Rock Cycle Stations
star
star
star
star
star
Last updated about 2 years ago
35 questions
Watch
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Read
Required
1
Required
1
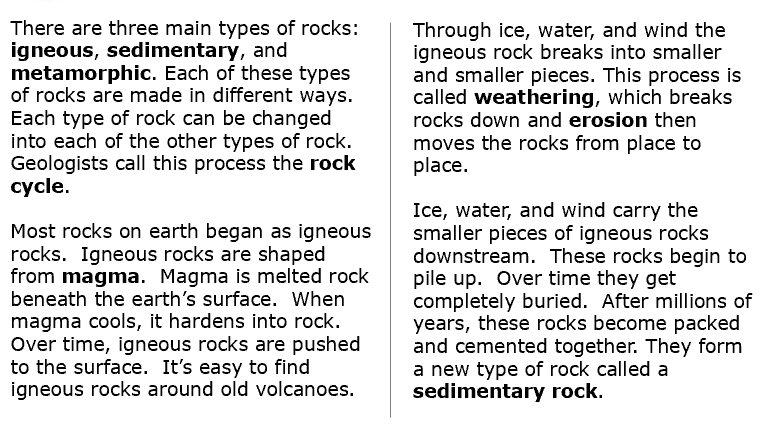
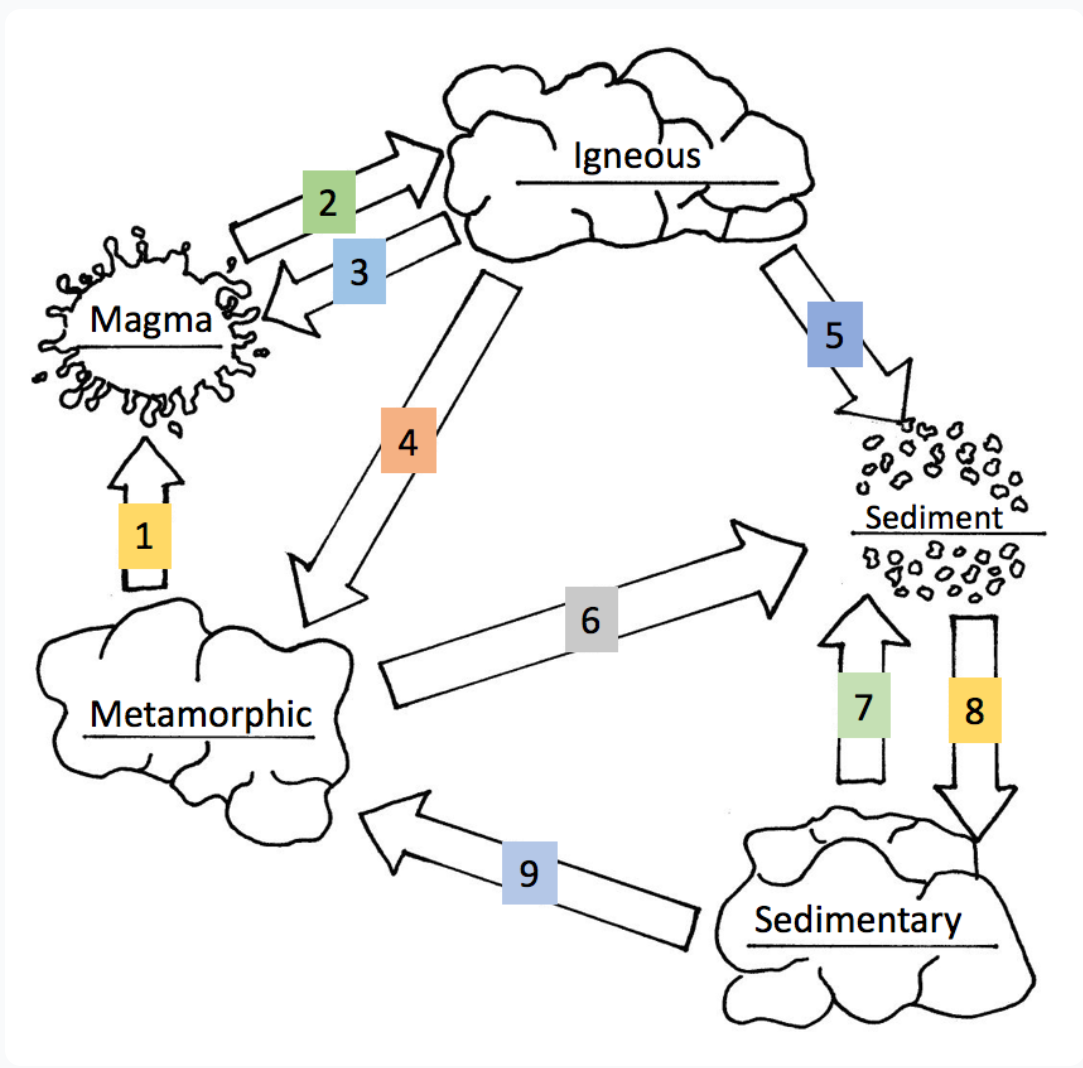
Explore - Igneous Rocks
Explore - Sedimentary Rocks
Explore - Metamorphic Rocks
Organize
Required
1
Assess
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Comparing Rocks and Minerals
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1