Unit 3 Assessment: Waterfalls
star
star
star
star
star
Last updated 11 months ago
8 questions
Note from the author:
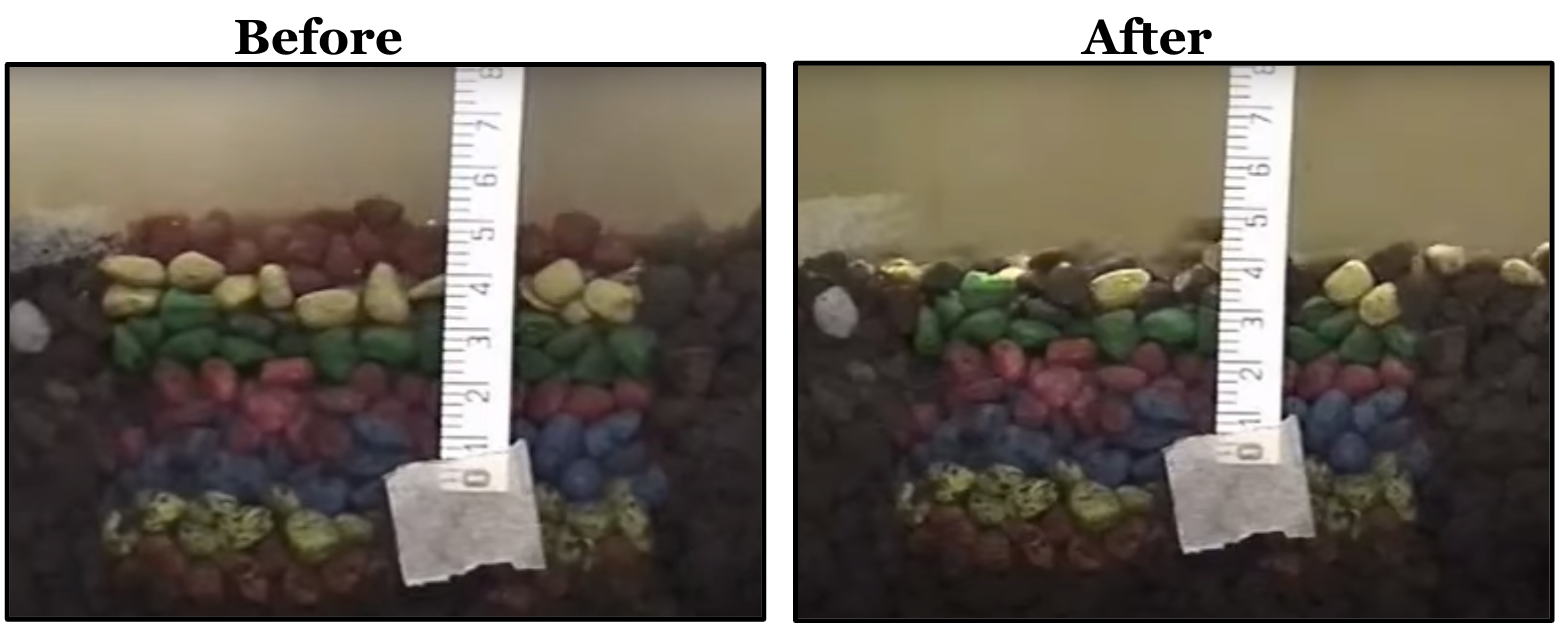
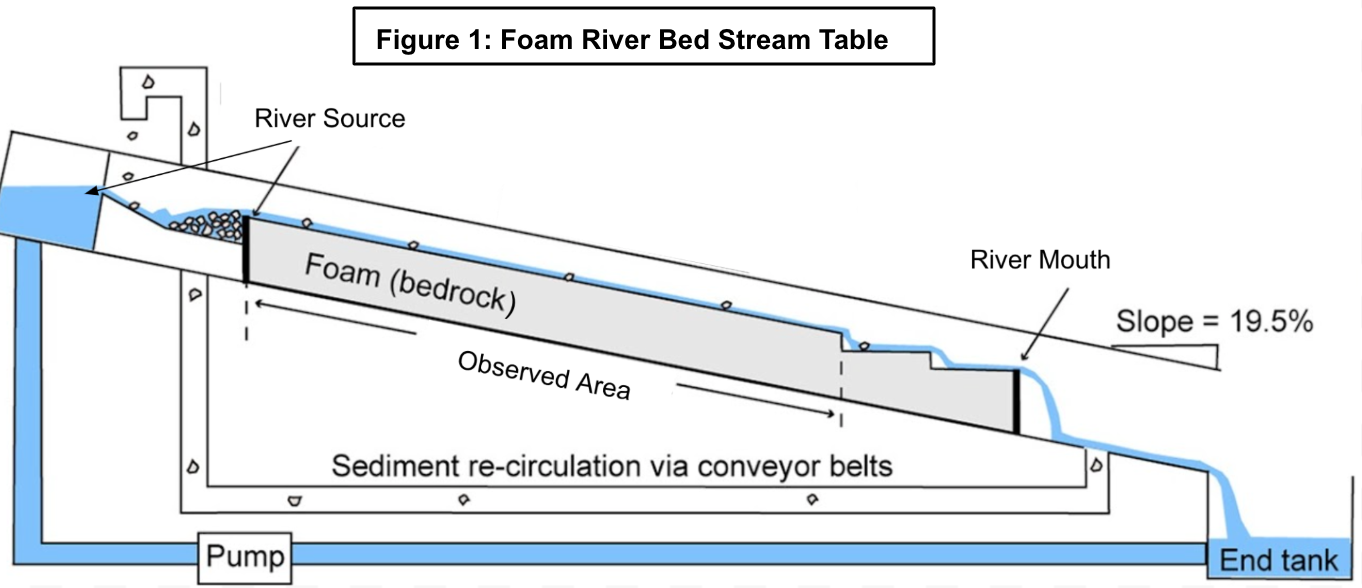
Waterfalls Assessment addresses earth science standards on how water affects the land. It includes an informational reading, comprehension questions, and vocabulary
Required
1