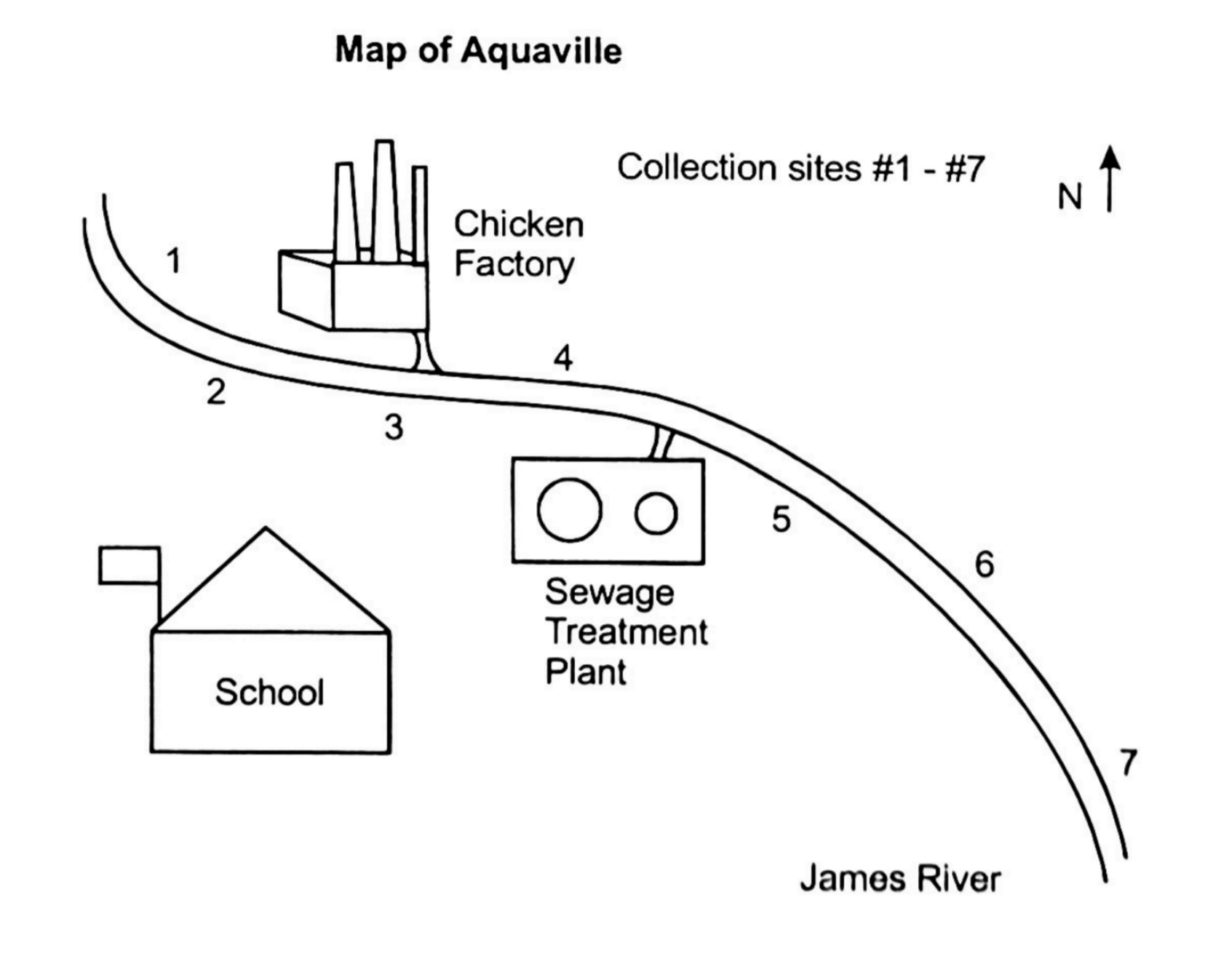
Test 3: Air and Water Quality, Human Impacts and Environmental Legislation
star
star
star
star
star
Last updated almost 2 years ago
15 questions
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1