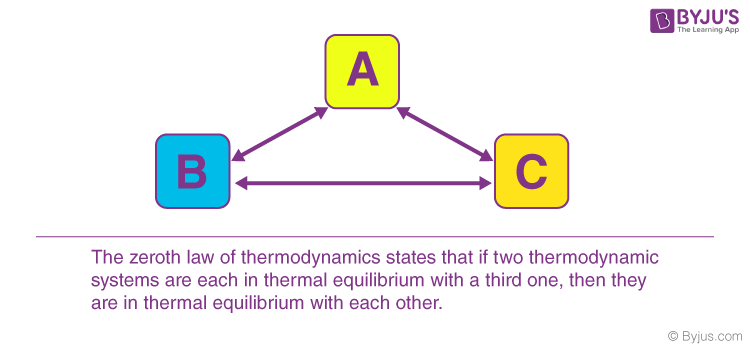
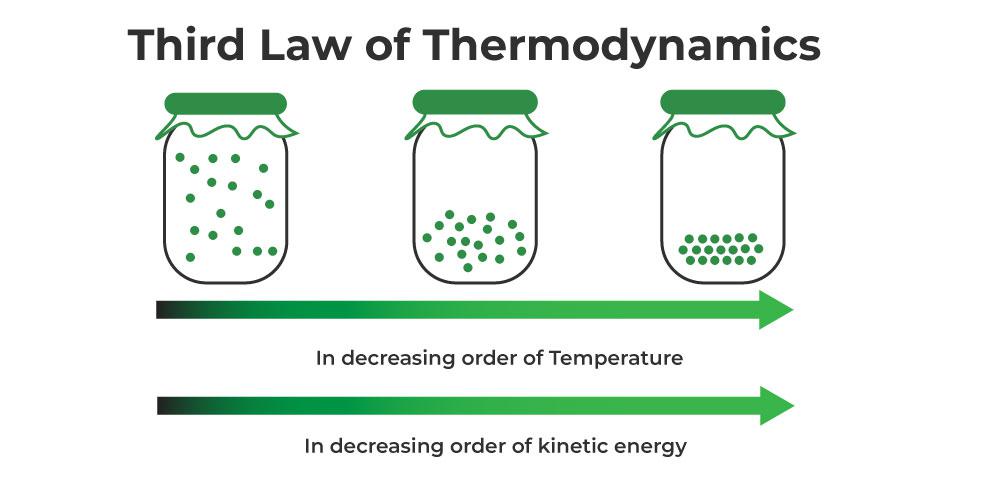
Unit B: Energy Flow and Technological Systems.
STS Outcome 3: Apply the principles of energy conservation and thermodynamics to investigate, describe, and predict the efficiency of energy transformation in technological systems
- 3.1 Describe, qualitatively and in terms of thermodynamic laws, the energy transformations occurring in devices and systems
- 3.2 Describe how the first and second laws of thermodynamics have changed our understanding of energy conversions
- 3.4 Recognizes that there are limits to the amount of “useful” energy that can be derived from the conversion of potential energy to other forms in a technological device
- 3.6 Apply concepts related to the efficiency of thermal energy conversion to analyze the design of a thermal device
- C6 Students will use technology to investigate and/or solve problems
4.4 generate new understandings of problematic situations by using some form of technology to facilitate the process
- C7 Students will use electronic research techniques to construct personal knowledge and meaning
4.2 analyze and synthesize information to determine patterns and links among ideas
- F4 Students will become discerning consumers of mass media and electronic information
4.2 evaluate the influence and results of digital manipulation on our perceptions