Please read below before answering the questions for a refresher. Each worksheet has a word bank to help you answer the questions as well. Don't worry about your score since this is for review, but it is important to understand these concepts for our upcoming unit on the brain.
Nerve Cells
Although the nervous system is very complex, nervous tissue consists of just two basic types of nerve cells: neurons and glial cells.
Neurons are the structural and functional units of the nervous system. They transmit electrical signals, called nerve impulses.
Neuron Structure
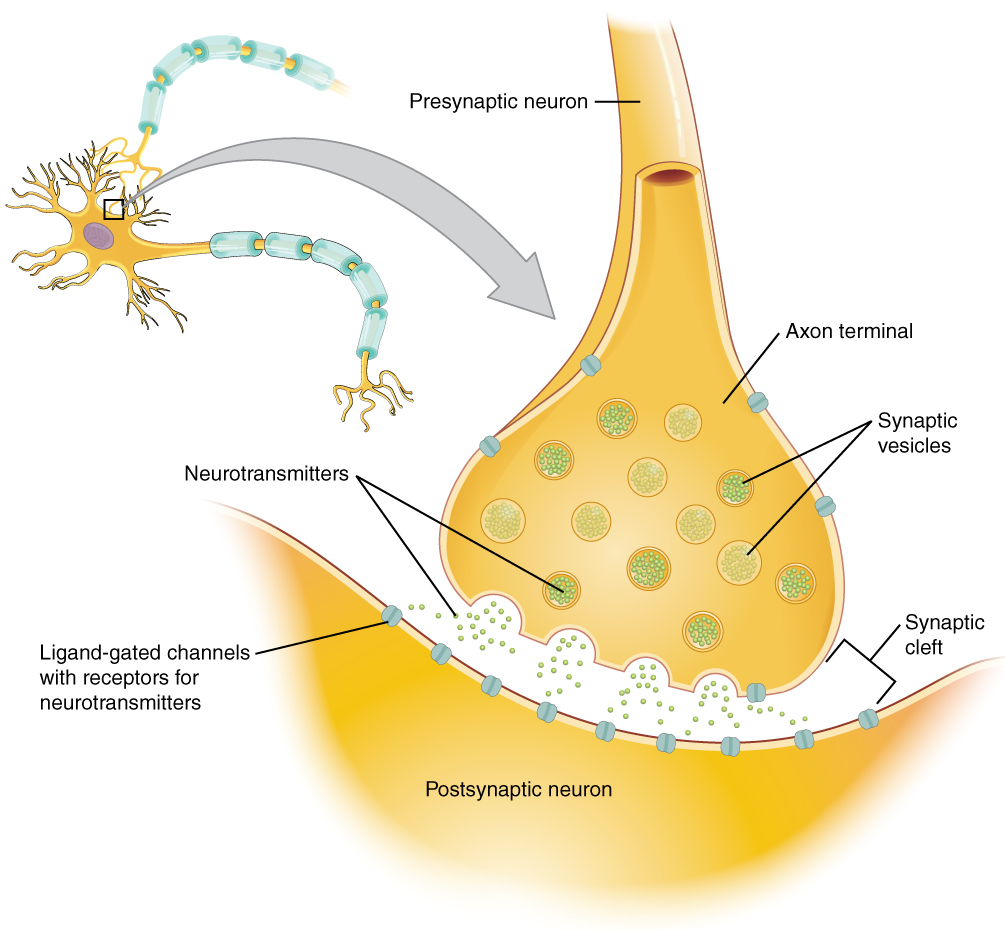
A neuron consists of three basic parts: the cell body, dendrites, and axon.
The cell body contains the nucleus and other cell organelles.
Dendrites extend from the cell body and receive nerve impulses from other neurons.
The axon is a long extension of the cell body that transmits nerve impulses to other cells. The axon branches at the end, forming axon terminals. These are the points where the neuron communicates with other cells.