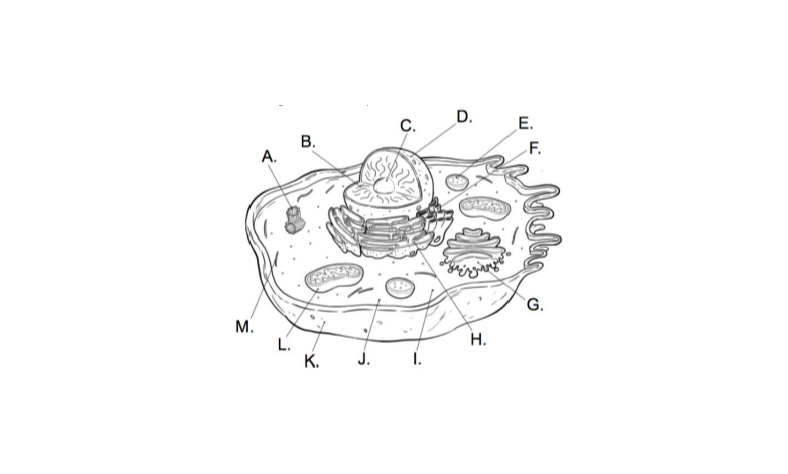
Unit 1 Cells On Level Exam
star
star
star
star
star
Last updated about 2 months ago
28 questions
Required
1
SB1a
Required
1
SB1a
Required
1
SB1a
Required
1
SB1a
Required
1
SB1a
Required
1
SB1a
Required
1
SB1a
Required
1
SB1a
Required
1
SB1a
Required
1
SB1a
Required
1
SB1a
Required
1
SB1a
Required
1
SB1a
Required
1
SB1a
SB1c
Required
1
SB1d
Required
1
SB1d
Required
1
SB1b
Required
1
SB1d
Required
1
SB1d
Required
1
SB1d
Required
1
SB1d
Required
1
SB1d
Required
1
SB1d
Required
1
SB4a