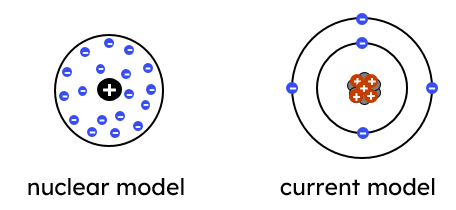
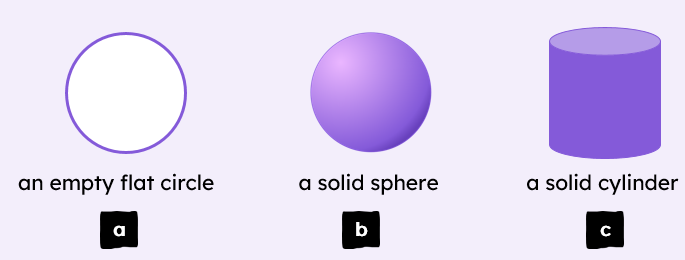
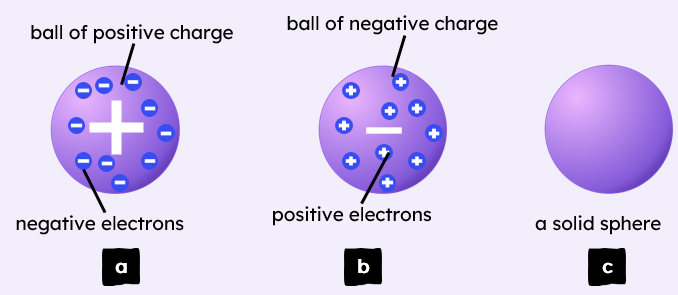
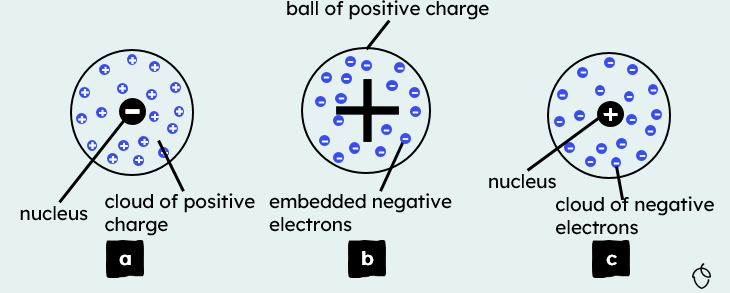
C1 Atomic Structure and Periodic Table
star
star
star
star
star
Last updated about 2 months ago
236 questions
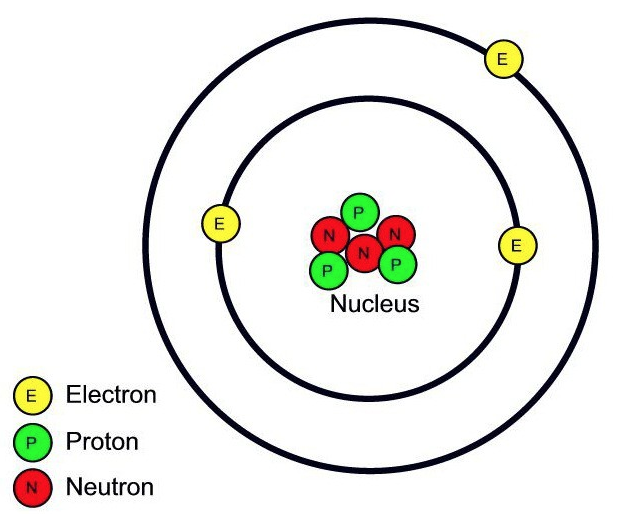
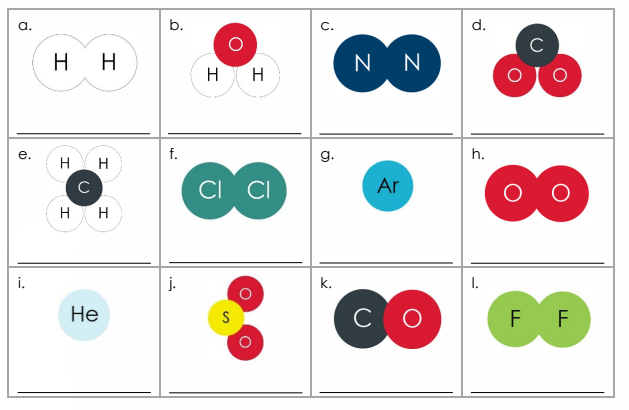
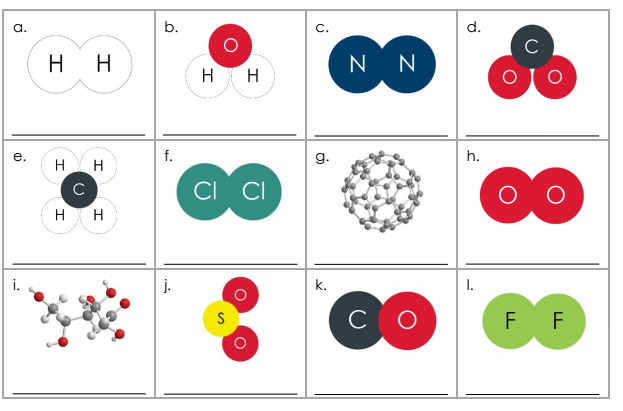
4.1.1.1 Atoms, Elements, and compounds
1
4.1.1.1
1
4.1.1.1
Required
1
4.1.1.1
Required
1
4.1.1.1
Required
1
4.1.1.1
1
4.1.1.1
Required
1
4.1.1.1
Required
1
4.1.1.1
Required
1
4.1.1.1
Required
1
4.1.1.1
Required
1
4.1.1.1
Required
1
4.1.1.1
1
4.1.1.1
1
4.1.1.1
Required
1
4.1.1.1
Required
1
4.1.1.1
Required
1
4.1.1.1
Required
1
4.1.1.1
Required
1
4.1.1.1
Required
1
4.1.1.1
Required
1
4.1.1.1
Required
1
4.1.1.1
Required
1
4.1.1.1
1
4.1.1.1
1
4.1.1.1
1
4.1.1.1
1
4.1.1.1
4.1.1.2 Mixtures
1
4.1.1.2
1
4.1.1.2
1
4.1.1.2
1
4.1.1.2
1
4.1.1.2
1
4.1.1.2
1
4.1.1.2
1
4.1.1.2
1
4.1.1.2
1
4.1.1.2
1
4.1.1.2
1
4.1.1.2
5.5.B
1
4.1.1.2
1
4.1.1.2
1
4.1.1.2
Required
1
4.1.1.2
Required
1
4.1.1.2
1
4.1.1.2
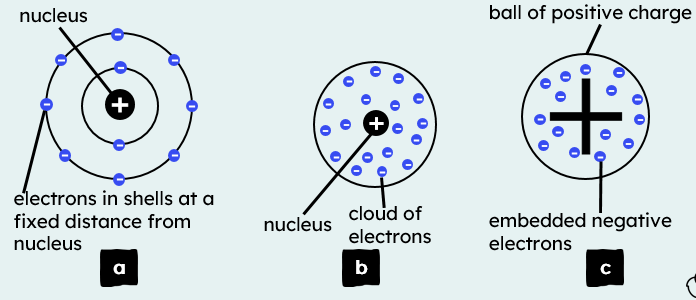
4.1.1.3 The Development of the model of the atom
1
4.1.1.3
4
4.1.1.3
1
4.1.1.3
Required
1
4.1.1.3
5
4.1.1.3
1
4.1.1.3
1
4.1.1.3
1
4.1.1.3
1
4.1.1.3
1
4.1.1.3
1
4.1.1.3
1
4.1.1.3
1
4.1.1.3
1
4.1.1.3
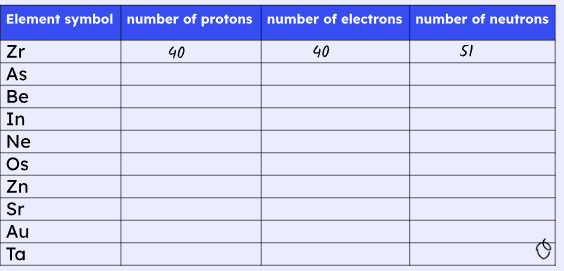
4.1.1.4 Relative electrical charges of subatomic particles
1
4.1.1.4
1
4.1.1.4
1
4.1.1.4
1
4.1.1.4
1
4.1.1.4
1
4.1.1.4
1
4.1.1.4
1
4.1.1.4
1
4.1.1.4
1
4.1.1.4
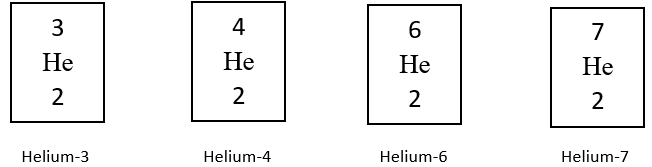
4.1.1.5 Size and mass of atoms
1
4.1.1.5
1
4.1.1.5
1
4.1.1.5
2
4.1.1.5
Required
1
4.1.1.5
Required
1
4.1.1.5
1
4.1.1.5
1
4.1.1.5
1
4.1.1.5
1
4.1.1.5
1
4.1.1.5
1
4.1.1.5
1
4.1.1.5
1
4.1.1.5
1
4.1.1.5
1
4.1.1.5
1
4.1.1.5
1
4.1.1.5
1
4.1.1.5
1
4.1.1.5
1
4.1.1.5
1
4.1.1.5
1
4.1.1.5
3
4.1.1.5
1
4.1.1.5
1
4.1.1.5
Required
1
4.1.1.5
Required
1
4.1.1.5
Required
1
4.1.1.5
Required
1
4.1.1.5
4.1.1.6 Relative Atomic Mass
1
4.1.1.6
1
4.1.1.6
1
4.1.1.6
1
4.1.1.6
1
4.1.1.6
1
4.1.1.6
1
4.1.1.6
1
4.1.1.6
1
4.1.1.6
1
4.1.1.6
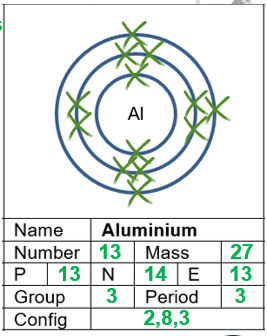
4.1.1.7 Electronic Structure
1
4.1.1.7
SCI.8.5b
SCI.8.5c
1
4.1.1.7
SCI.8.5c
1
4.1.1.7
1
4.1.1.7
1
4.1.1.7
Required
1
4.1.1.7
Required
1
4.1.1.7
1
4.1.1.7
Required
1
4.1.1.7
Required
1
4.1.1.7
Required
1
4.1.1.7
Required
1
4.1.1.7
1
4.1.1.7
1
4.1.1.7
1
4.1.1.7
1
4.1.1.7
1
4.1.1.7
Required
1
4.1.1.5
4.1.1.7
Required
1
4.1.1.5
4.1.1.7
Required
1
4.1.1.5
4.1.1.7
Required
1
4.1.1.5
4.1.1.7
Required
1
4.1.1.5
4.1.1.7
1
4.1.1.7
1
4.1.1.7
1
4.1.1.7
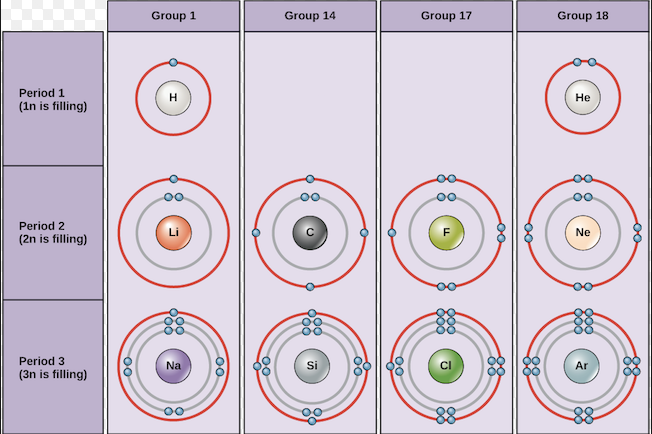
4.1.2.1 The Periodic Table
1
4.1.2.1
1
4.1.2.1
1
4.1.2.1
1
4.1.2.1
1
4.1.2.1
1
4.1.2.1
1
4.1.2.1
1
4.1.2.1
1
4.1.2.1
1
4.1.2.1
1
4.1.2.1
1
4.1.2.1
1
4.1.2.1
1
4.1.2.1
1
4.1.2.1
4.1.2.2 Development of the Periodic Table
1
4.1.2.2
1
4.1.2.2
1
4.1.2.2
1
4.1.2.2
4.1.2.3 Metals and non-metals
1
4.1.2.3
1
4.1.2.3
4.1.2.4 Group 0
Required
1
4.1.1.7
4.1.2.4
Required
1
4.1.1.7
4.1.2.4
Required
1
4.1.2.4
1
4.1.2.4
1
4.1.2.4
1
4.1.2.4
1
4.1.2.4
1
4.1.2.5 Group 1
1
4.1.2.5
1
1
4.1.1.1
1
4.1.1.7
4.1.2.5
1
4.1.1.7
4.1.2.5
Required
1
4.1.2.5
4.2.1.2
Required
1
4.1.2.5
4.2.1.2
Required
1
4.1.2.5
4.2.1.2
Required
1
4.1.2.5
Required
2
4.1.2.5
4.1.2.6 Group 7
Required
1
4.1.2.6
4.2.1.2
Required
1
4.1.2.6
4.2.1.2
Required
1
4.1.2.6
Required
1
4.1.2.6
Required
1
4.1.2.6
Required
1
4.1.1.1
4.1.2.6
Required
1
4.1.2.6
Required
1
4.1.2.6
4.2.2.1
Required
1
4.1.2.6
Required
1
4.1.2.6
1
4.1.2.6
1
4.1.2.6
4
4.1.2.6
1
4.1.2.6
1
4.1.2.6
4.1.3 Properties of Transition Metals
1
4.1.3.2
SEP.11.7
1
4.1.3.1
1
4.1.3.1
1
4.1.3.2
SEP.11.7
Required
1
4.1.3.1
4.1.3.2
1
4.1.3.1
4.1.3.2
1
4.1.3.1
4.1.3.2