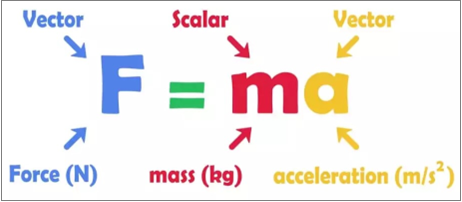
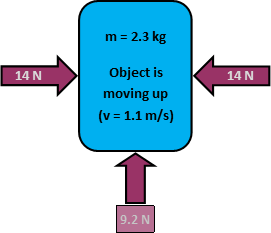
For each diagram or scenario, answer each multiple choice question. Some questions have hints. Remember that the direction of the acceleration is always in the same direction as the net force (Fnet). The motion of the object may be in a different direction, however.