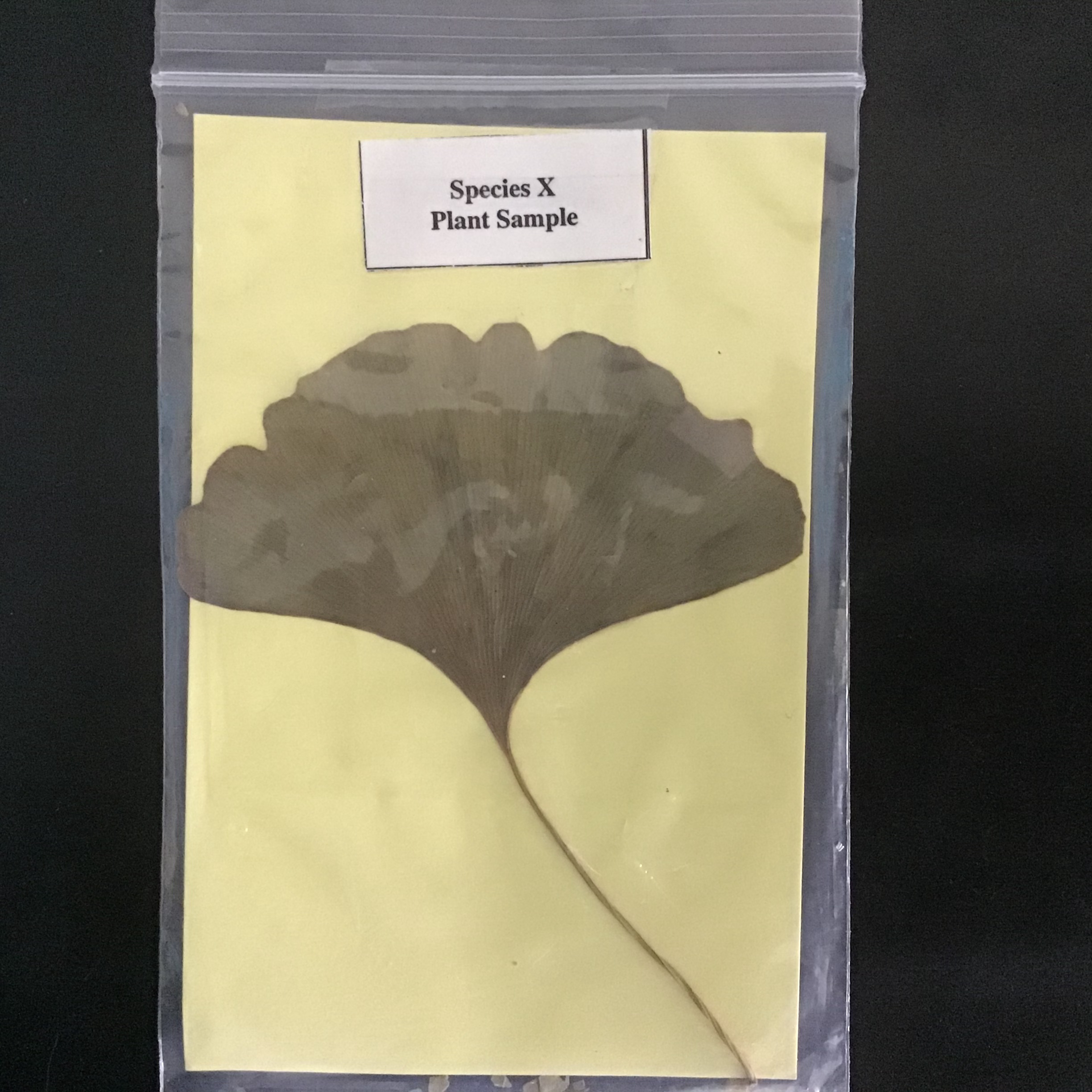
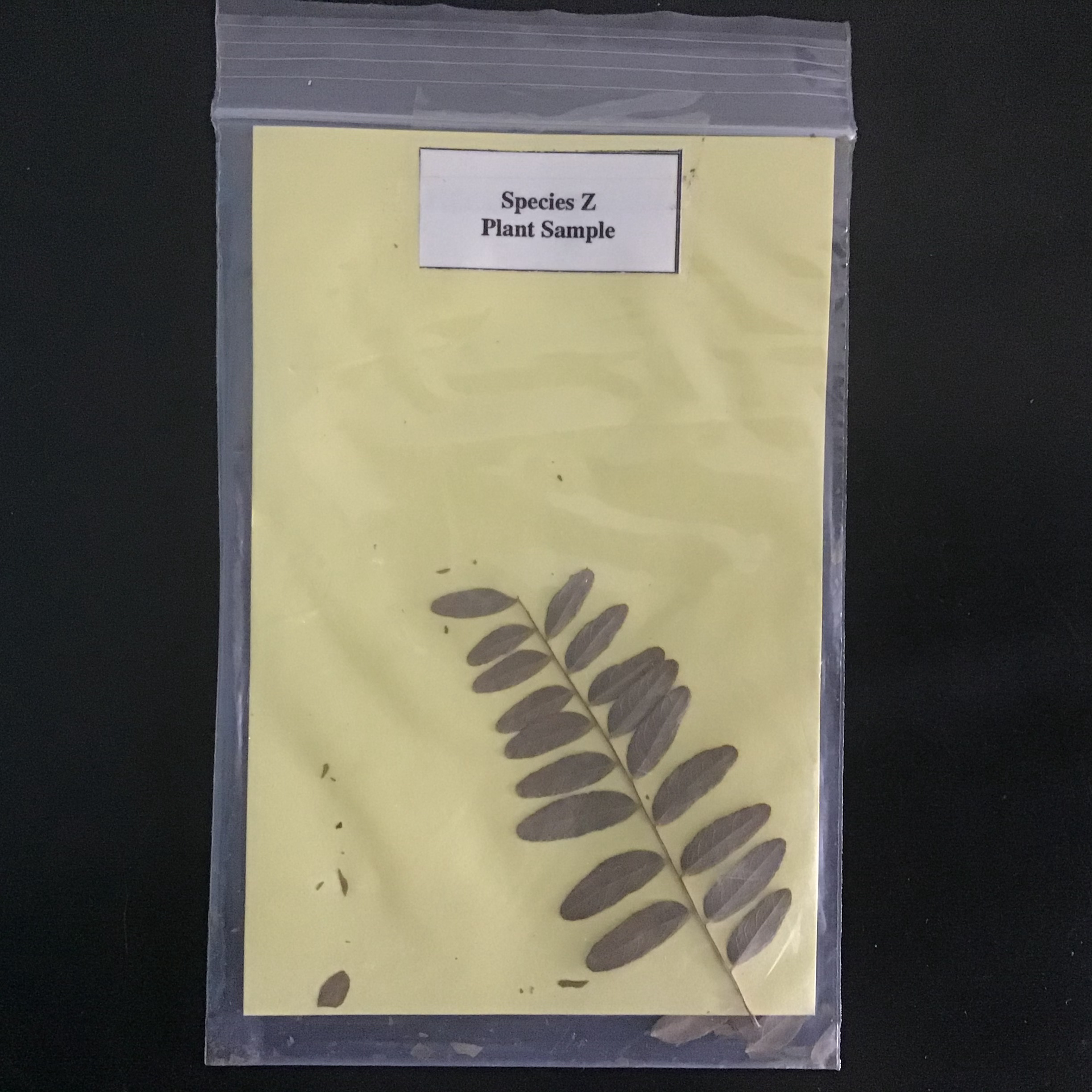
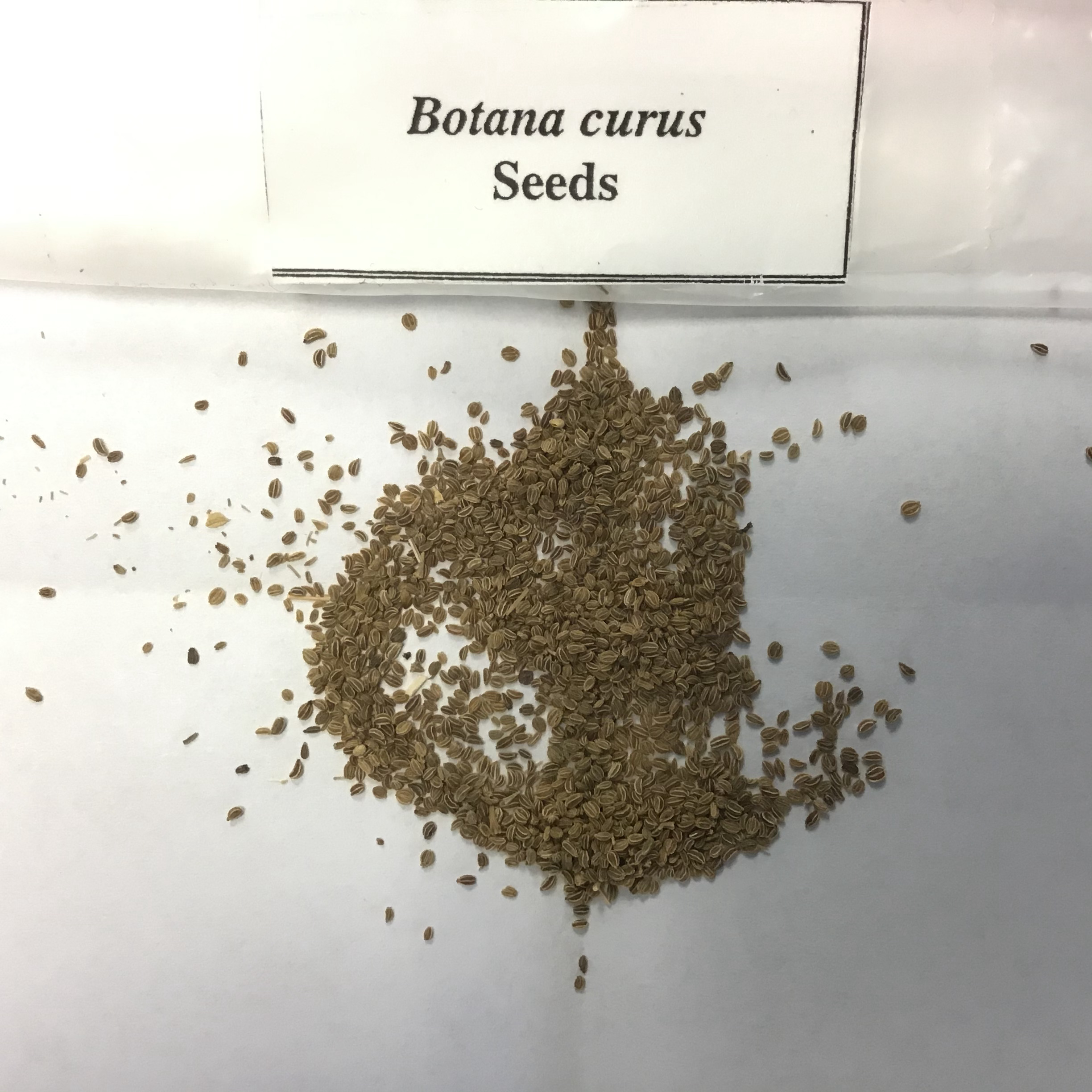
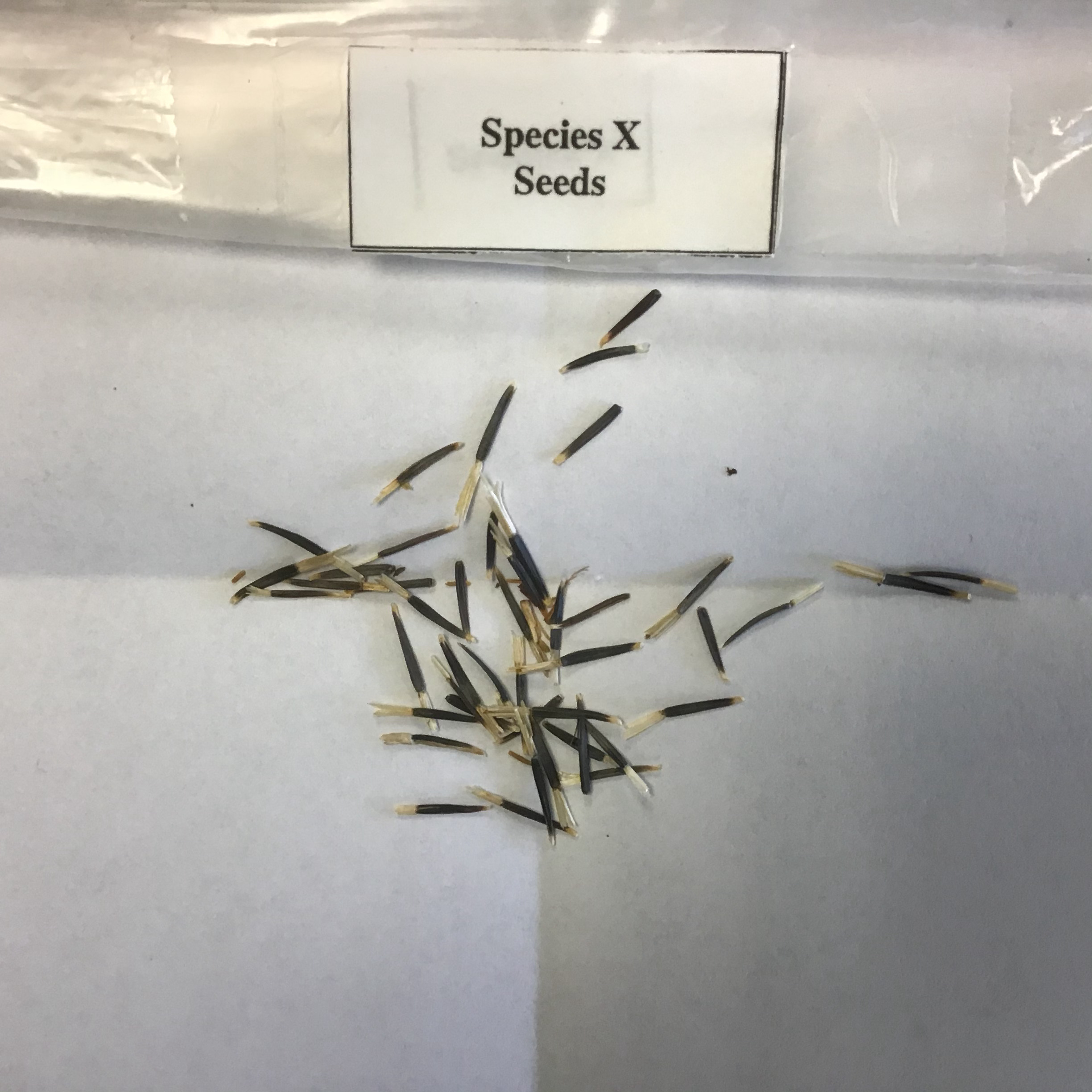
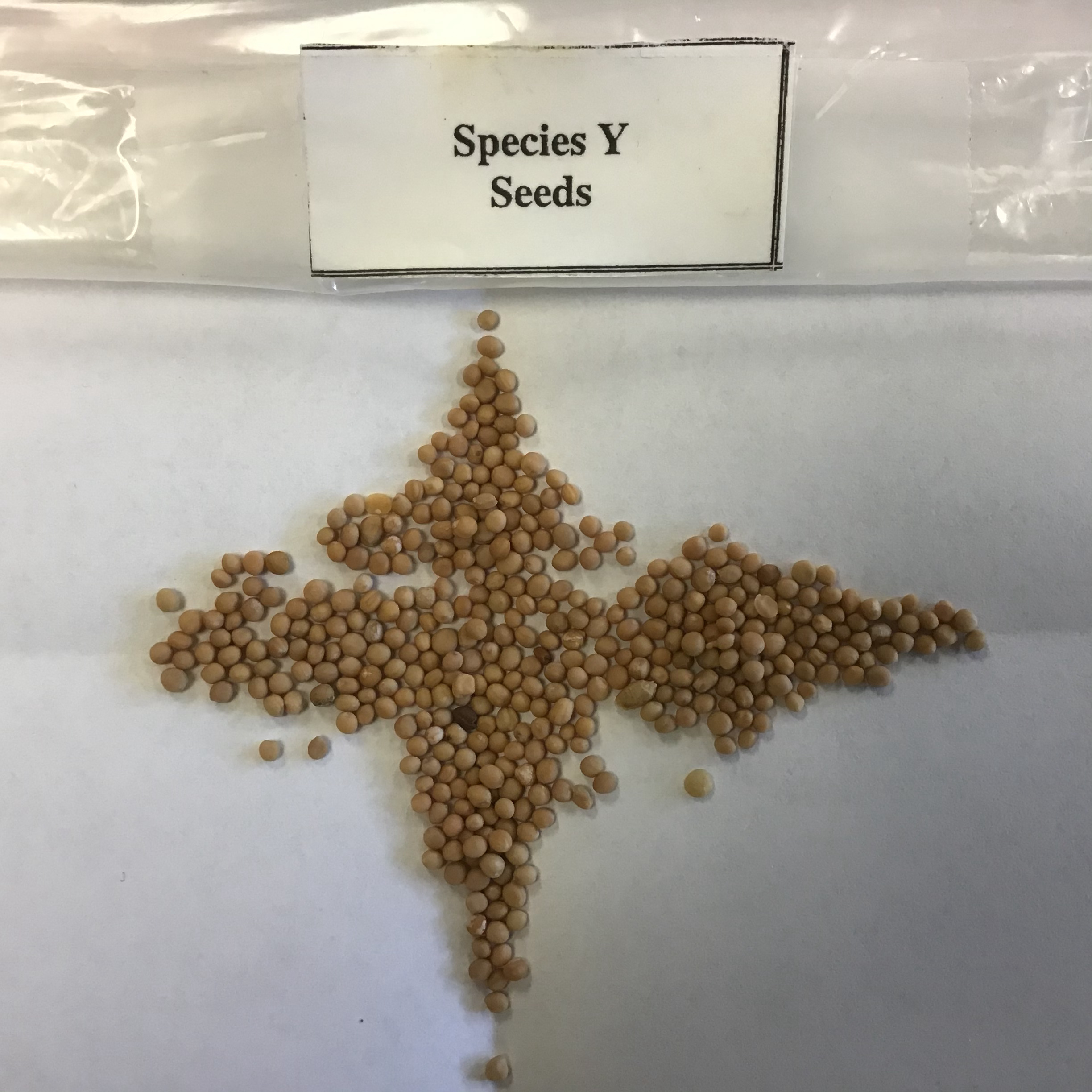
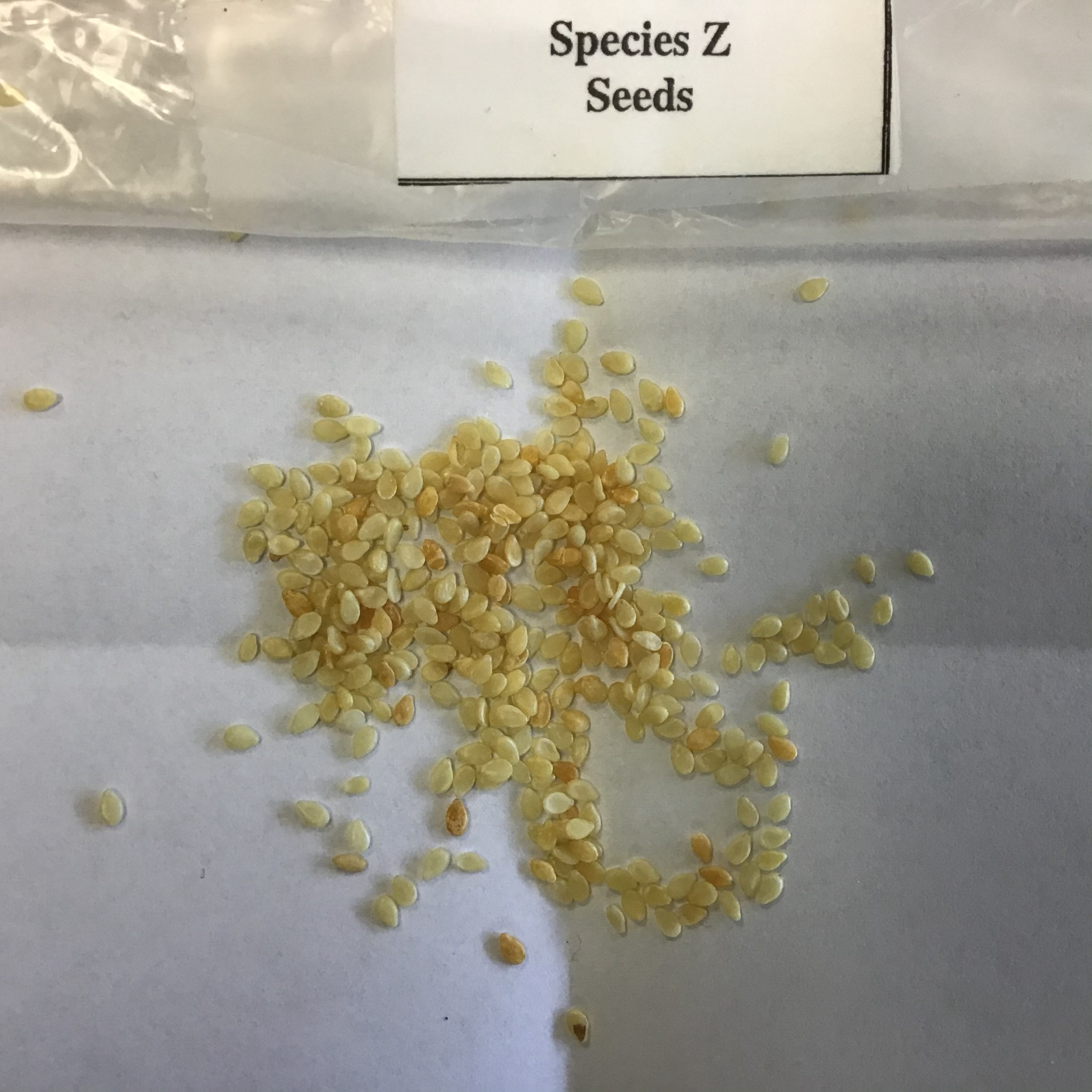








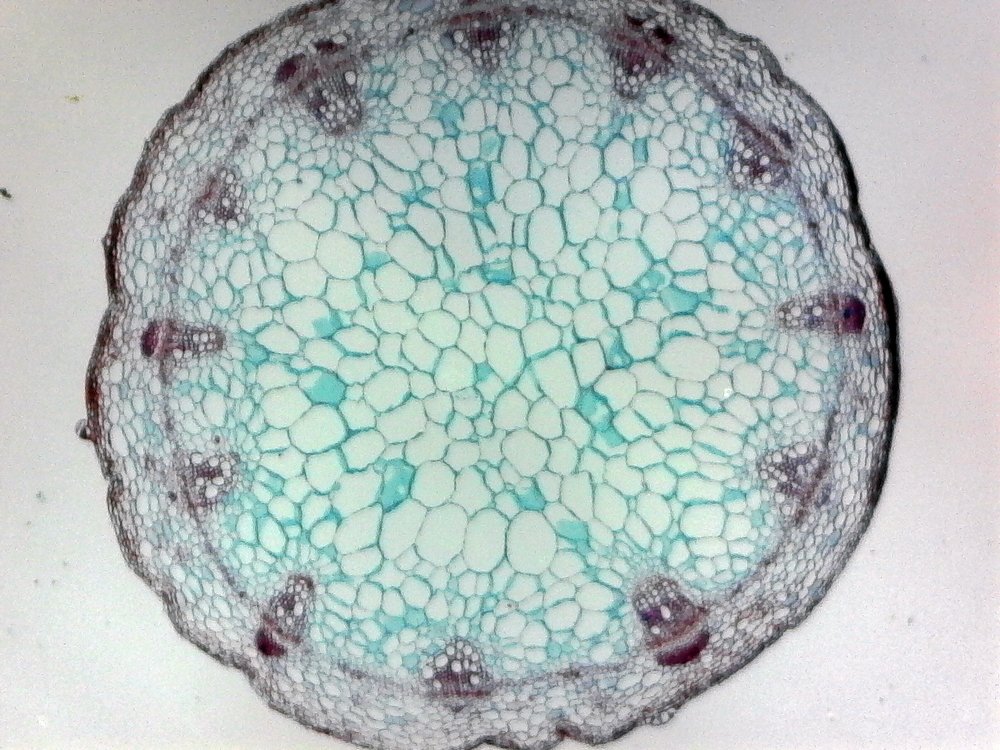
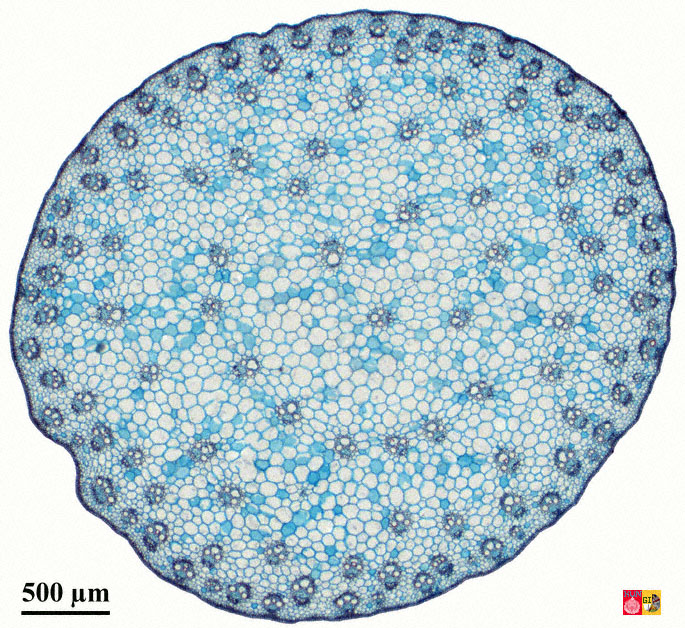
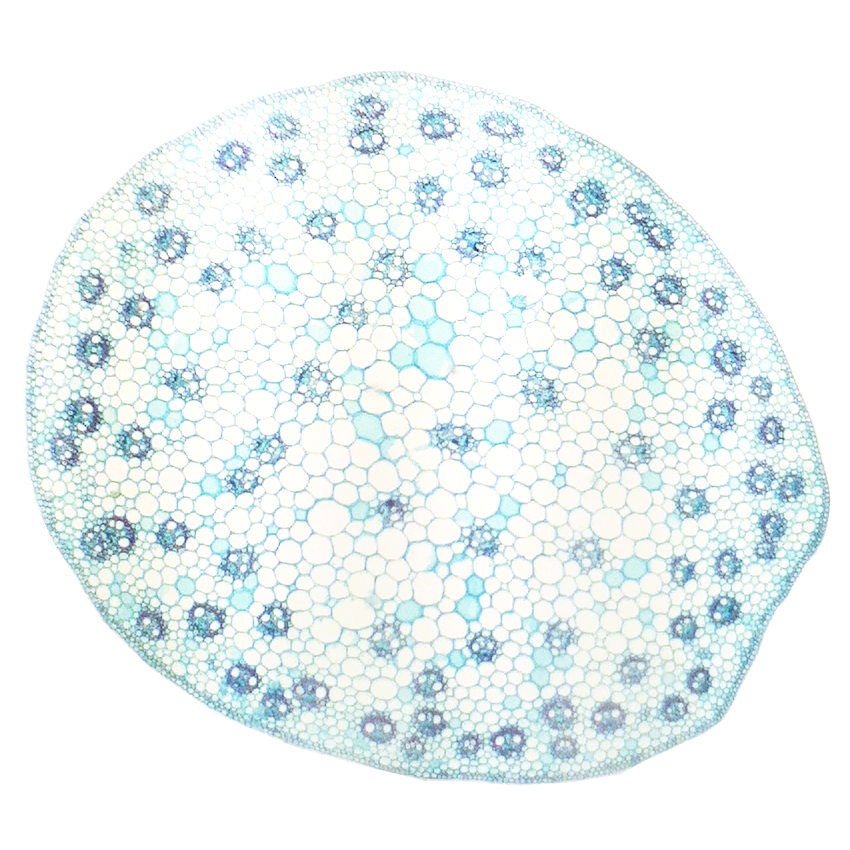
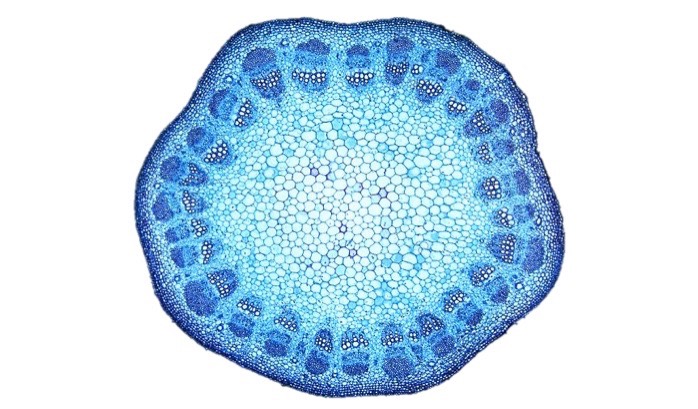
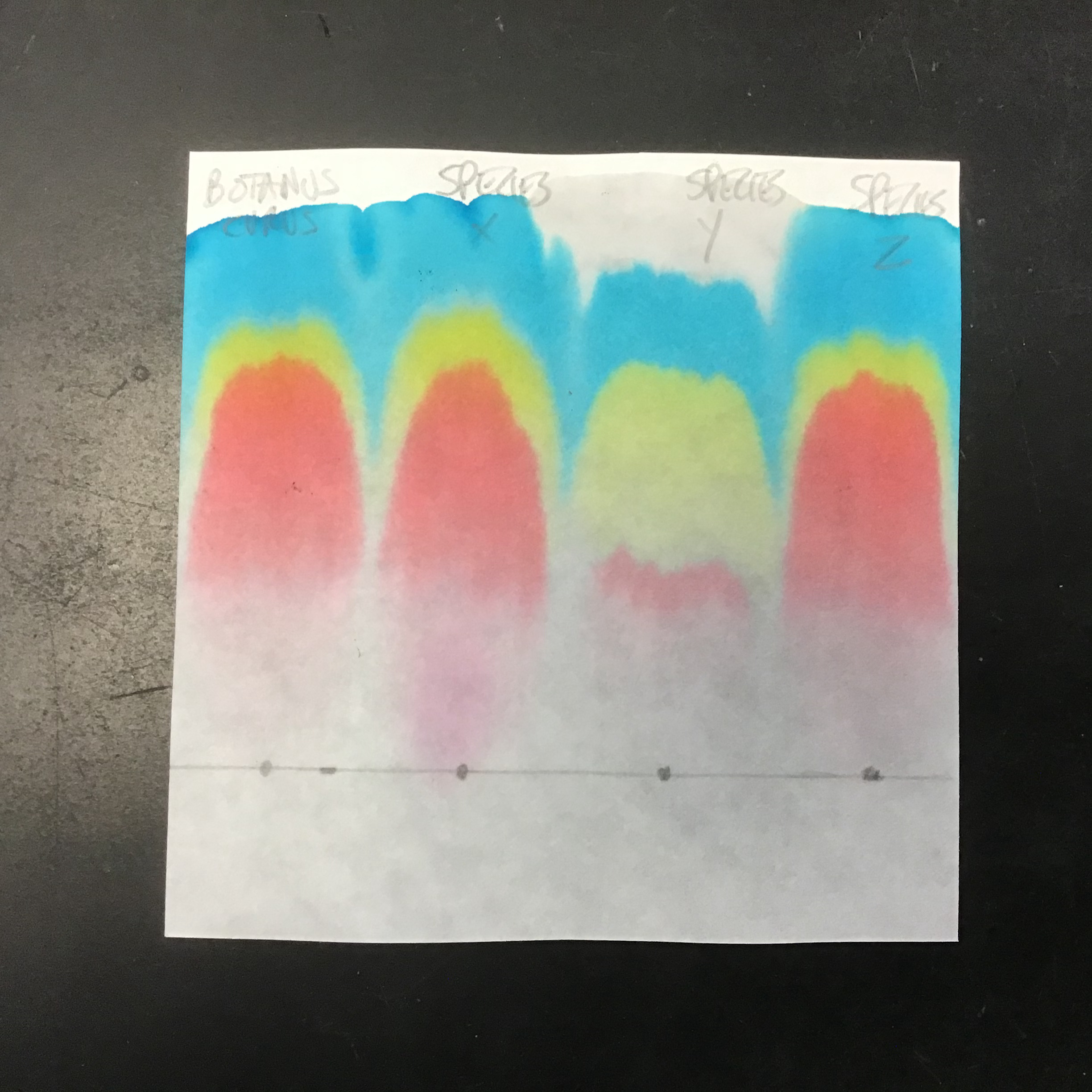
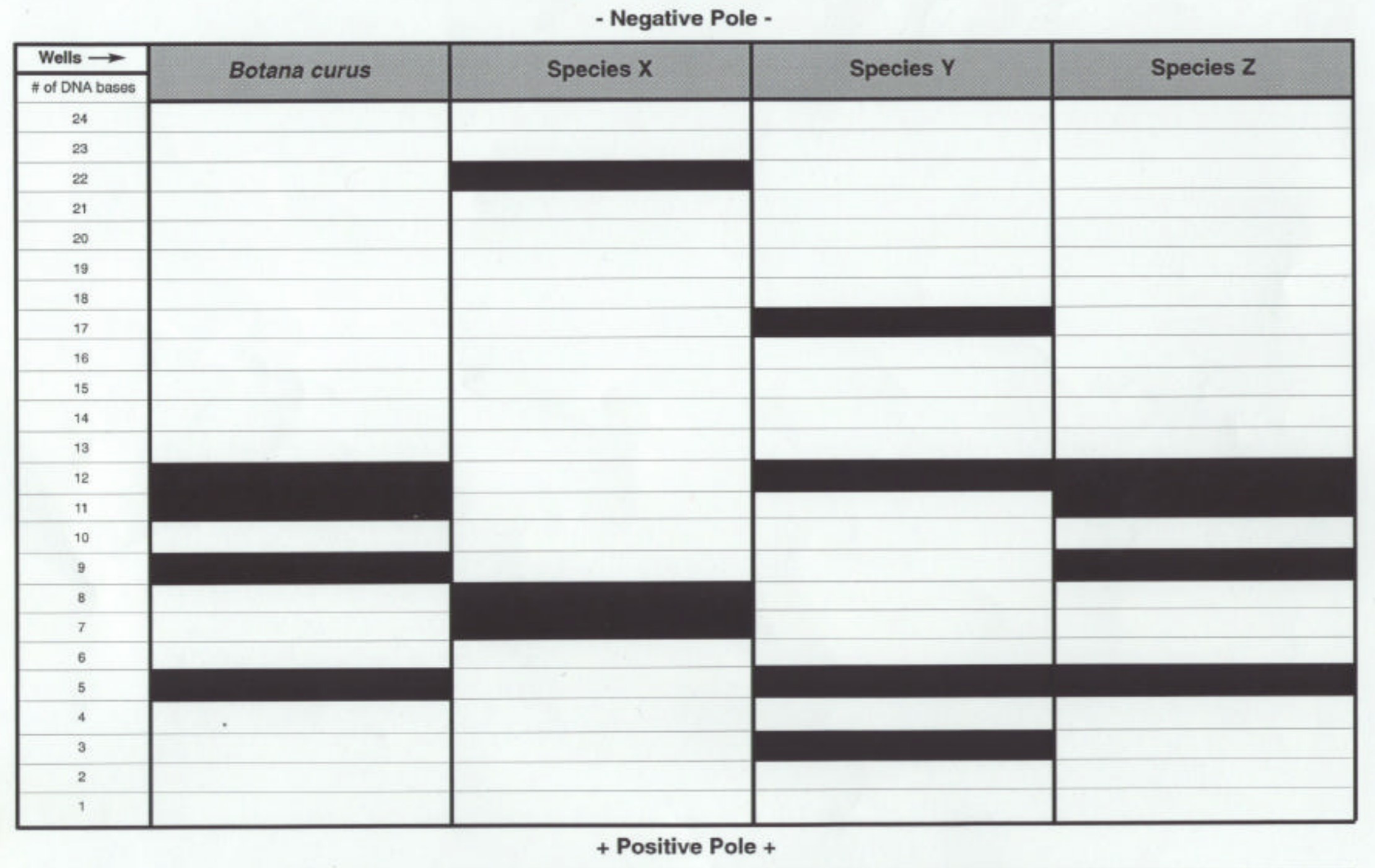
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt |
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt |
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt |
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt |
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt |
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt |
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt |
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt |




| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
GUC | arrow_right_alt | CCG |
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt |



| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
THR | arrow_right_alt | ACG |
TYR | arrow_right_alt | UAU |
GLN | arrow_right_alt | CAA |