SUHSD Geography B EOC EXAM
star
star
star
star
star
Last updated almost 2 years ago
24 questions
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
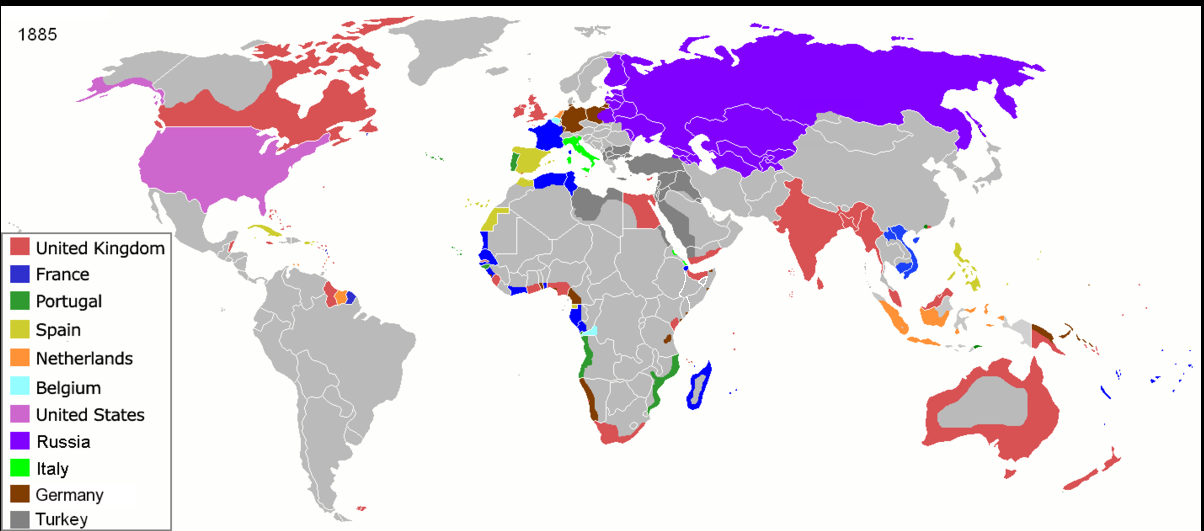
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
African Union (AU) | arrow_right_alt | Worldwide health-related issues |
European Union (EU) | arrow_right_alt | Promote unity and development in Africa |
World Health Organization (WHO) | arrow_right_alt | Promote peace and stability in Europe |
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
Global | arrow_right_alt | African Union (AU) |
Eastern Europe | arrow_right_alt | World Health Organization (WHO) |
Sub-Saharan Africa | arrow_right_alt | European Union (EU) |
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
Multi-state nation | arrow_right_alt | The study of the effects of geography on politics and international relations |
Nation-state | arrow_right_alt | A nation that stretches across borders and states |
Geopolitics | arrow_right_alt | A sovereign state whose citizens are united by language and culture |
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
Sovereignty | arrow_right_alt | An area of land under jurisdiction of a state |
Borders | arrow_right_alt | The authority of a state to govern itself |
Territory | arrow_right_alt | The geographical boundaries of a state |
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
Resource Scarcity | arrow_right_alt | Policies and wars over natural resources |
Colonialism | arrow_right_alt | Domination over indigenous population, resources and territory |
Globalization | arrow_right_alt | Interdependence and interaction among states and nations |
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
Third Agricultural Revolution | arrow_right_alt | Domestication of plants and animals |
Second Agricultural Revolution | arrow_right_alt | Genetic modification and mechanization of agriculture |
First Agricultural Revolution | arrow_right_alt | Introduction of new technologies and improvement of farming techniques |
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
Third Agricultural Revolution | arrow_right_alt | Increased food production, Industrial Revolution |
First Agricultural Revolution | arrow_right_alt | Population boom, environmental concerns |
Second Agricultural Revolution | arrow_right_alt | Start of settled life, towns & cities |