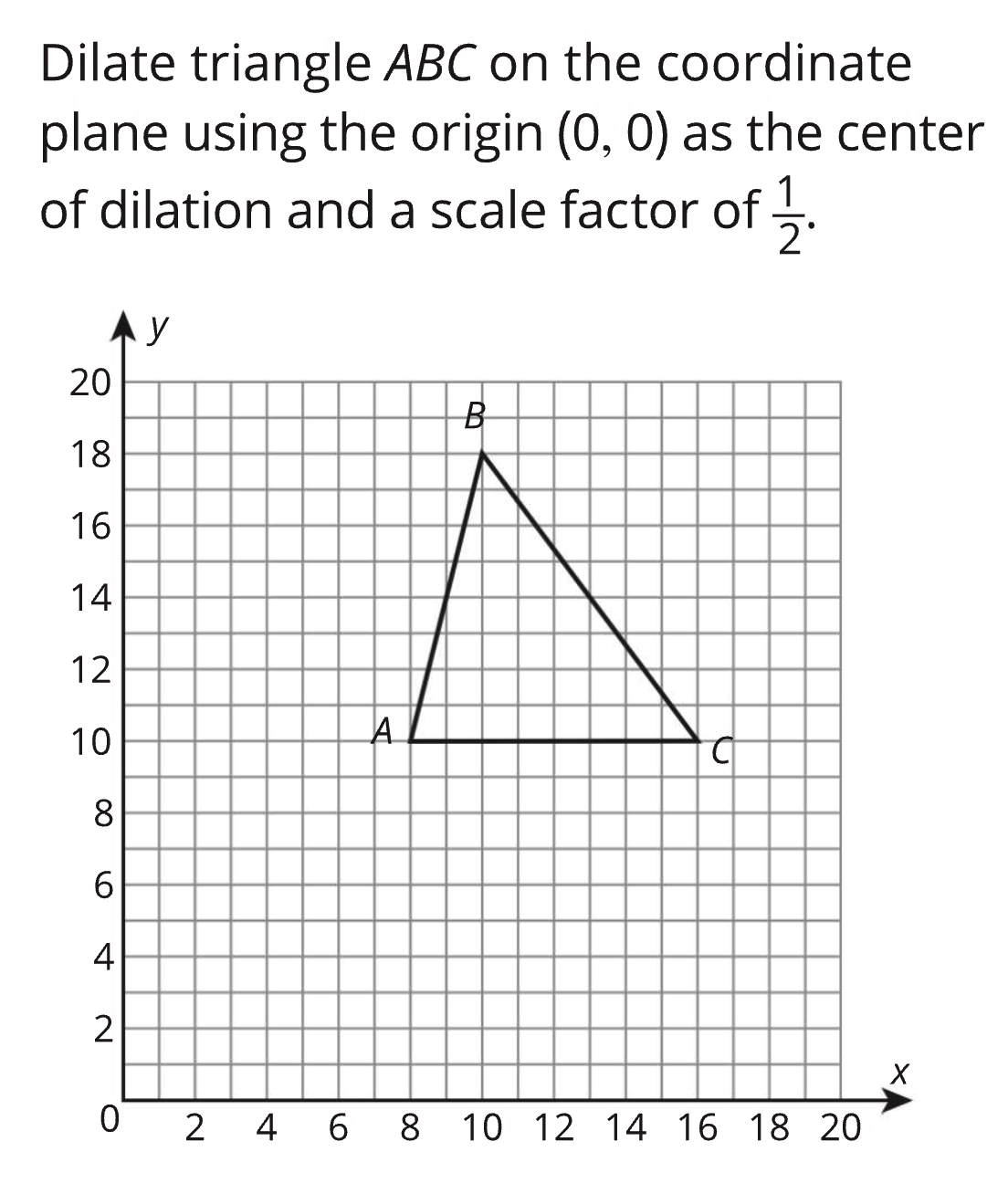
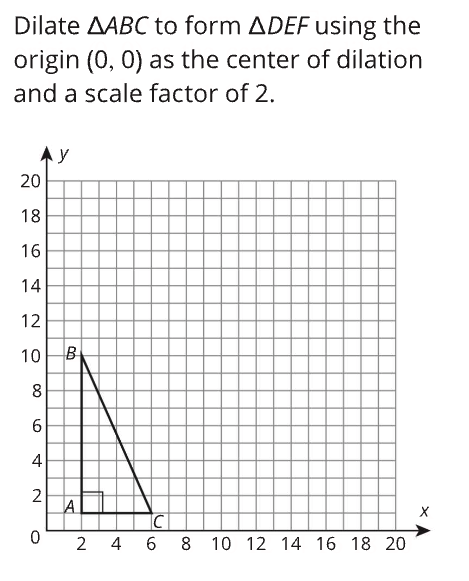
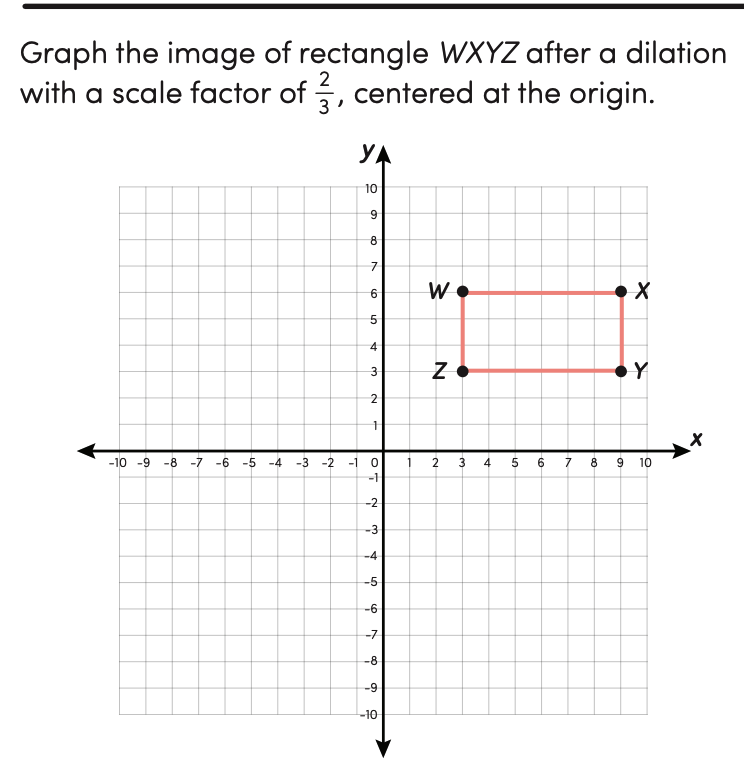
Dilations and Similar Figures
star
star
star
star
star
Last updated 6 months ago
23 questions
Note from the author:
Success Criteria 1: I can determine if the scale factor will result in an enlargement or reduction.
1
Success Criteria 2: I can apply the scale factor to the pre-image to calculate the coordinates of the image.
Success Criteria 3: I can calculate the scale factor when given the pre-image and the image.
1
1
1
Success Criteria 4: I can explain the effect of a dilation on a coordinate plane. (Assessment Aligned)
1
1
1
1
Success Criteria 5: I can explain the effect on the perimeter and area of a figure after a dilation.
1
1
1