C5 Energy Changes
star
star
star
star
star
Last updated about 2 months ago
33 questions
4.5.1.1 Energy transfer during exothermic and endothermic reactions
1
4.5.1.1
1
4.5.1.1
2
4.5.1.1
1
4.5.1.1
1
4.5.1.1
2
4.5.1.1
1
4.5.1.1
1
4.5.1.1
1
4.5.1.1
1
4.5.1.1
1
MS2b
WS3.7
1
4.4.1.2
4.5.1.1
WS3.5
1
WS4.1
6
WS3.5
WS3.8
1
4.5.1.1
1
4.5.1.1
1
4.5.1.1
MS2b
4
4.5.1.1
4.5.1.3
2
4.5.1.1
WS2.6
4.5.1.2 Reaction profiles
1
4.5.1.2
1
4.5.1.2
1
4.5.1.2
1
4.5.1.2
1
4.5.1.2
1
4.5.1.2
1
4.5.1.2
4.5.1.3 The energy change of reactions
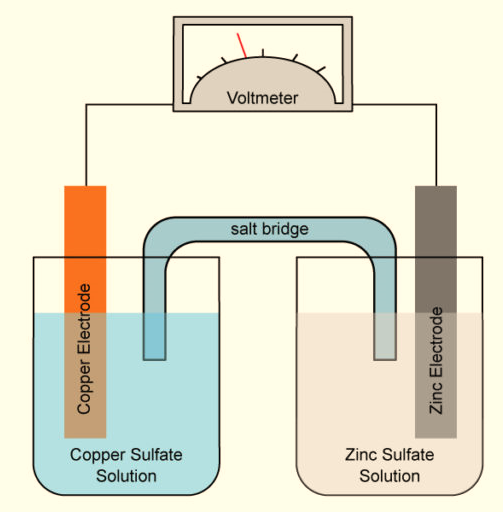
4.5.2.1 Cells and batteries
1
4.5.2.1
1
4.5.2.1
1
4.5.2.1
1
4.5.2.1
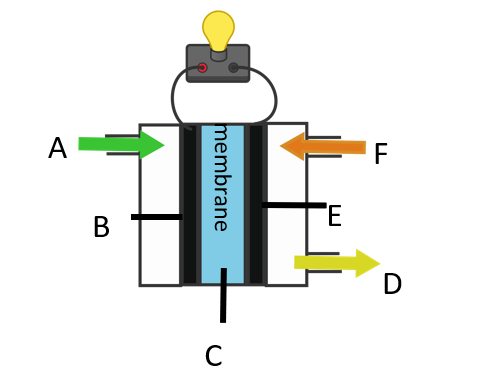
4.5.2.2 Fuel cells
1
4.5.2.2
1
4.5.2.2
6
4.5.2.2