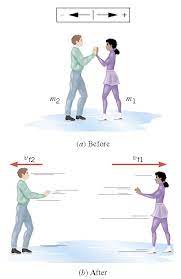
Two friends, Al and Jo, have a combined mass of 168 kg. At an ice skating rink they stand close together on skates, at rest and facing each other, with a compressed spring between them. The spring is kept from pushing them apart because they are holding each other. When they release their arms, Al moves off in one direction at a speed of 0.90 m/s, while Jo moves off in the opposite direction at a speed of 1.2 m/s. Assuming that friction is negligible, find Al’s mass. Round your answer to the nearest whole number.