C8 Chemical Analysis
star
star
star
star
star
Last updated about 2 months ago
61 questions
4.8.1.1 Pure substances
Required
1
4.8.1.1
Required
1
4.8.1.1
Required
1
4.8.1.1
Required
1
4.8.1.1
2
4.8.1.1
Required
1
4.8.1.1
Required
1
4.8.1.1
Required
1
4.8.1.1
Required
1
4.8.1.1
1
4.8.1.1
5.5.A
Required
1
4.8.1.1
4.8.1.2 Formulations
Required
1
4.8.1.2
MS1c
Required
1
4.8.1.2
MS1c
Required
1
4.8.1.2
Required
1
4.8.1.2
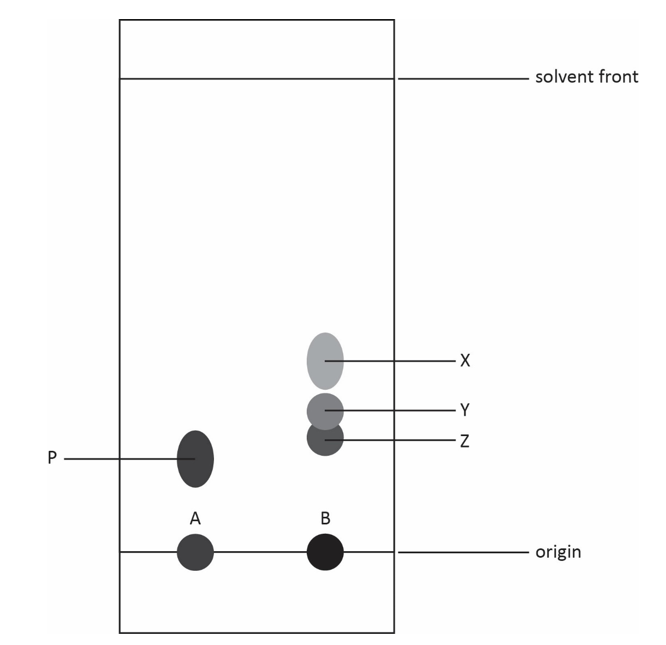
4.8.1.3 Chromatography
1
4.8.1.3
0
4.8.1.3
1
4.8.1.3
MS1a
1
4.8.1.3
1
4.8.1.3
1
4.8.1.3
1
4.8.1.3
2
4.8.1.3
4.8.2 Identification of common gases
1
4.8.2.1
4.8.2.2
Required
1
4.8.2.1
4.8.2.2
8
4.8.1.3
4.8.3.1 Flame Tests
2
4.8.3.1
5
4.8.3.1
5
1
4.8.3.1
1
4.8.3.1
1
4.8.3.1
1
4.8.3.1
1
4.8.3.1
4.8.3.2 Metal Hydroxides
1
4.8.3.2
1
4.8.3.2
1
4.8.3.2
1
4.8.3.2
1
4.8.3.2
1
4.8.3.2
1
4.8.3.2
1
4.8.3.2
1
4.8.3.2
1
4.8.3.2
1
4.8.3.2
4.8.3.3/4/5 Antions (Carbonate, Halide, Sulfate)
1
4.8.3.5
3
4.8.3.3
4.8.3.4
4.8.3.5
1
4.8.2.3
4.8.3.3
1
4.8.3.4
4.8.3.6 Instrumental Methods
4.8.3.7 Flame Emission Spectroscopy
2
4.8.3.1
4.8.3.7
2
4.8.3.7
1
4.8.3.7
1
4.8.3.7
1
4.8.3.7