GEOL 1301 DC Earth Science Test 4 Fall 2024
star
star
star
star
star
Last updated over 1 year ago
22 questions
Streams and Drainage Patterns
1
1
1
1
1
Oceans and Shorelines
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
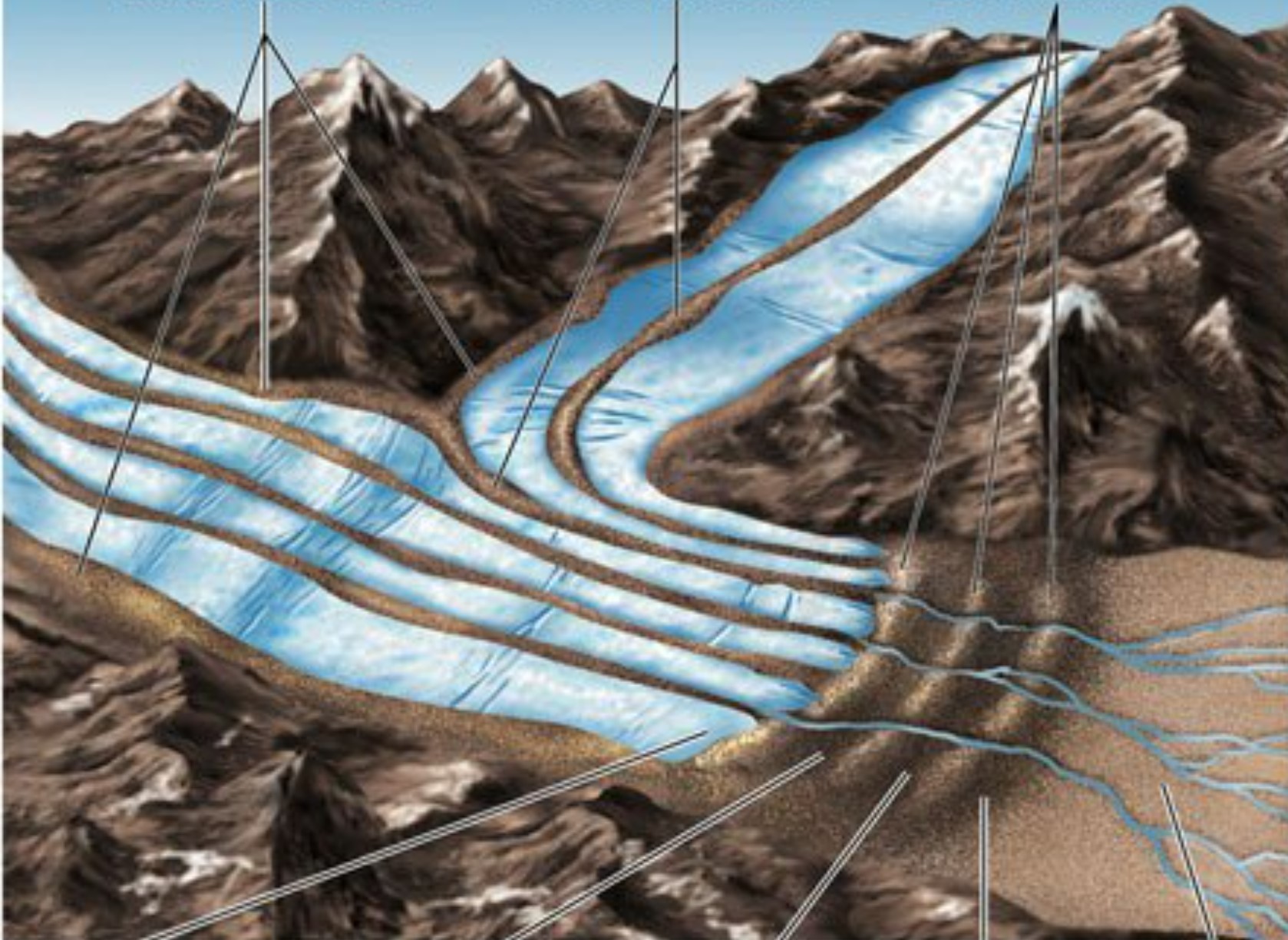
Glaciers and Glaciations
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt |
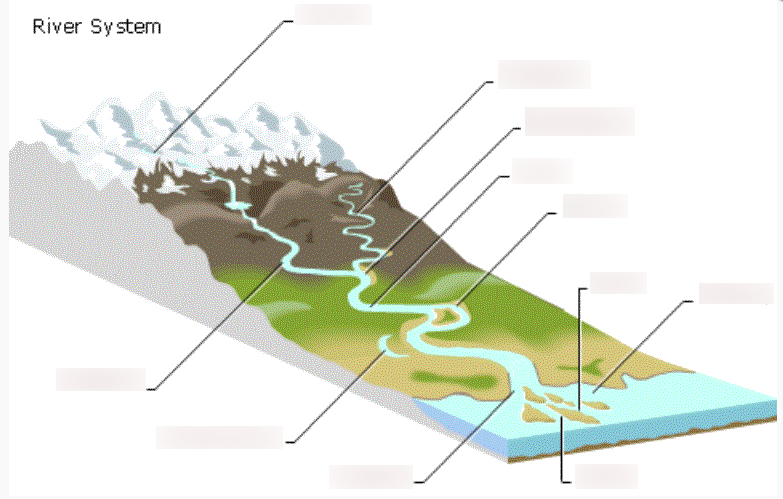
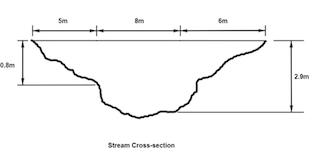
| Draggable item | arrow_right_alt | Corresponding Item |
|---|---|---|
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt | ||
| arrow_right_alt |
