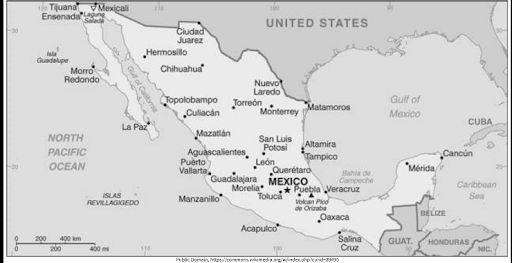
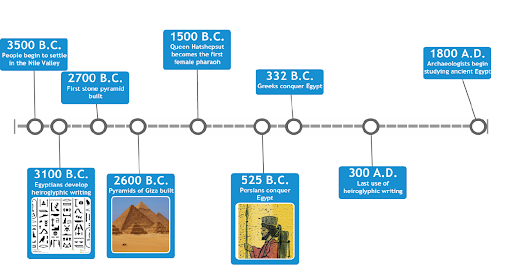
Grade 6 SS Midterm 2024
star
star
star
star
star
Last updated about 2 months ago
36 questions
Required
2.5
6.RST4
Required
2.5
6.RH7
Required
2.5
6.RH7
Required
2.5
6.RH7
Required
2.5
6.RH7
Required
2.5
6.RH7
Required
2.5
Required
2.5
Required
2.5
6.RH4
Required
2.5
6.2.d.i
Required
2.5
6.2.c.ii
Required
2.5
6.2.d.i
Required
2.5
6.2.d.i
Required
2.5
6.3.d.ii
Required
2.5
6.3.d.ii
Required
2.5
6.3.d.ii
Required
2.5
6.3.d.ii
Required
2.5
Required
2.5
Students will examine the unique achievements of each of the selected complex societies and civilizations that served as lasting contributions.
Required
2.5
Students will examine the unique achievements of each of the selected complex societies and civilizations that served as lasting contributions.
Required
2.5
Required
2.5
Required
2.5
Required
2.5
Required
2.5
Required
2.5
Required
2.5
Required
2.5
Required
2.5
Required
2.5
Required
3
Required
3
Required
3
Required
3
Required
3
Required
10