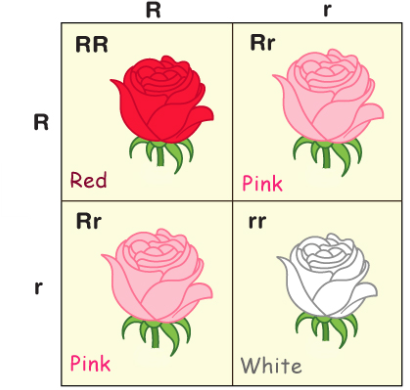
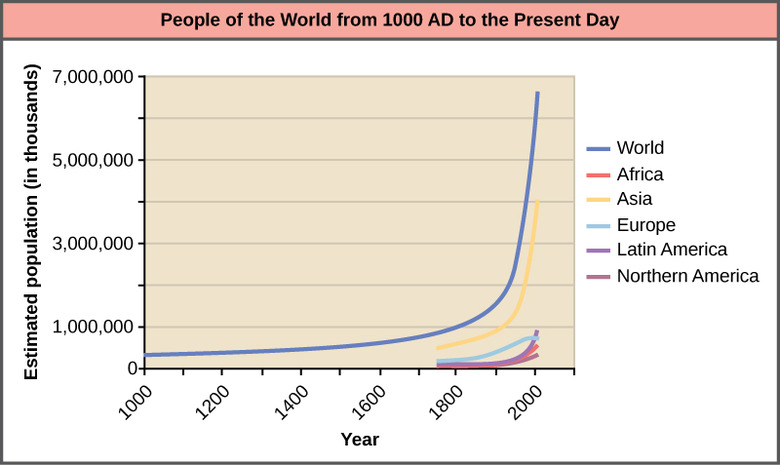
R_Biology Sem-2 Final
star
star
star
star
star
Last updated about 2 months ago
60 questions
Required
3
Required
3
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
3
Required
3
Required
1
Required
1
Required
3
Required
2
Required
3
Required
3
Required
2
Required
1
Required
1
Required
4
Required
4
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
5
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
3
Required
1
Required
1
Required
3
Required
4
Required
1
6
Required
1
Required
6
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
3
Required
1
Required
1
Required
2
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
1
Required
4
Required
5