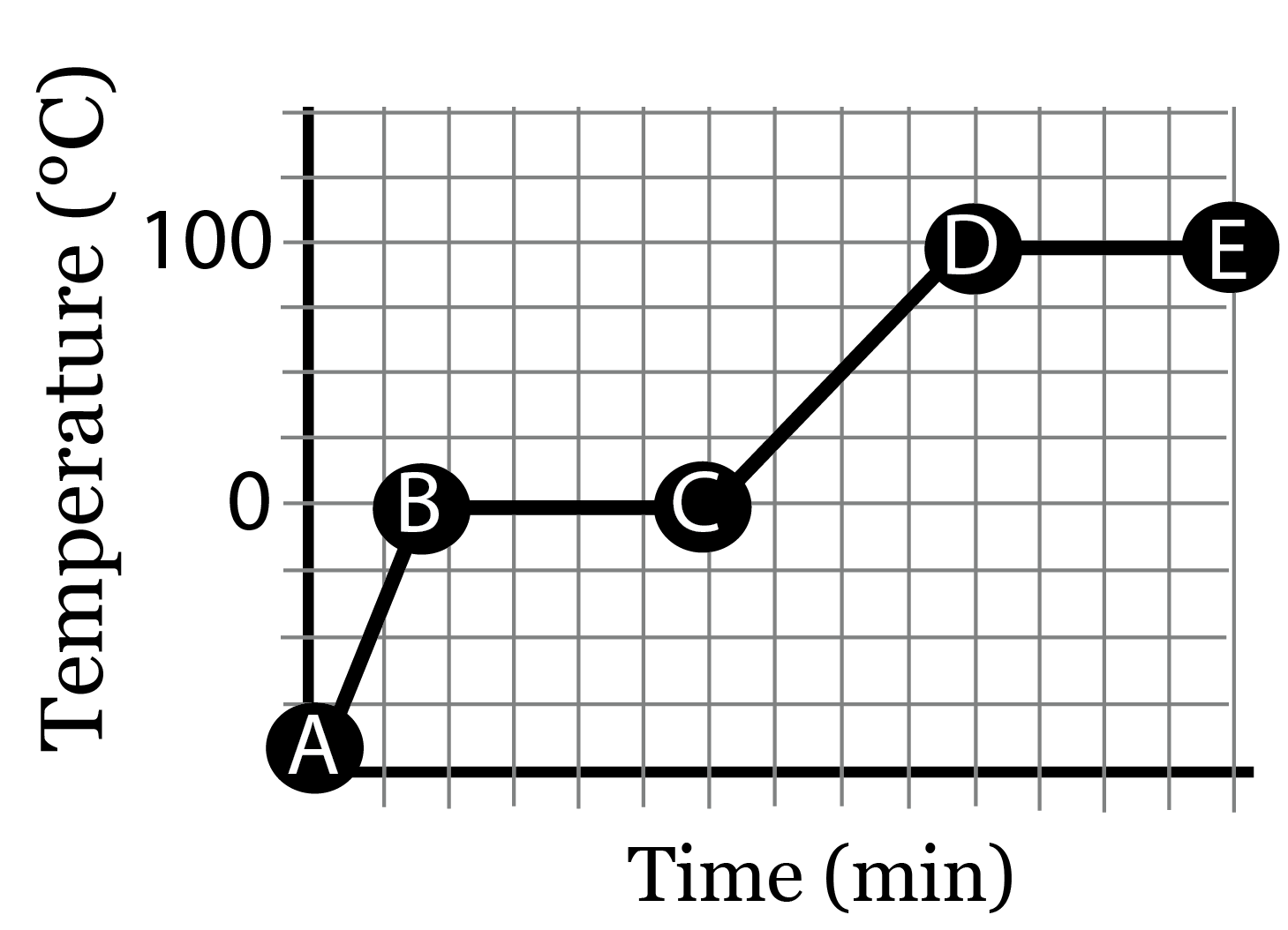
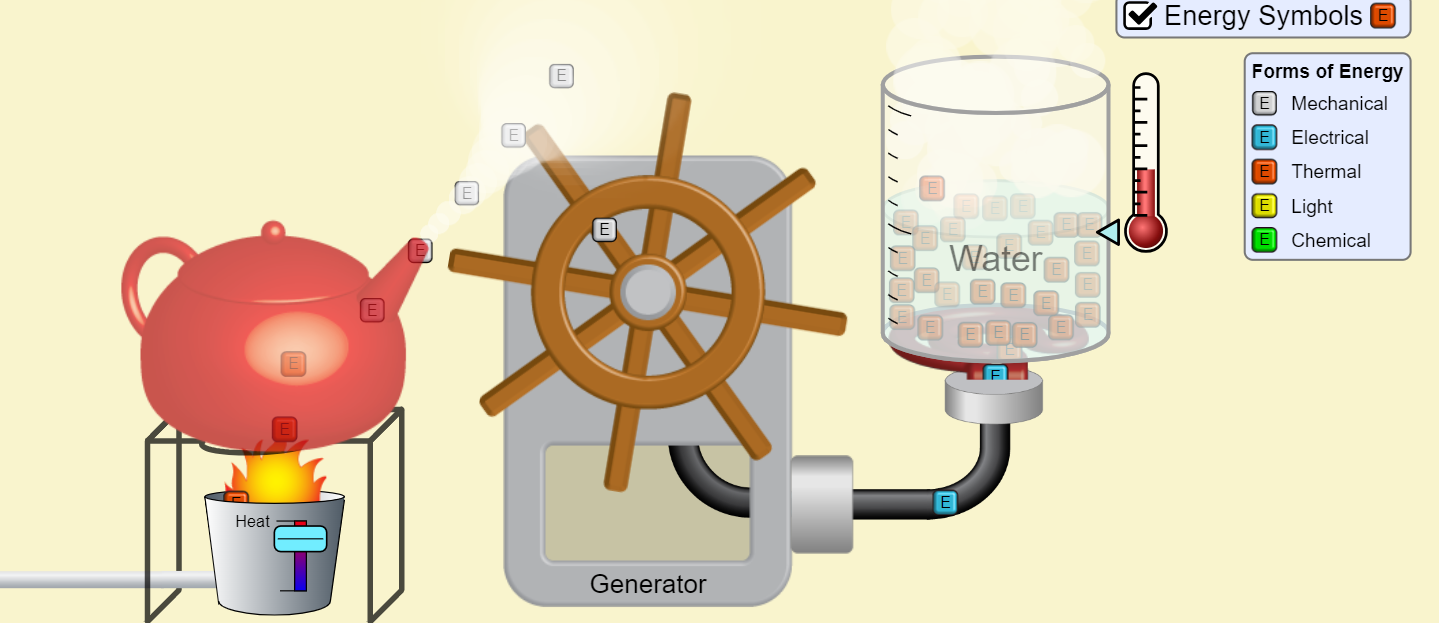
Lesson 2.6 Energy Transfer and Heat Capacity Review
star
star
star
star
star
Last updated 10 months ago
26 questions
Untitled Section
23
4
Revewing Heat Capacity
1
1
1
1
1
10
4
6
Reviewing Energy Transfer
7
5
2
2
1
1
2
2
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt |