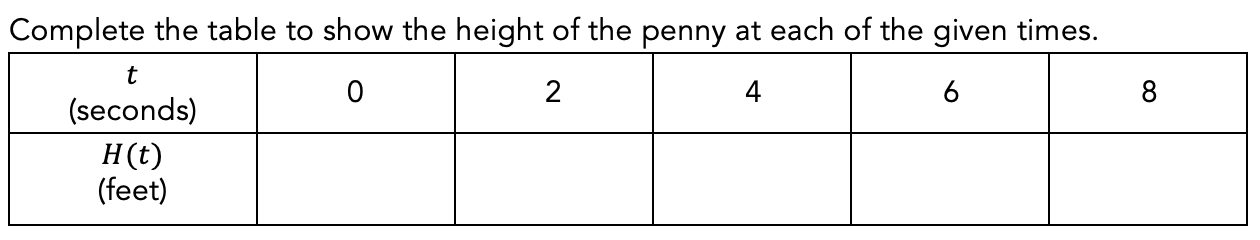
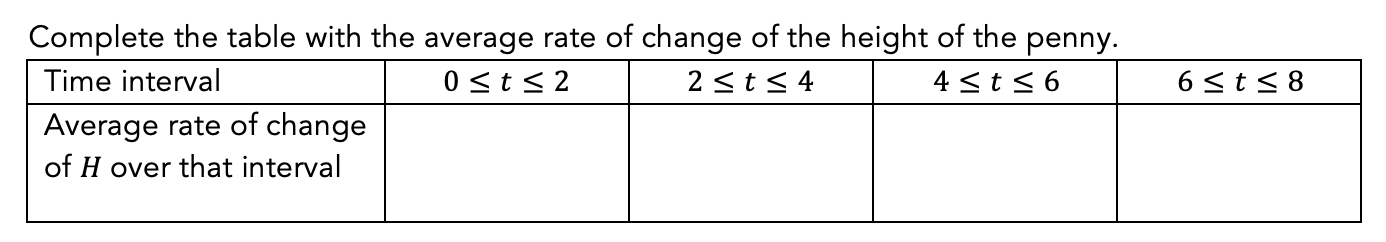
1.4 How Fast Does a Penny Fall from the Empire State Building?
star
star
star
star
star
Last updated over 2 years ago
20 questions
Note from the author:
Experience
1
1
0
0
1
0
Formalize
0
0
1
0
1
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
Exponential | arrow_right_alt | |
Cubic | arrow_right_alt | |
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt |