C7 Organic Chemistry
star
star
star
star
star
Last updated about 2 months ago
59 questions
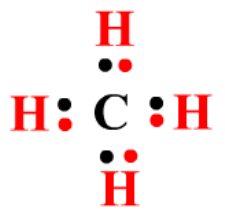
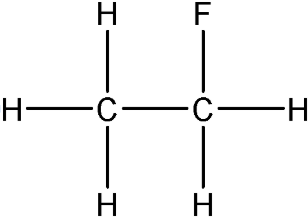
4.7.1.1 Crude oil, hydrocarbons and alkanes
1
4.7.1.1
1
4.7.1.1
7
4.7.1.1
1
4.7.1.1
1
4.7.1.1
1
4.7.1.1
1
4.7.1.1
1
4.7.1.1
1
4.7.1.1
5
4.7.1.1
1
4.7.1.1
1
4.7.1.1
1
WS1.1
1
WS1.1
1
4.7.1.1
2
4.7.1.1
4.7.1.2 Fractional distillation and petrochemicals
1
4.7.1.2
2
4.7.1.2
1
4.7.1.2
1
4.7.1.2
1
4.8.1.1
4.8.1.2
3
4.7.1.2
MS2a
4
4.7.1.2
1
4.7.1.2
1
4.7.1.2
1
4.7.1.2
1
4.7.1.2
1
4.7.1.2
1
4.7.1.2
4.7.1.3 Properties of hydrocarbons
8
4.7.1.3
4
4.7.1.3
9
4.7.1.1
4.7.1.3
6
4.7.1.3
1
4.3.1.1
4.7.1.3
4.7.1.4 Cracking and alkenes
1
4.7.1.4
1
4.7.1.4
1
4.7.1.4
1
4.7.1.4
1
4.7.1.4
1
4.7.1.4
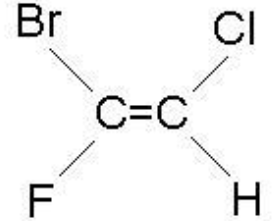
4.7.2.1 Structure and formulae of alkenes
4.7.2.2 Reactions of alkenes
1
4.7.2.2
1
4.7.2.2
1
4.7.2.2
4.7.3.1
1
4.7.2.2
4.7.2.3 Alcohols
1
4.7.2.3
1
4.7.2.3
4.7.2.4 Carboxylic acids
1
4.7.2.4
1
4.7.2.4
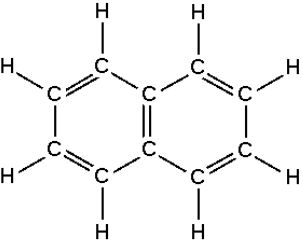
4.7.3 Synthetic and naturally occurring polymers
1
4.7.3.2
1
4.2.2.5
4.7.3.2
1
4.7.3.4
1
4.7.3.4
1
4.7.3.2
4.7.3.4
1
4.7.3.2