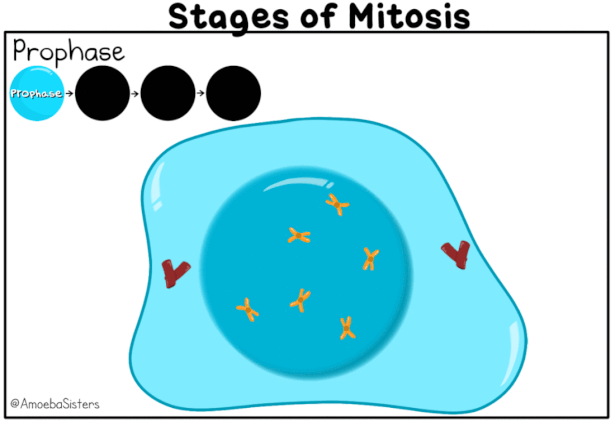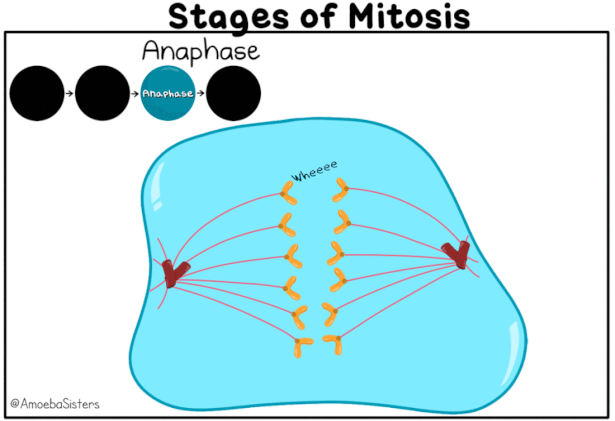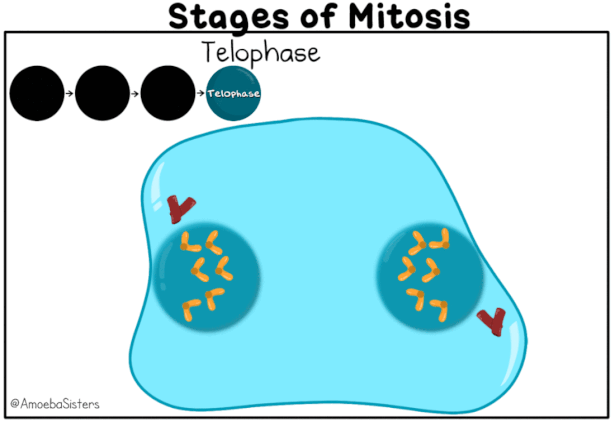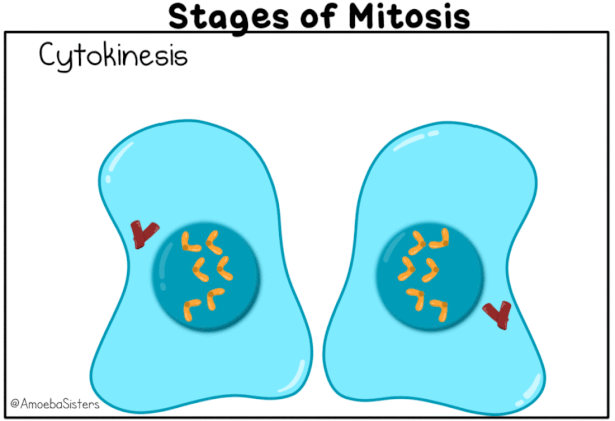
The first and longest stage of mitosis. In this stage, the cell's chromatin condenses into chromosomes. Each chromosome is a single structure that contains the genetic material that was replicated in interphase.
As prophase continues, the nucleolus starts to disappear. Microtubule structures called spindle fibers from in the cytoplasm.
In animal cells centrioles migrate to the ends of the cell. These centrioles have aster fibers, which have a starlike appearance. The whole structure is called the spindle apparatus. The spindle apparatus is important in moving and organizing the chromosomes before cell division.
Near the end of prophase, the nuclear envelope disappears and spindle fibers attach to sister chromatids of each chromosome on both sides of the centromere. Then, they attach to opposite poles of the cell. This arrangement ensures that each new cell receives one complete copy of DNA.