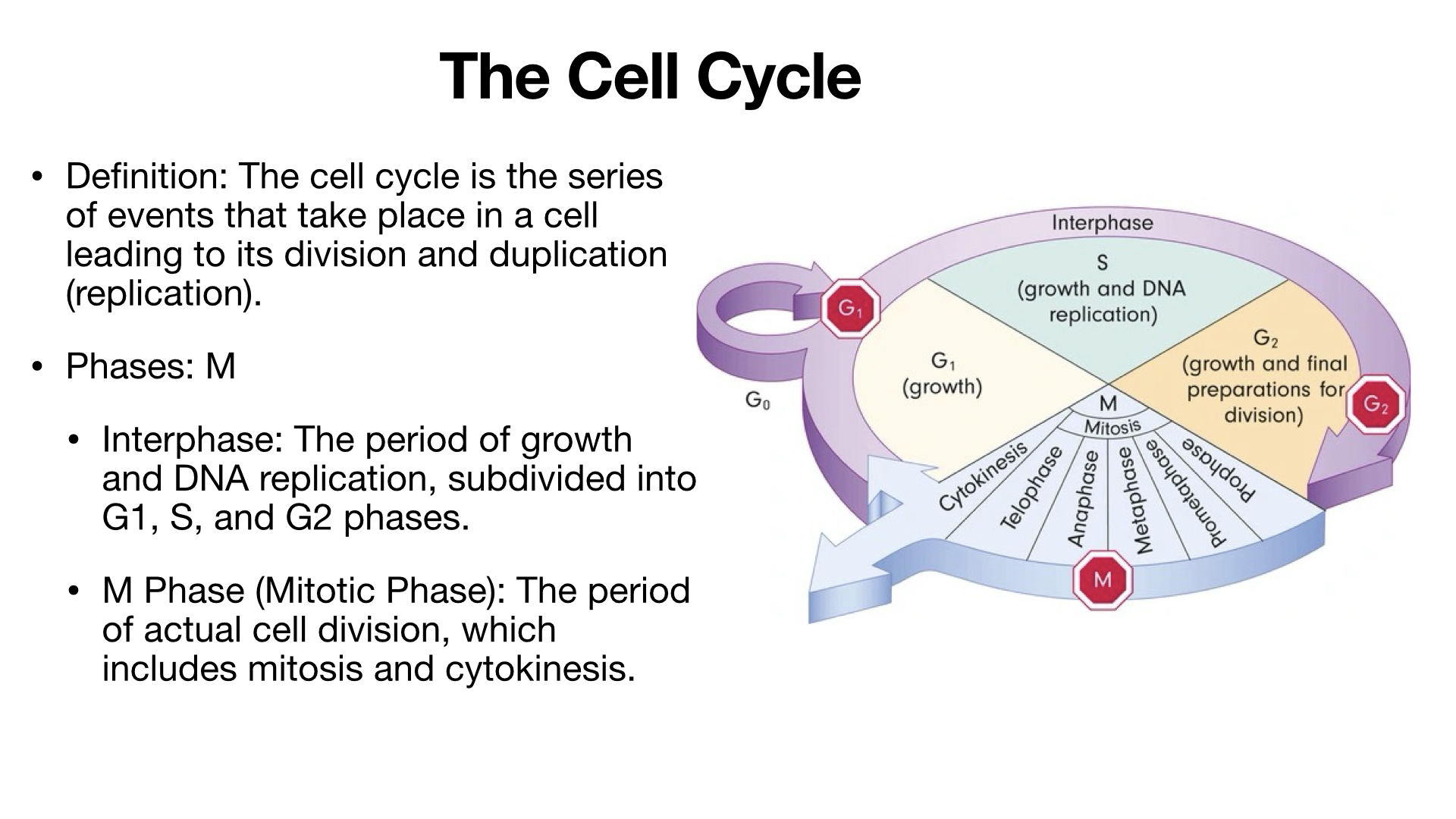
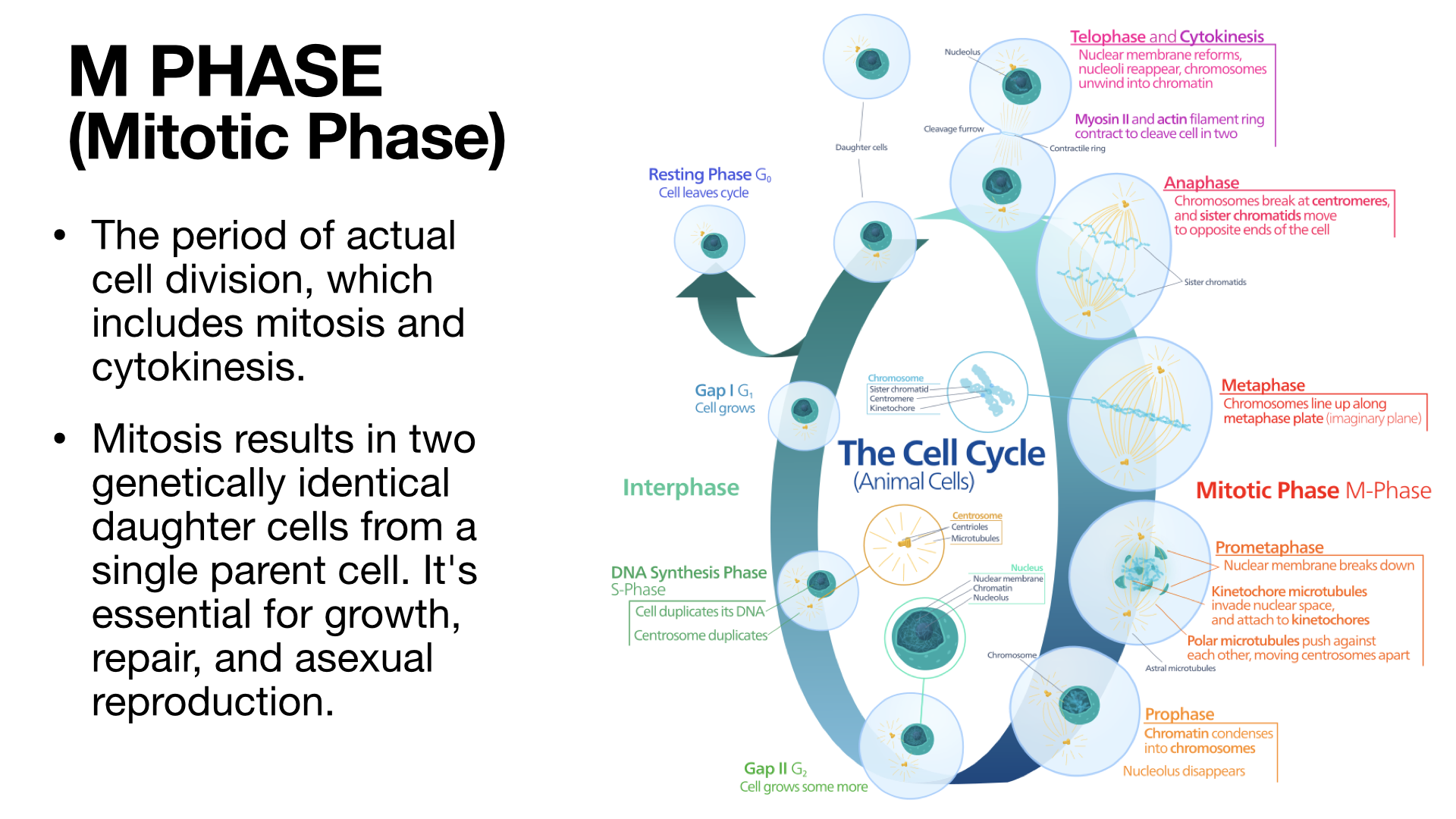
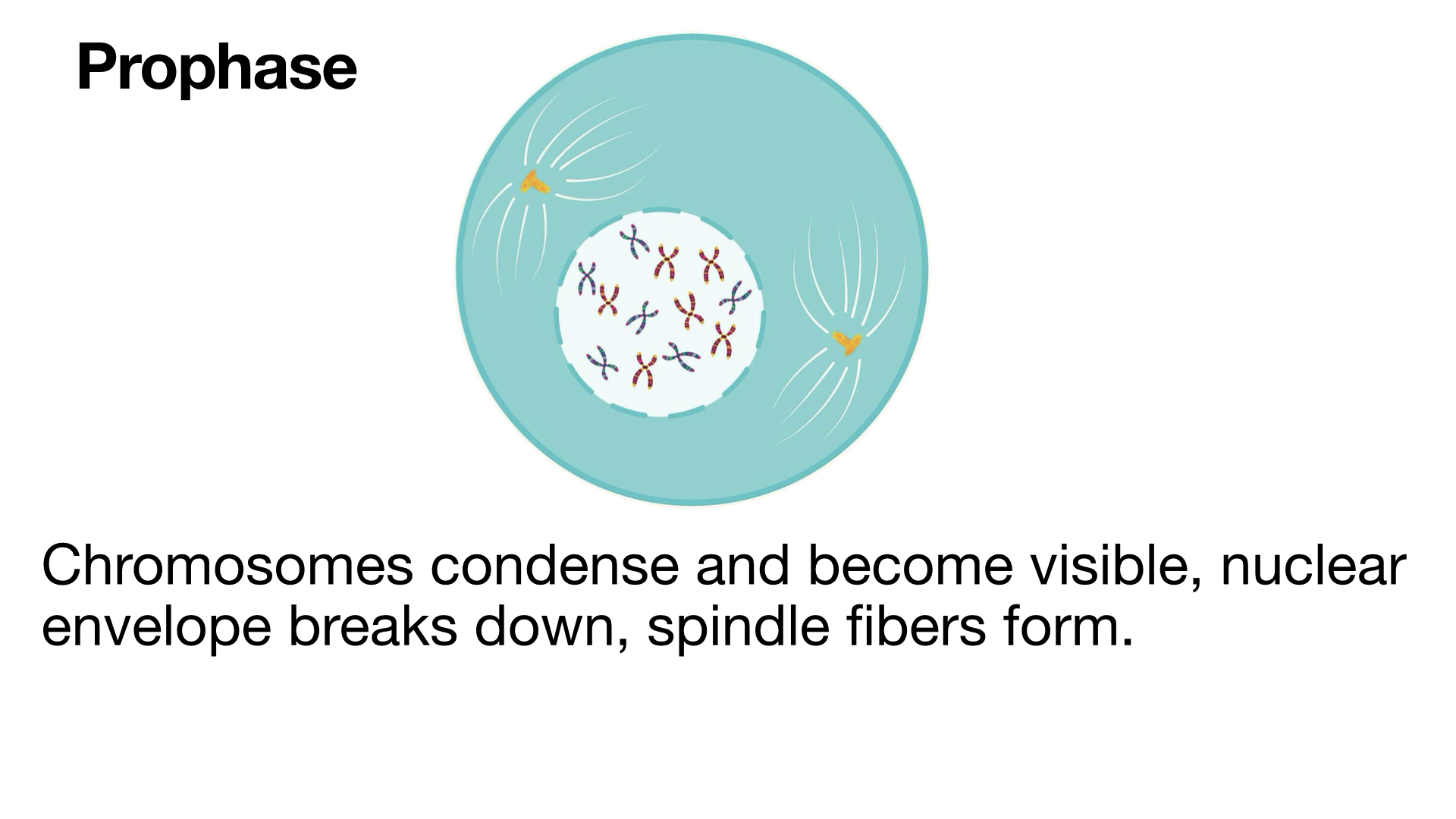
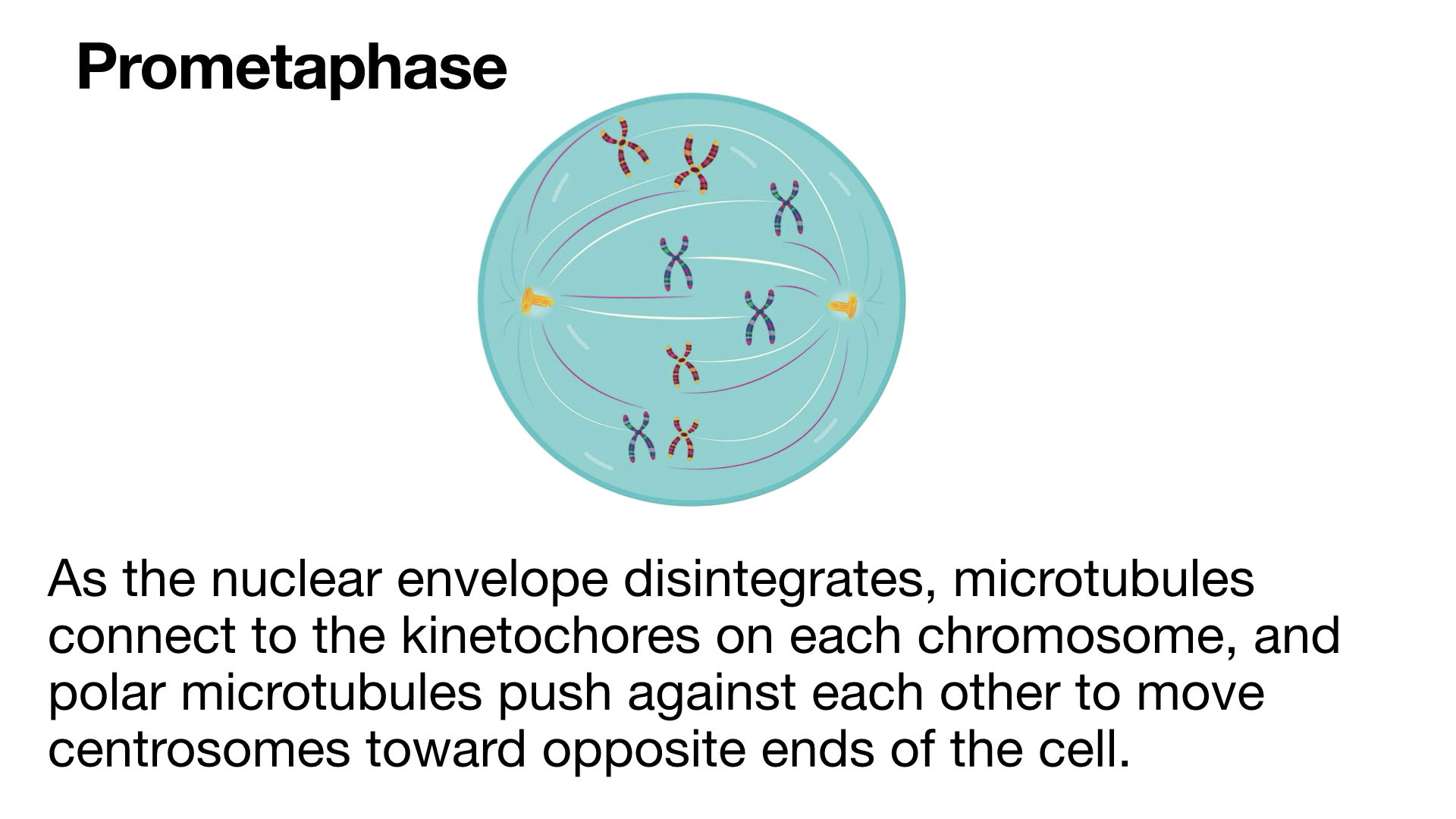
Copy of Mitosis, Meiosis, and Asexual Reproduction (4/27/2024)
star
star
star
star
star
Last updated almost 2 years ago
32 questions
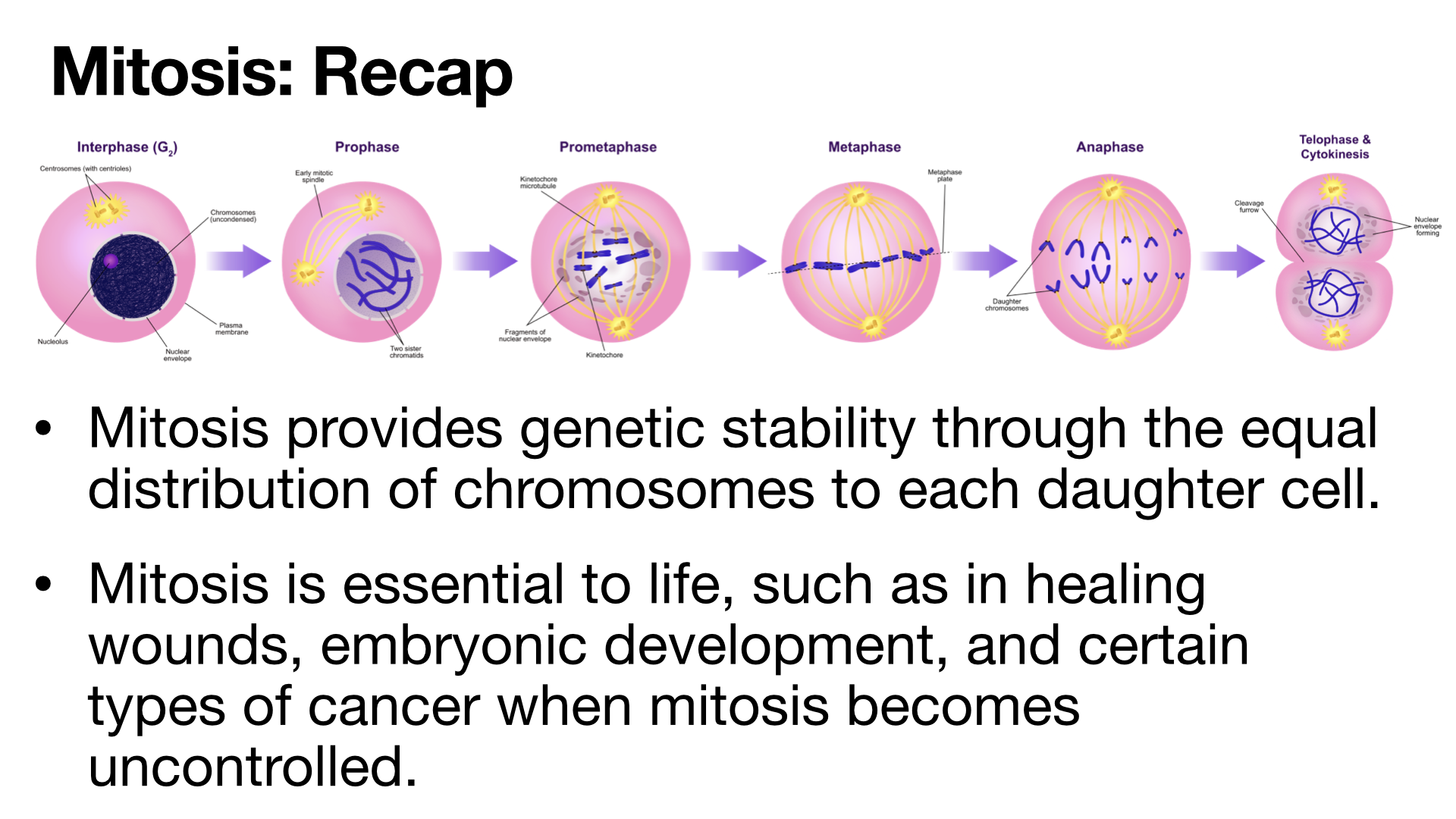
Mitosis
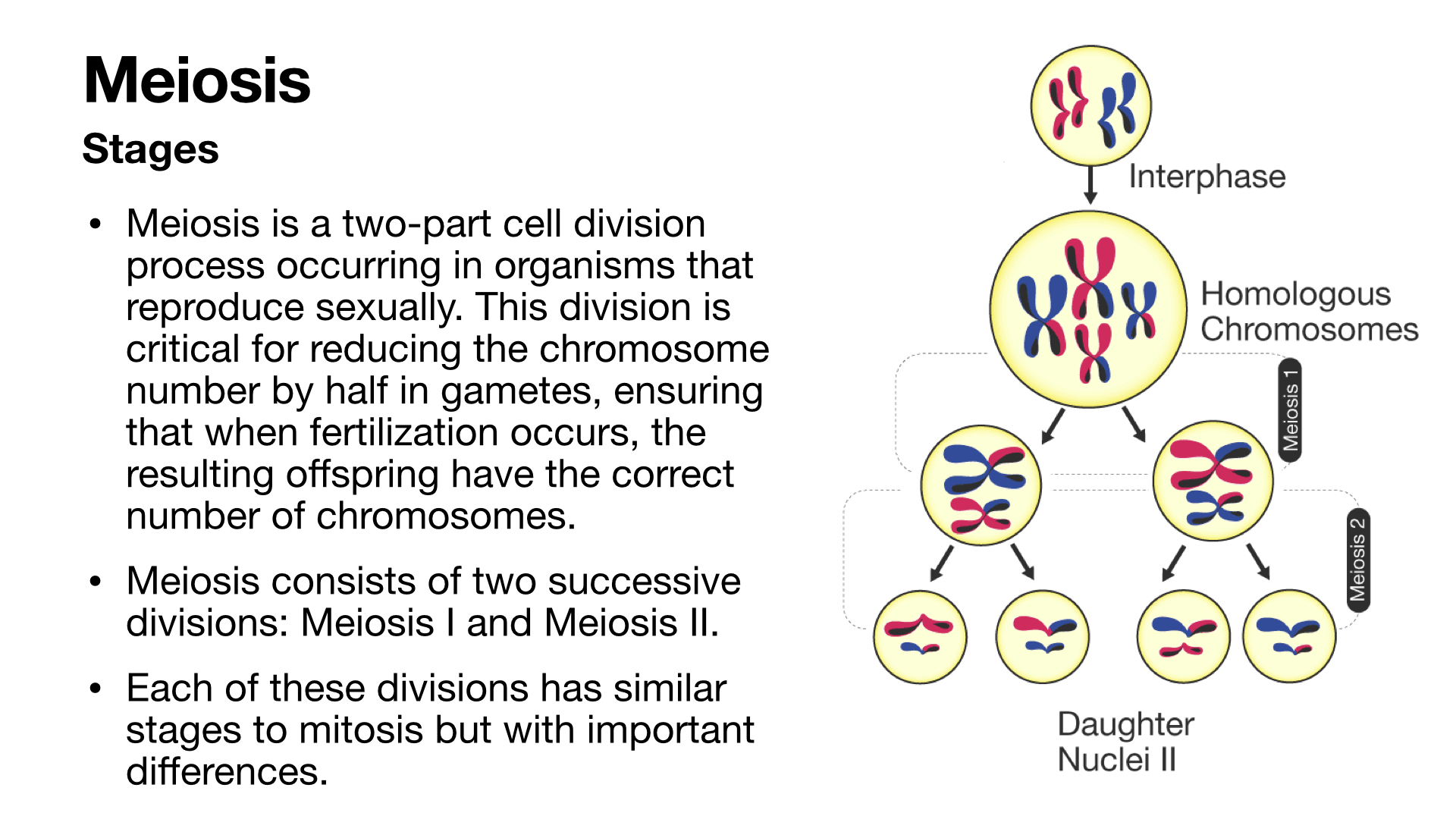
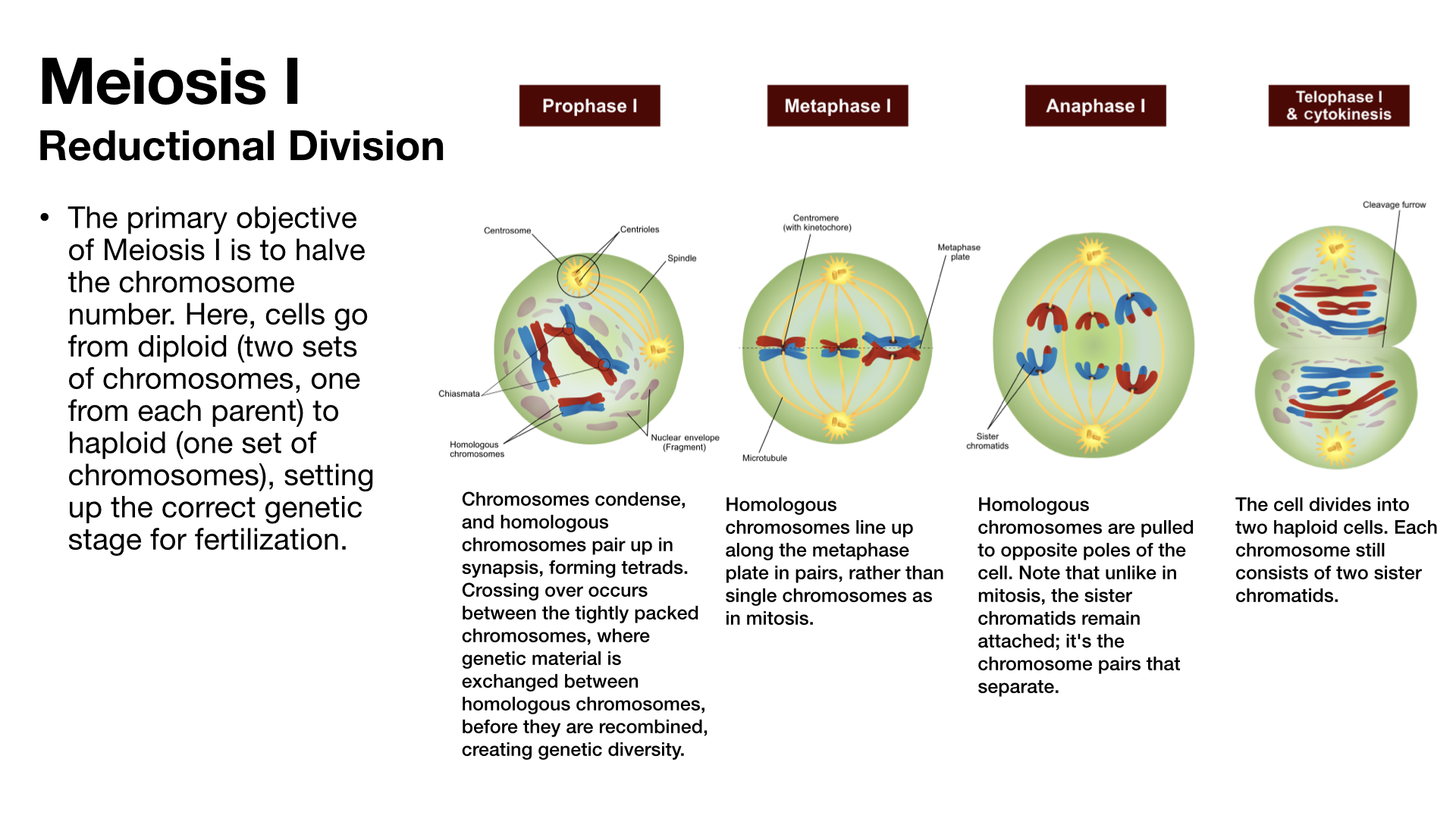
Meiosis
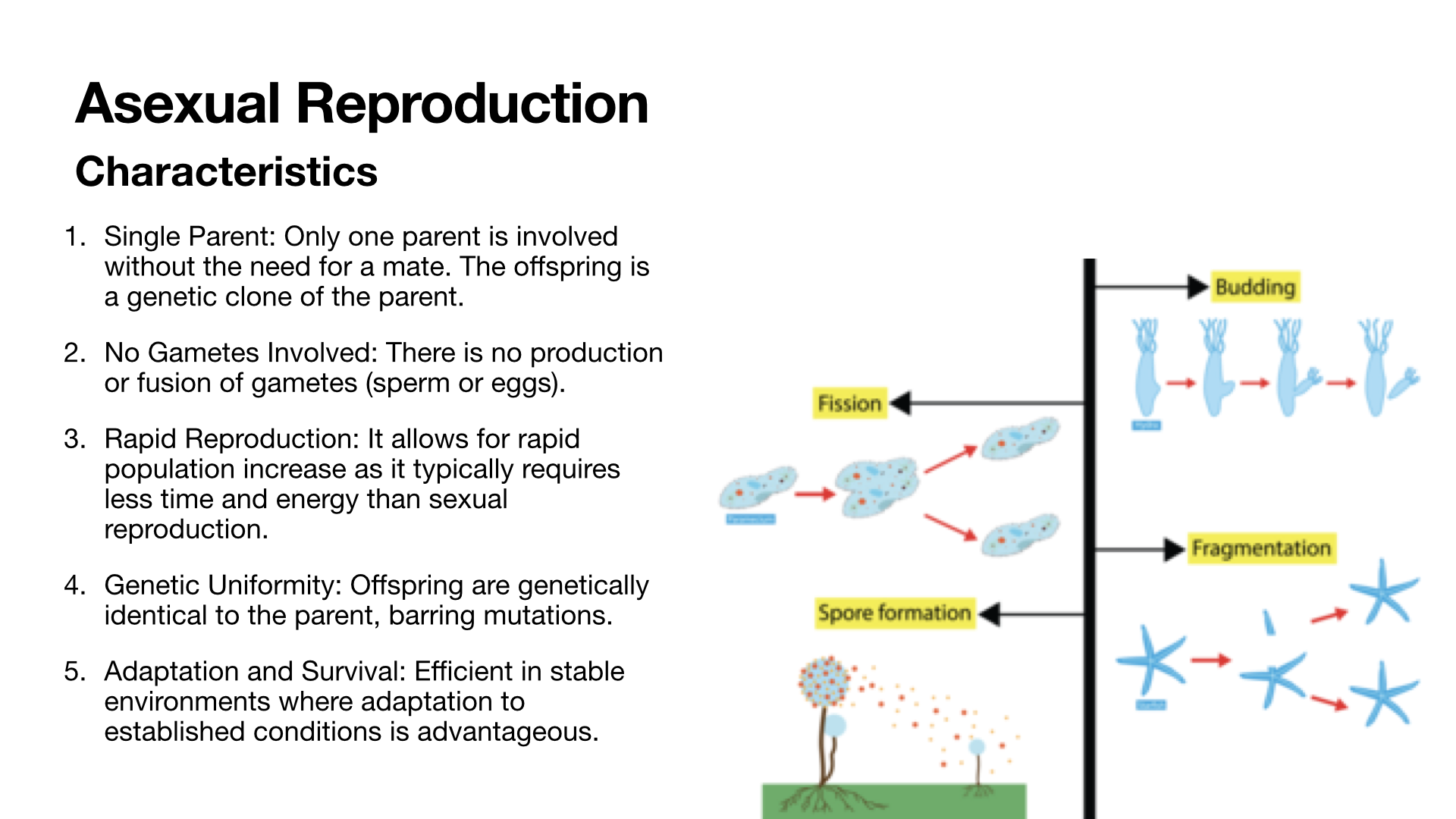
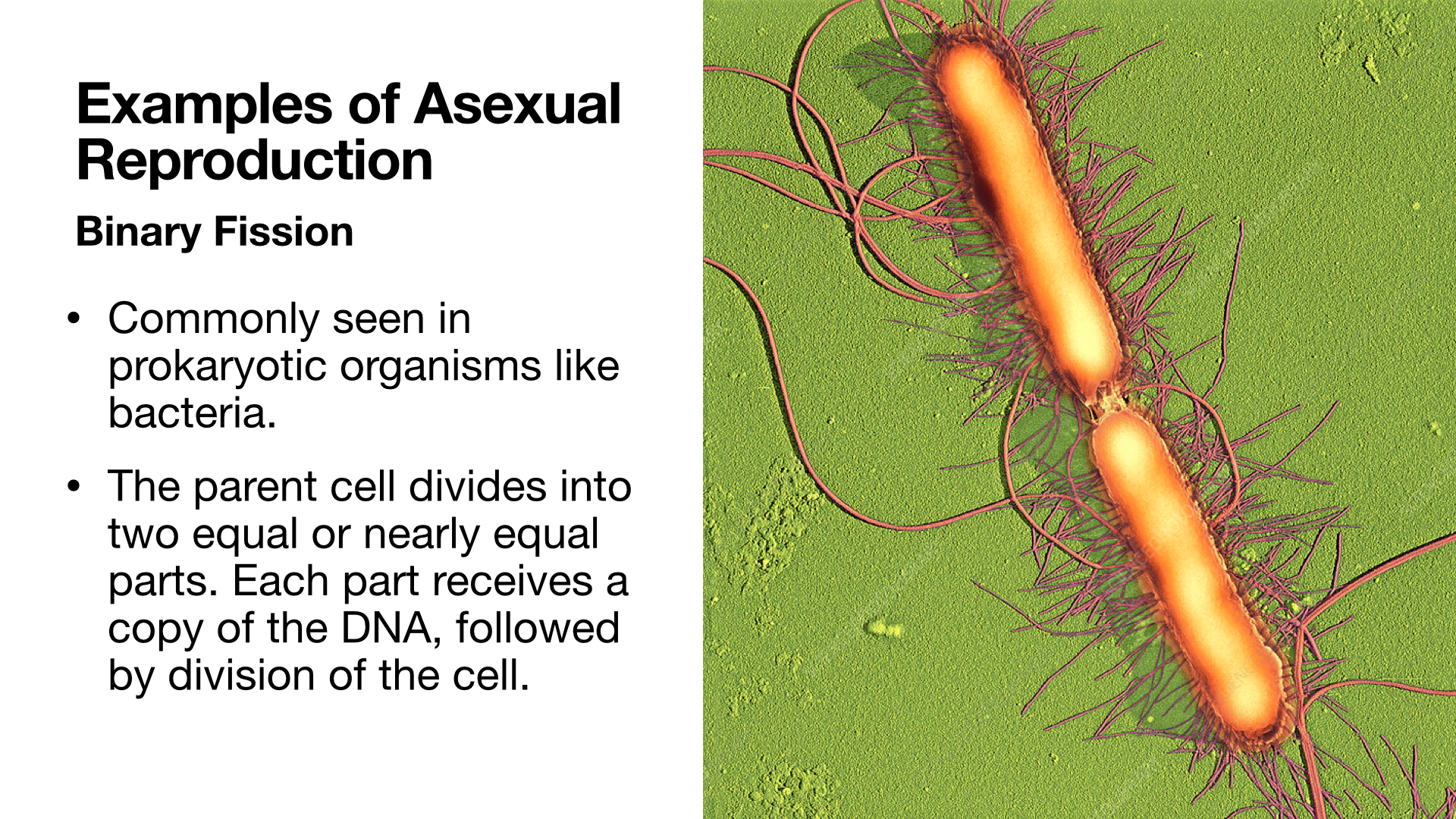
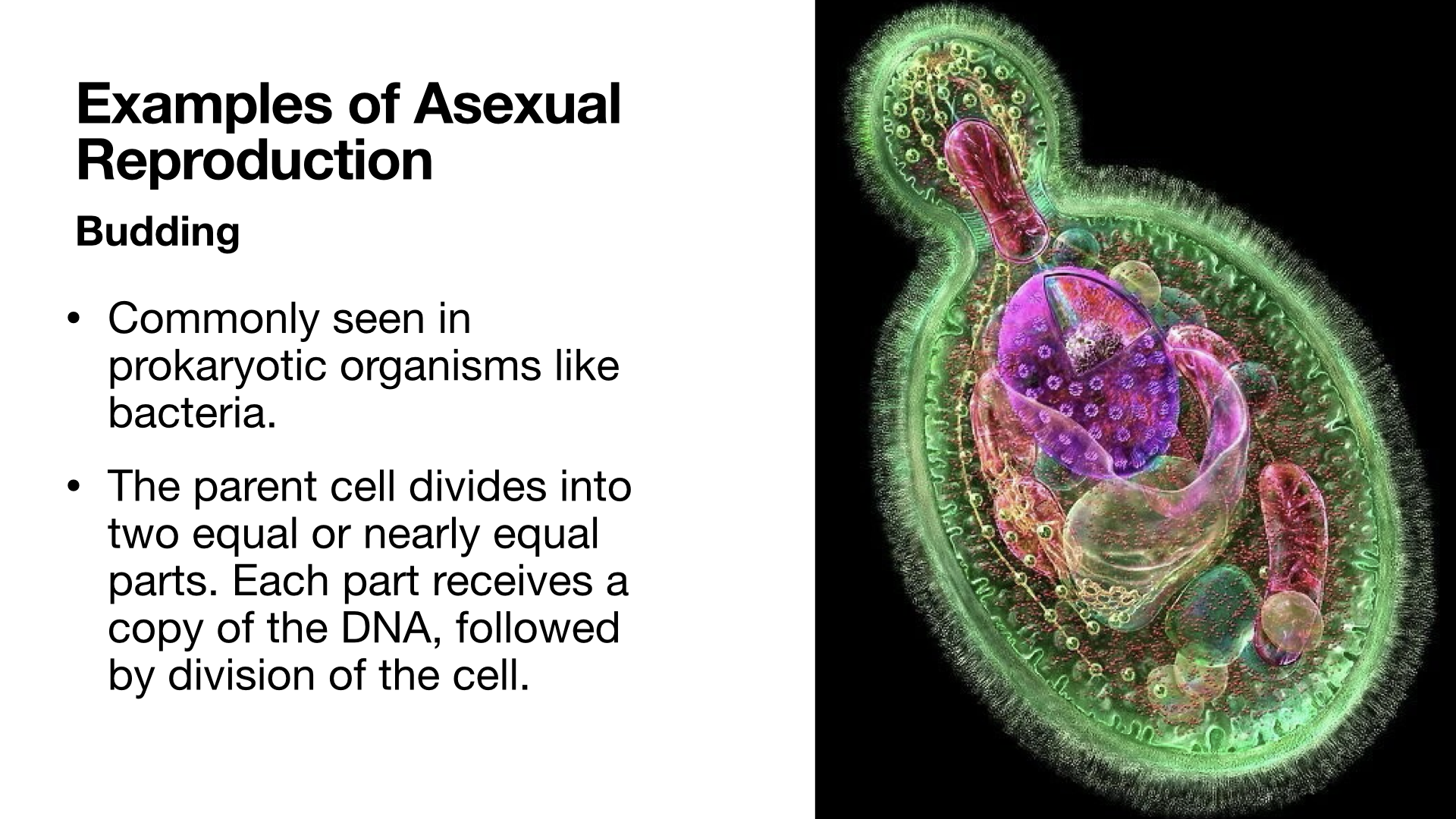
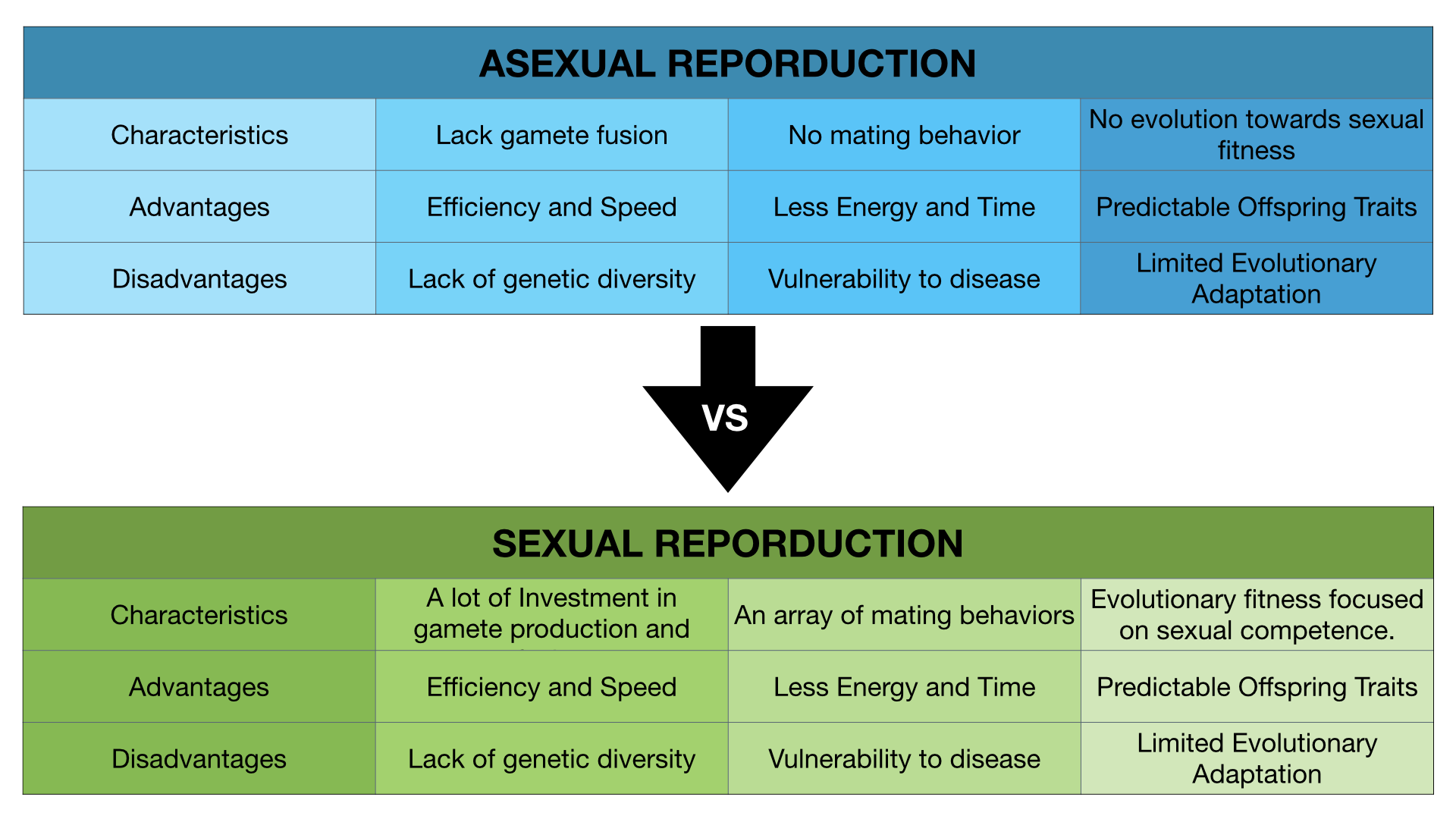
Asexual Reproduction
Assessment
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1