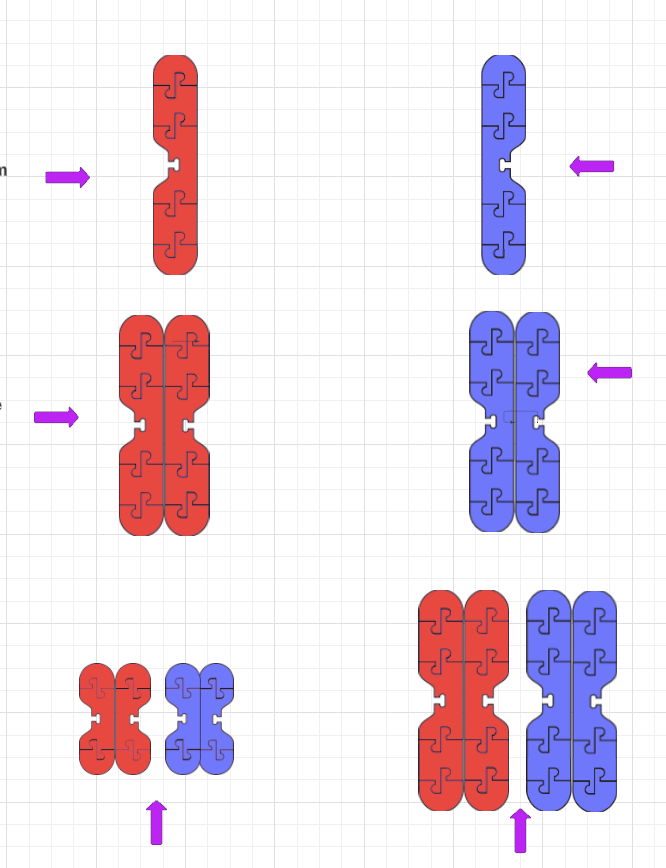
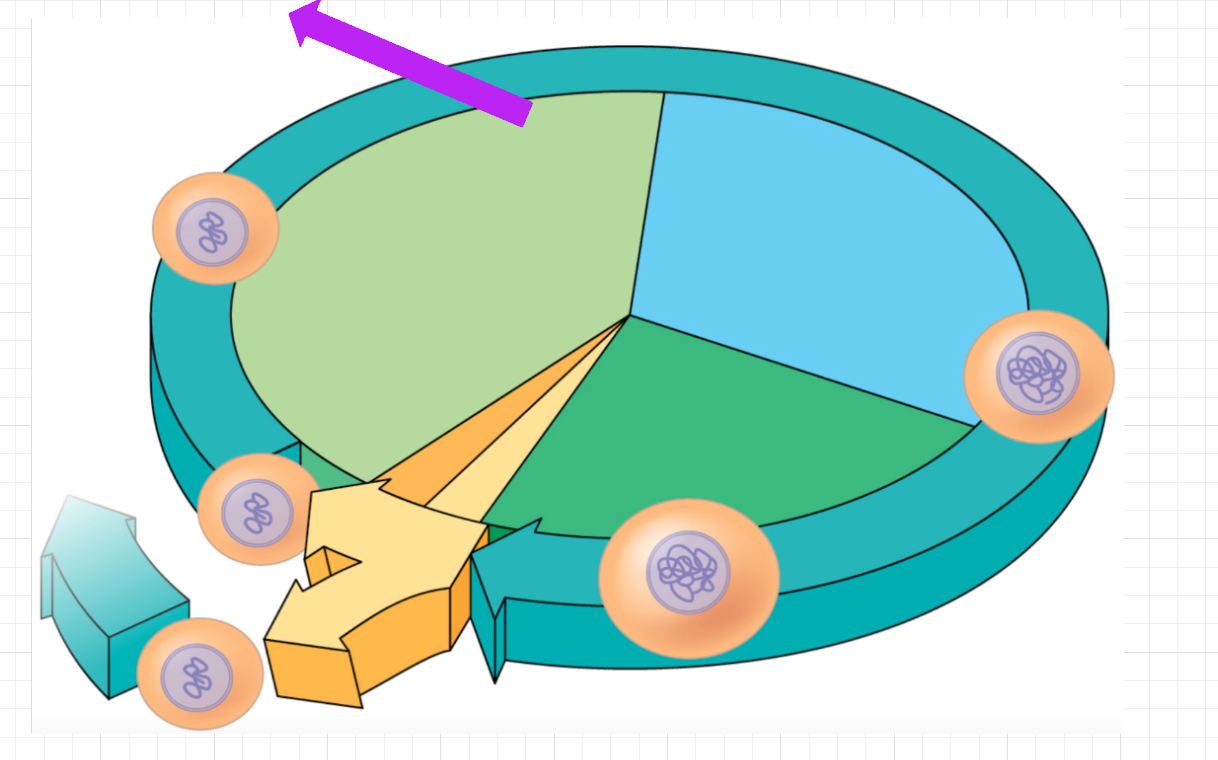
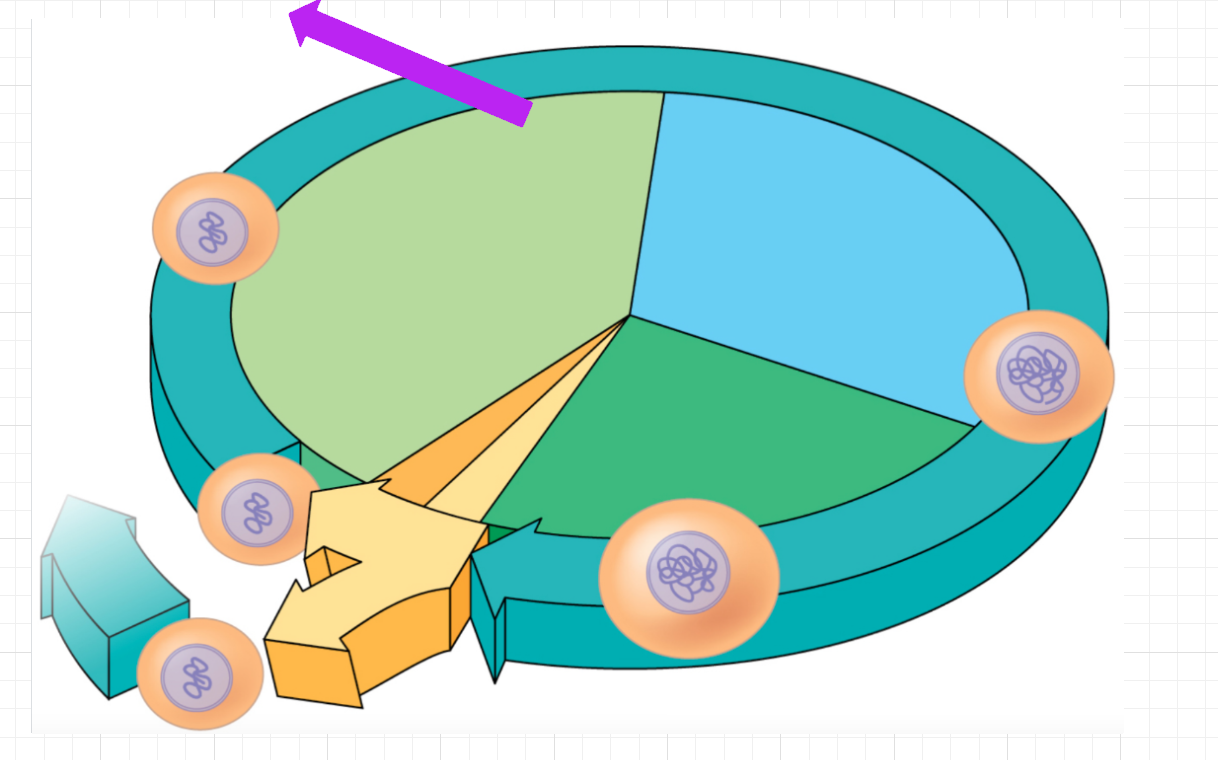
Cell Cycle/Mitosis & Cancer Practice/Review
star
star
star
star
star
Last updated almost 2 years ago
32 questions
Required
6
Required
7
Required
4
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
3
Required
3
1
Required
1
Required
4
Required
1
Required
2
Required
1
Required
5
Required
1
Required
1
1
1
3