Protein Synthesis Practice Worksheet
star
star
star
star
star
Last updated about 2 years ago
26 questions
4
4
4
0
4
0
4
4

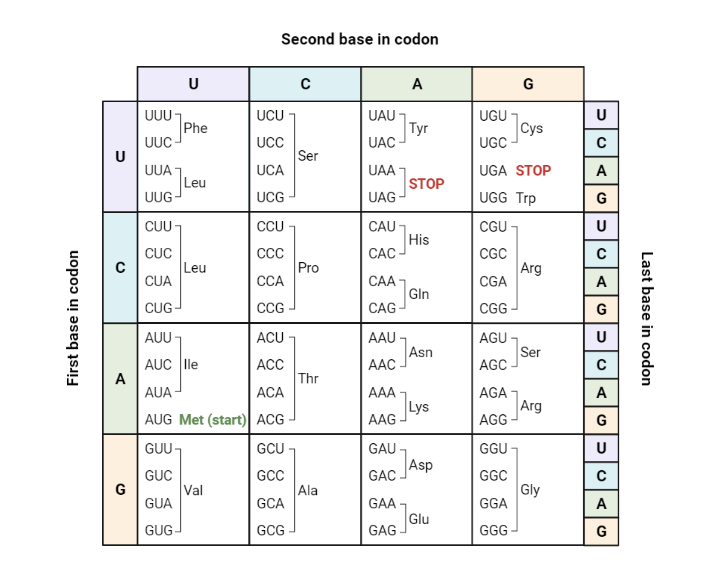
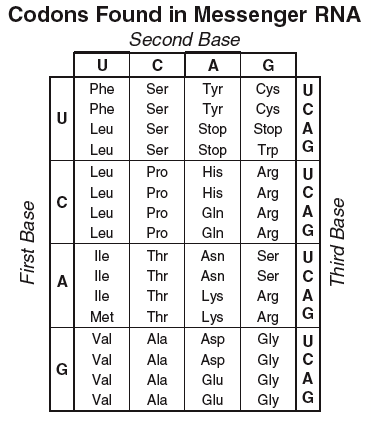

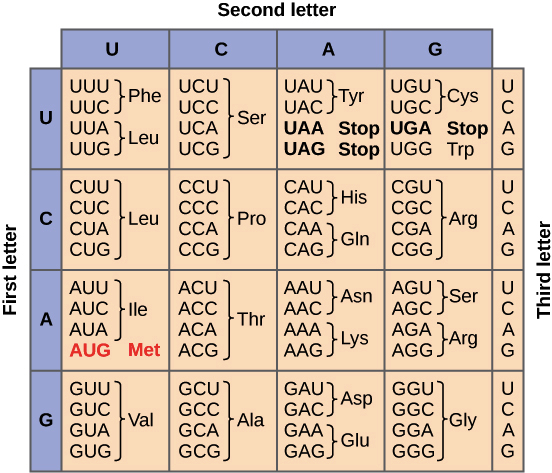
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
Frameshift | arrow_right_alt | A mutation that causes the reading frame to shift, altering the sequence. |
Nonsense | arrow_right_alt | Premature termination of protein synthesis due to a stop codon. |
Missense | arrow_right_alt | A mutation that changes one amino acid to another. |