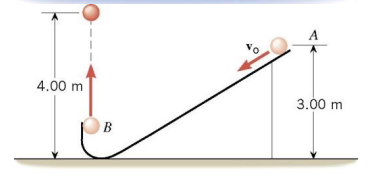
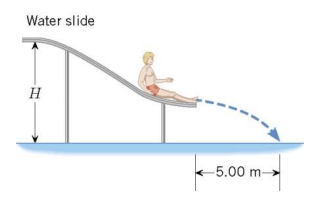
5. A water slide is constructed so that swimmers, starting from rest at the top of the slide, leave the end of the slide traveling horizontally. As the drawing shows, one person hits the water 5.00 m from the end of the slide in a time of 0.500 s after leaving the slide. Ignoring friction and air resistance, find the height H in the drawing. (Hint: Start by using projectile motion to find the speed when the person hits the water, then use conservation of mechanical energy to find the height.)