Building Tough: Earthquake-Resistant Structures
star
star
star
star
star
Last updated over 1 year ago
12 questions
1. Make sure to read the text before answering questions
2. Use pages 32-35 in our textbook to support your responses
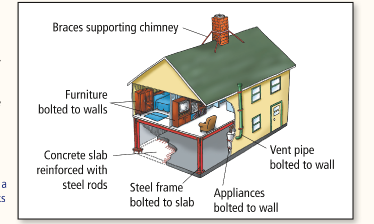
Explain the concept of earthquake-resistant structures and why they are important for saving lives and reducing damage during seismic events.
Identify key design features and materials used in earthquake-resistant structures, such as base isolators, flexible foundations, and damping systems.
Required
1
MS-ESS3-2