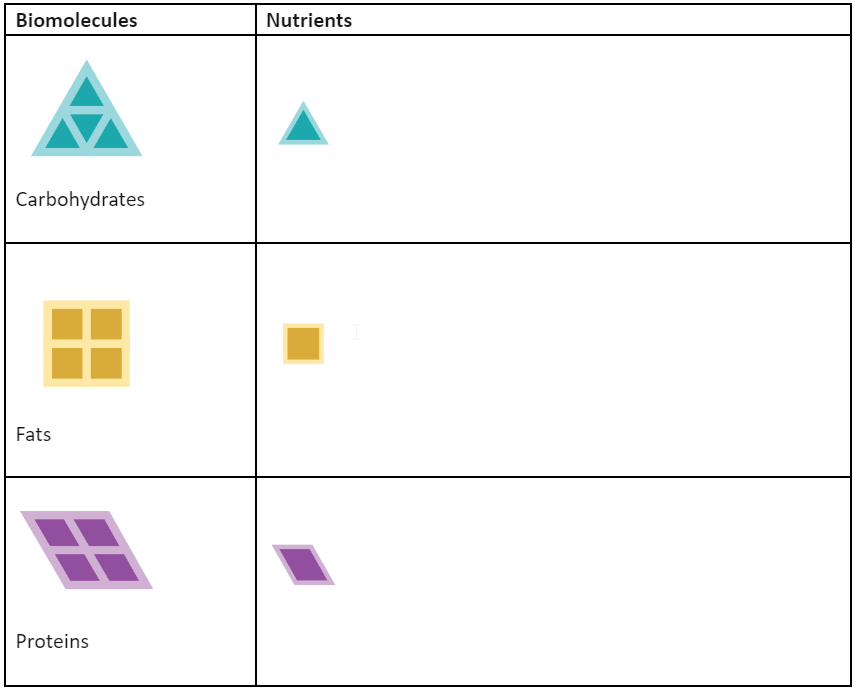
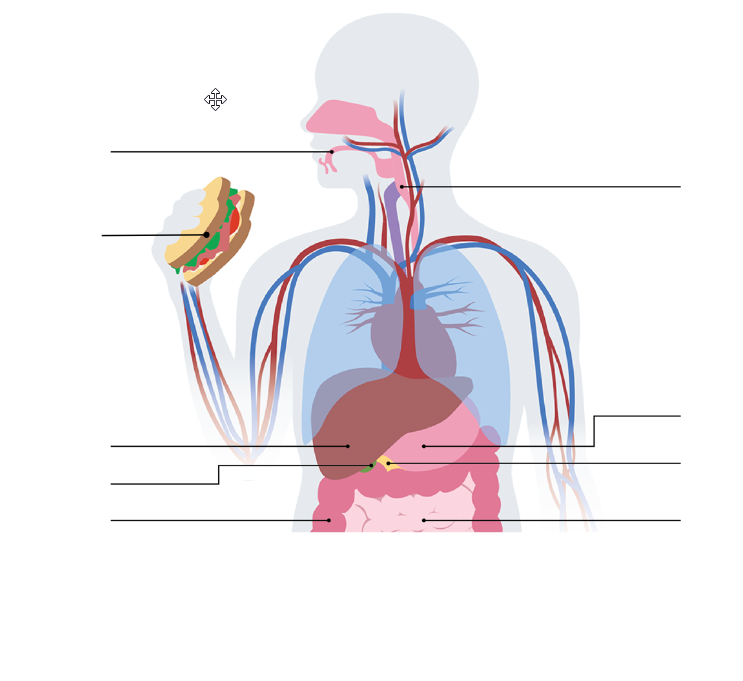
03 Biomolecules on the Menu
star
star
star
star
star
Last updated over 2 years ago
14 questions
Note from the author:
Required
3
Required
3
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
2
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1