Enzymes, Cells & Cell Transport
star
star
star
star
star
Last updated over 1 year ago
20 questions
Required
1
1
B.C.9C
1
1
1
B.C.4A
1
B.C.4A
1
B.C.4B
1
1
B.C.4B
1
B.C.4B
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
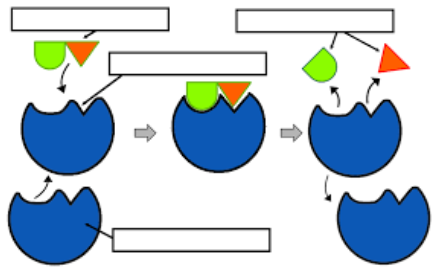
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt |
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt |