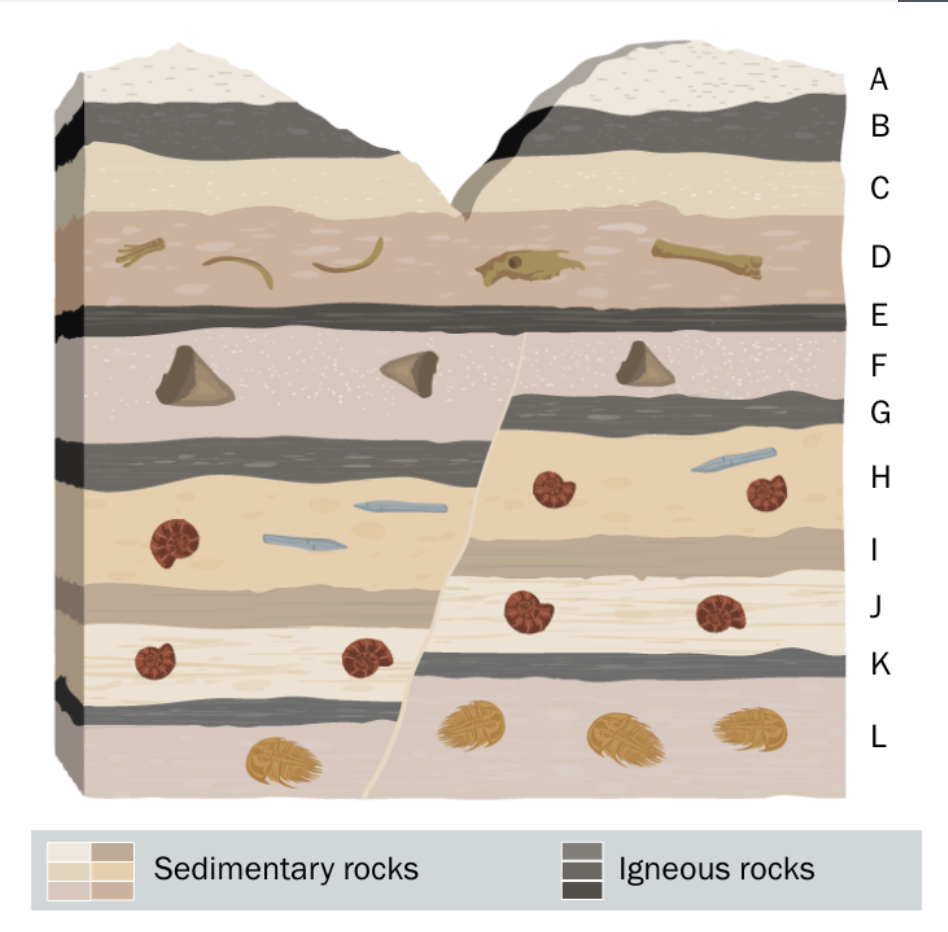
MS-ESS1-4 : A Fascinating Fossil
star
star
star
star
star
Last updated over 1 year ago
10 questions
Required
5
Required
7
Required
1
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
Absolute Dating | arrow_right_alt | techniques allow us to predict a numerical age or range for past events relatively accurately. |
Geologic Time Scale | arrow_right_alt | Technique that relies heavily on looking at the radioactive elements in rocks and the decay that took over time. |
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt |
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt |