Pre AP Biology Semester 1 Exam Review
star
star
star
star
star
Last updated over 2 years ago
69 questions
1
Required
0
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Required
0
1
1
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
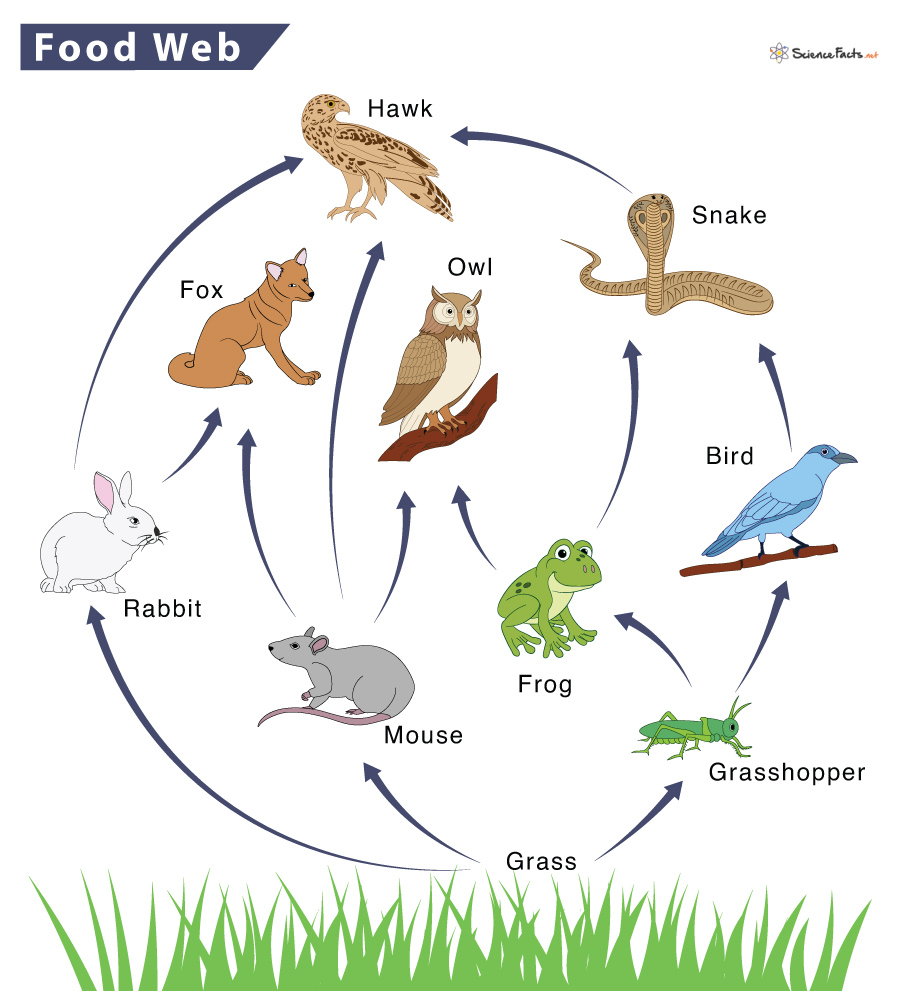
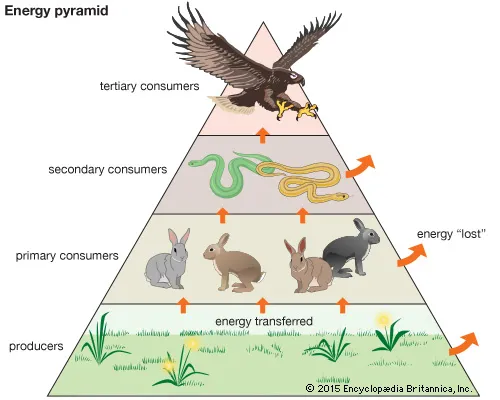
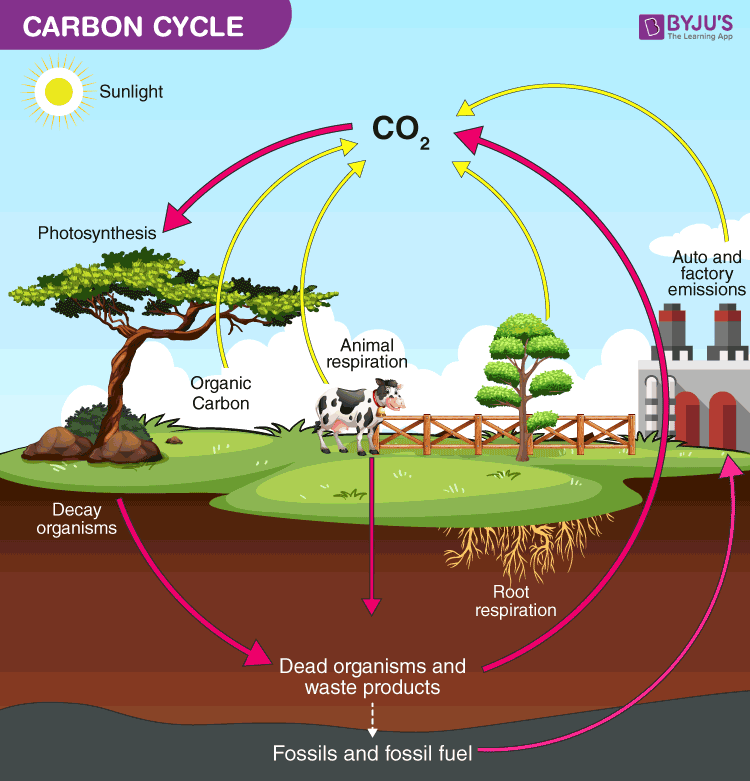
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
Respiratory system | arrow_right_alt | Transports oxygen, nutrients, and waste throughout the body |
Circulatory system | arrow_right_alt | Breaks down food and absorbs nutrients |
Digestive system | arrow_right_alt | Takes in oxygen and removes carbon dioxide |
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
Nervous system | arrow_right_alt | Muscles |
Skeletal system | arrow_right_alt | Brain |
Muscular system | arrow_right_alt | Bones |
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
Integumentary system | arrow_right_alt | Regulates hormones and body functions |
Endocrine system | arrow_right_alt | Fights off infections and diseases |
Immune system | arrow_right_alt | Protects the body and regulates temperature |
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
Excretory system | arrow_right_alt | Filters waste from the blood and removes it from the body |
Lymphatic system | arrow_right_alt | Helps in immunity and fluid balance |
Reproductive system | arrow_right_alt | Allows for the production of offspring |
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt |
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
Plantae | arrow_right_alt | Heterotrophic decomposers with chitin cell walls. |
Fungi | arrow_right_alt | Multicellular organisms that ingest food. |
Animalia | arrow_right_alt | Photosynthetic organisms with cellulose cell walls. |
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
Protista | arrow_right_alt | Mostly single-celled eukaryotes with various nutritional modes. |
Archaea | arrow_right_alt | Prokaryotic organisms with unique cell walls and membrane lipids. |
Eubacteria | arrow_right_alt | Prokaryotic organisms with peptidoglycan cell walls. |
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
Homologous Structure | arrow_right_alt | Similar structures found in different species indicating a common ancestor. |
Analogous Structure | arrow_right_alt | Process by which organisms that are best adapted to their environment survive and reproduce. |
Natural Selection | arrow_right_alt | |
| arrow_right_alt |
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
Genetic Drift | arrow_right_alt | Change in gene frequencies due to random events in small populations. |
Mutation | arrow_right_alt | Breeding of organisms by humans for desired traits. |
Gene Flow | arrow_right_alt | |
| arrow_right_alt |
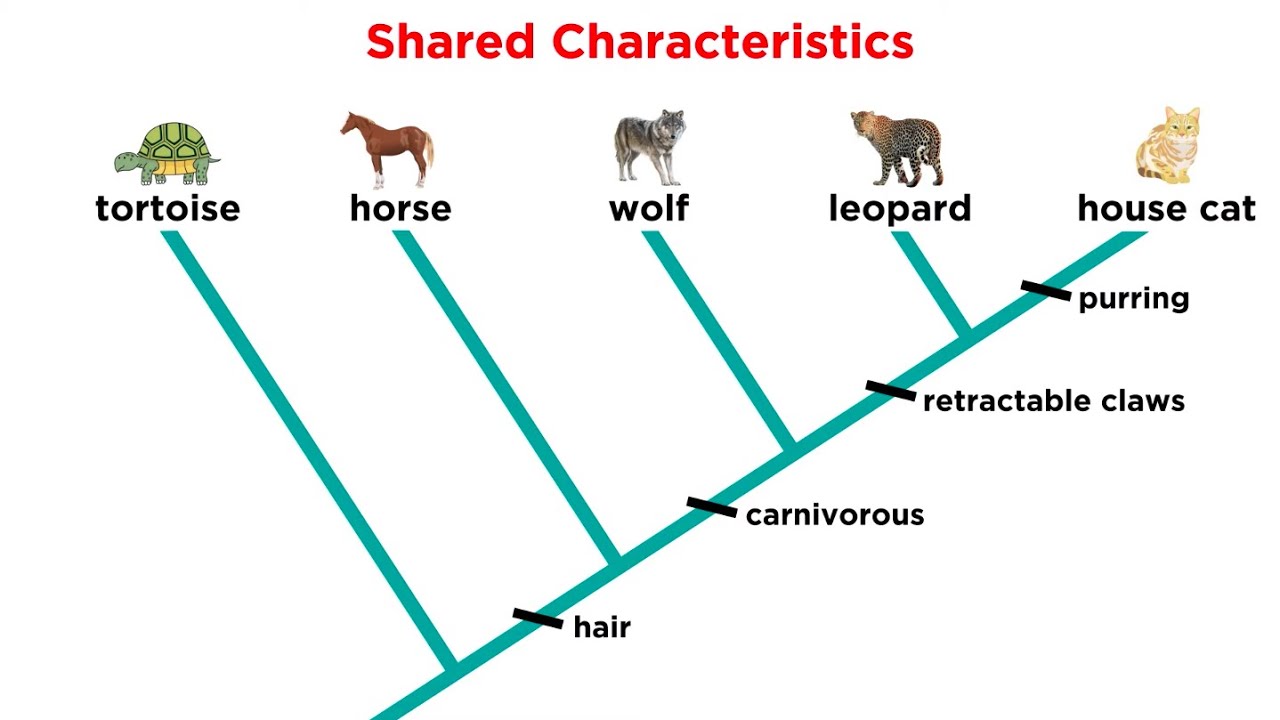
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
Cellulose | arrow_right_alt | Plants |
Peptidoglycan | arrow_right_alt | Bacteria |
Chitin | arrow_right_alt | Fungi |