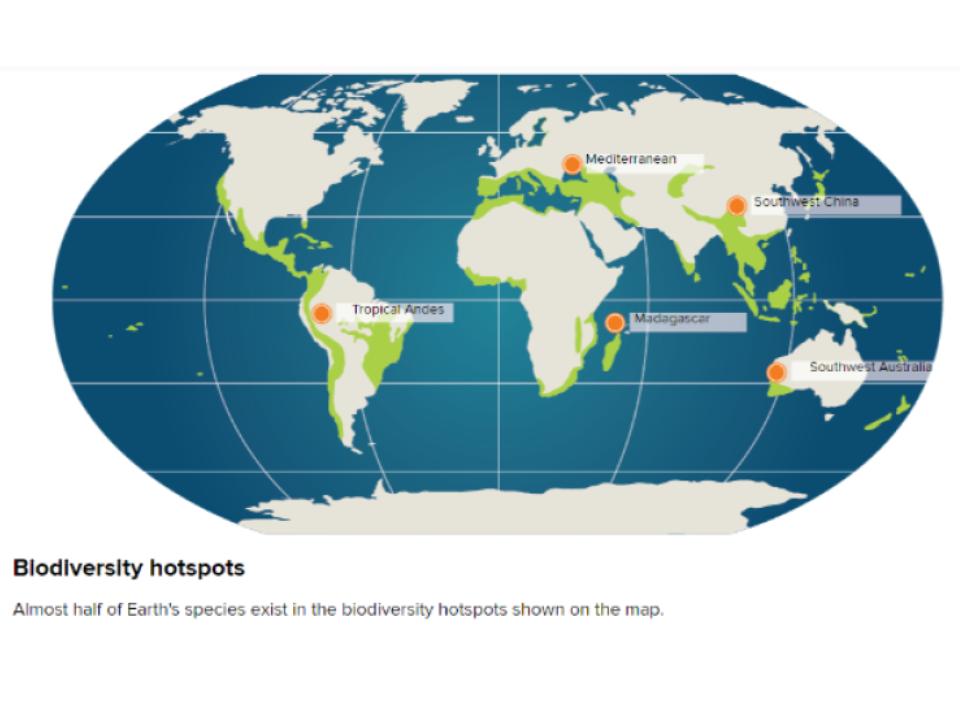
Conservation biologists have identified locations around the world that are characterized by exceptional levels of endemic species, or critical levels of habitat loss. Endemic species are organisms that are only found in a specific geographic location. To be called a hotspot, a region must meet 2 criteria.
1. There must be at least 1500 species of vascular plants that are endemic.
2. The region must have lost at least 70% of its original habitat.
There are 36 internationally recognized hotspots!
Approximately half of all plant and animal species are found in hotspots. There hotspots originally covered 17% of Earth's surface, however currently only about 1/10th of those habitats remain.
Biologists in favor of recovery efforts in these areas argue that focusing on a limited area would save the greatest number of species possible. Other biologists argue that concentrating funding on saving species in these hotspots does not address the serious problems that are occurring elsewhere. These biologists think that funding should be spent in areas around the world rather than focused on the biodiversity hotspots.
For example, saving a wetland area might save fewer species, but the wetland provides greater services by filtering water, regulating floods, and providing a nursery for fish.